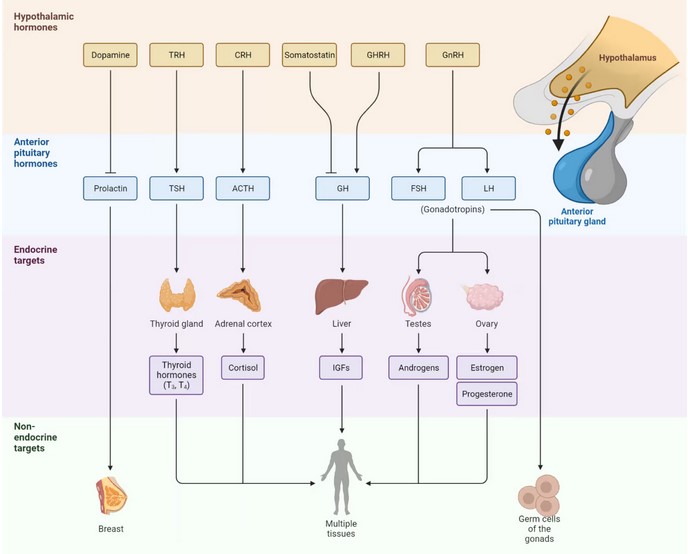
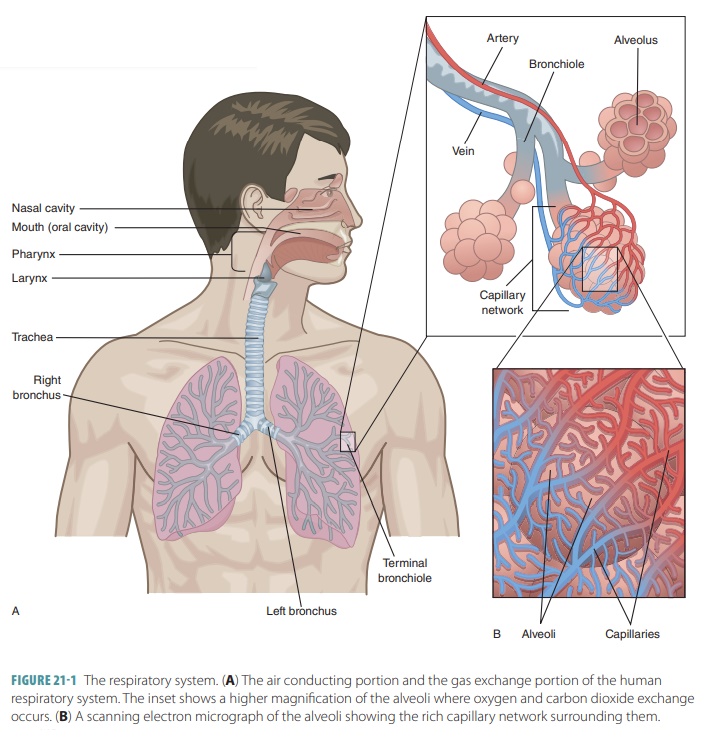
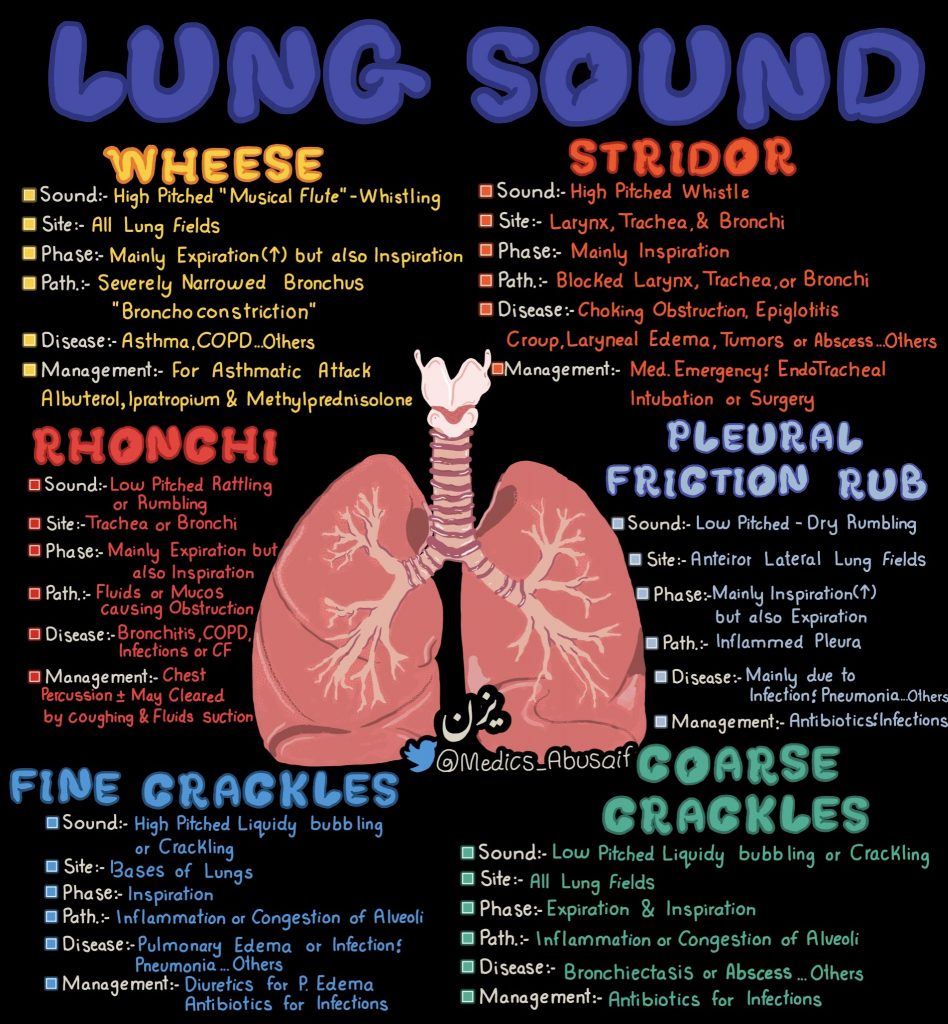
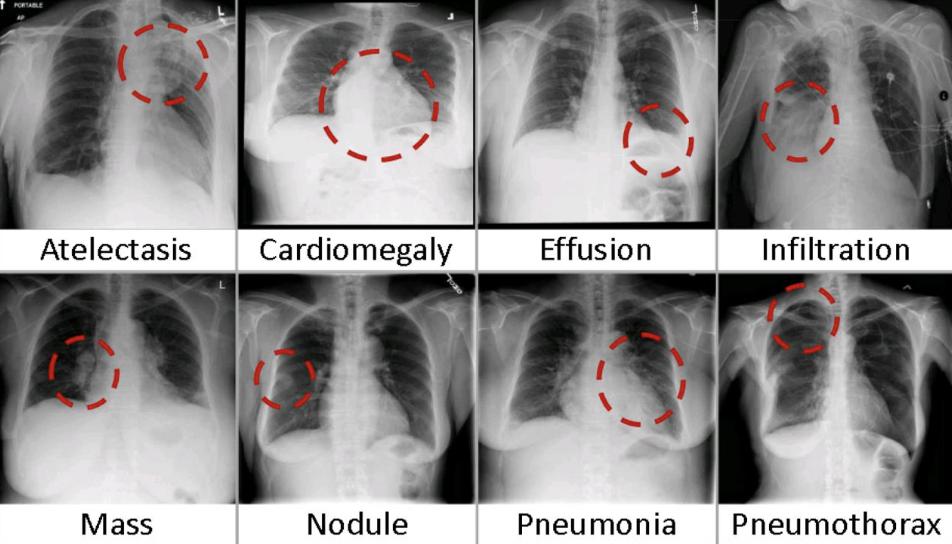
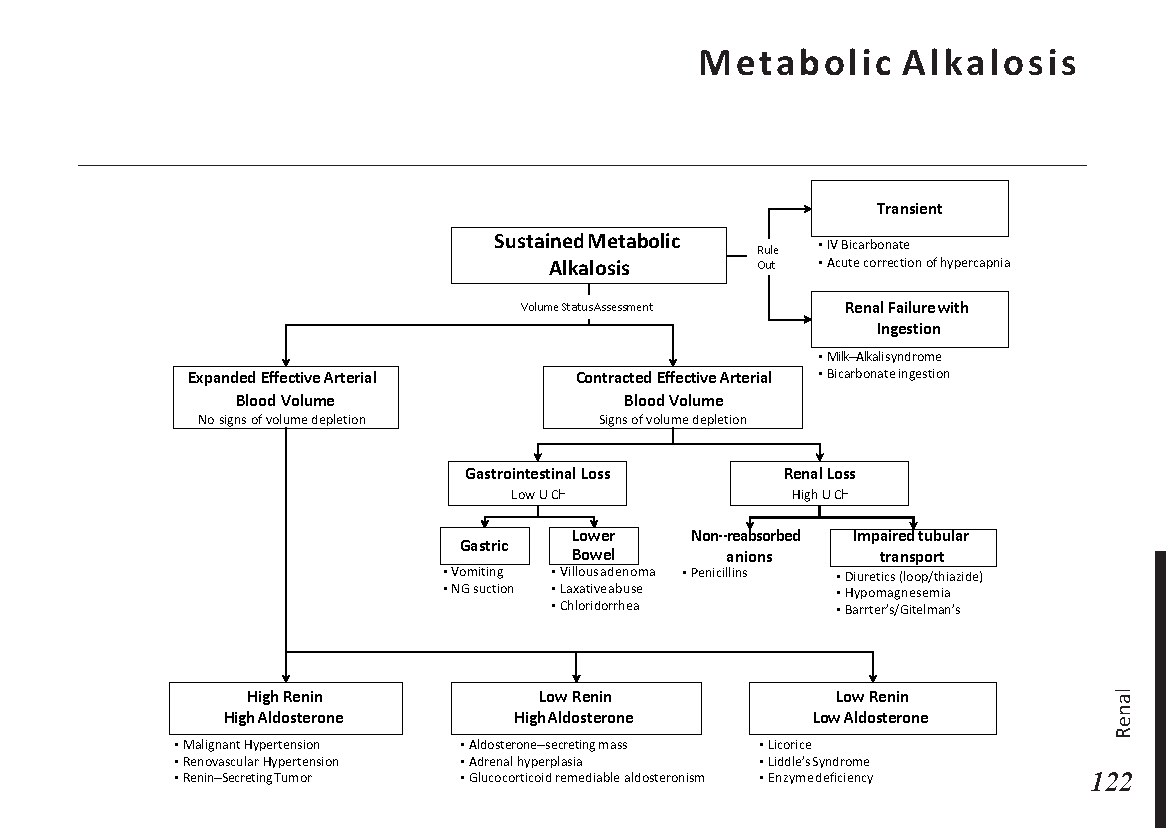
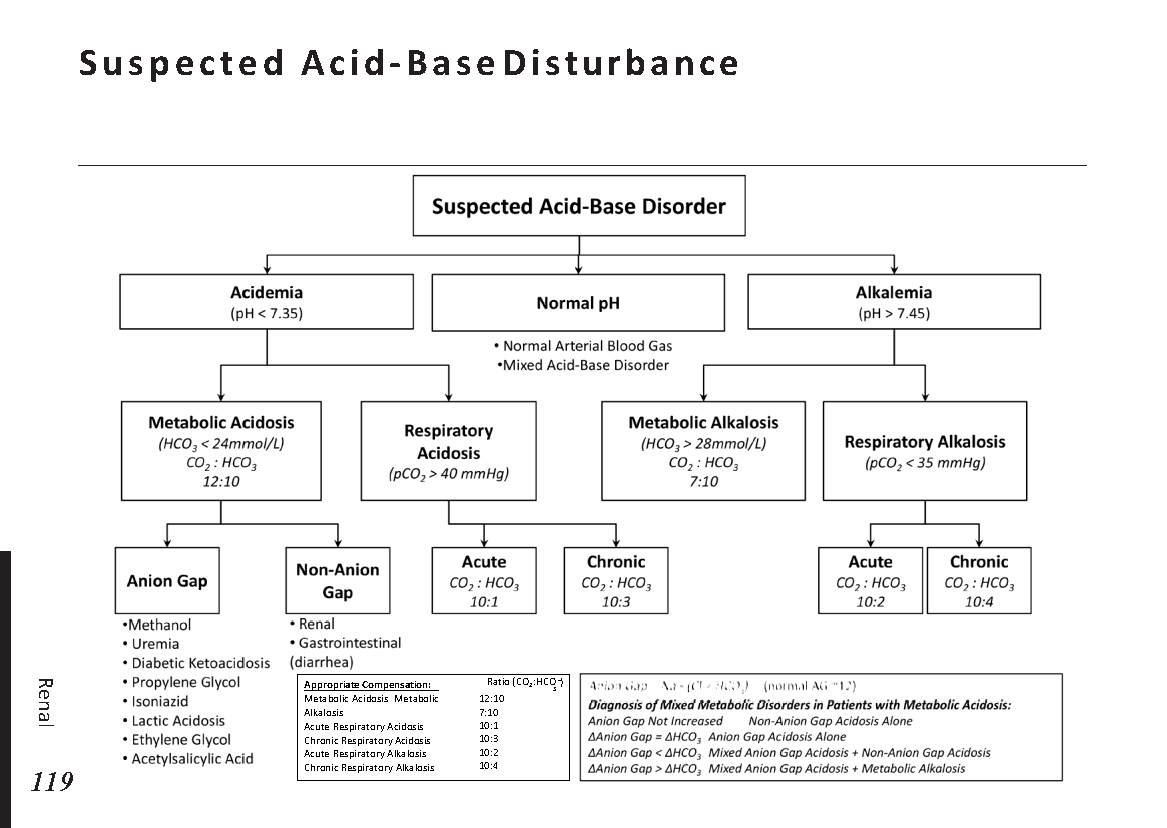
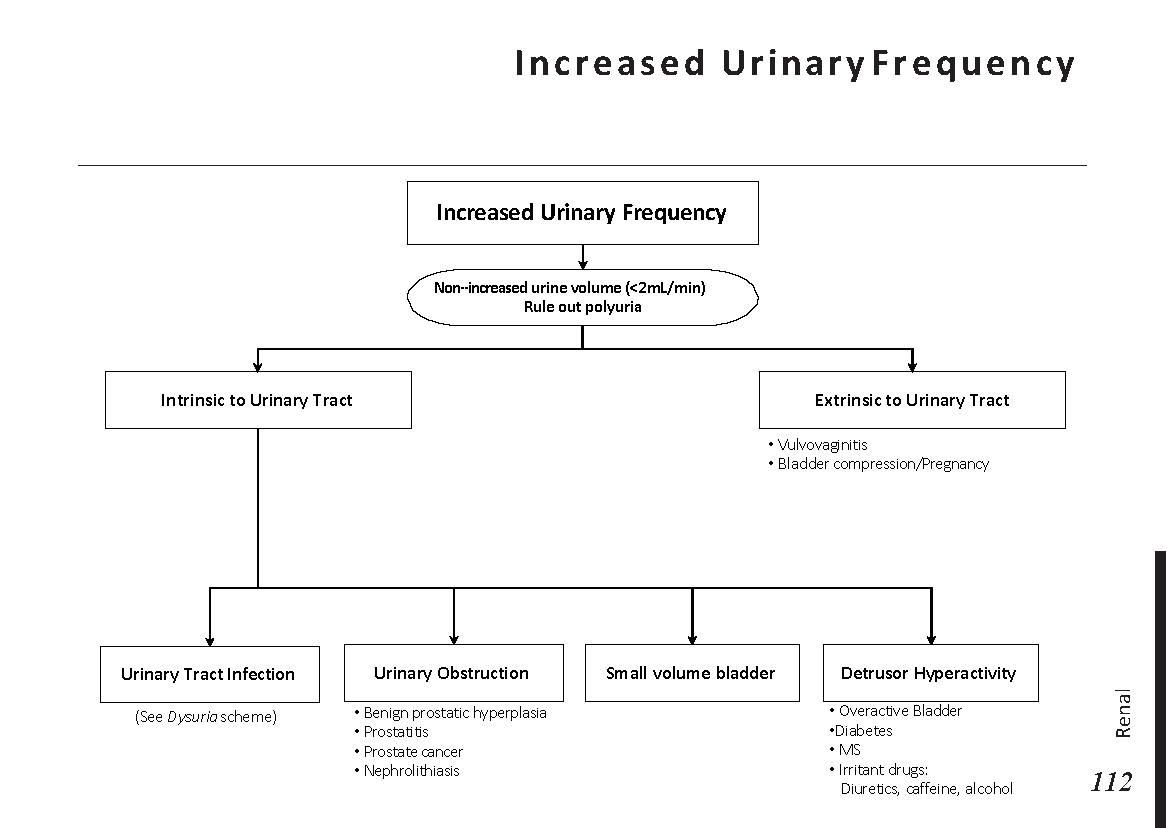
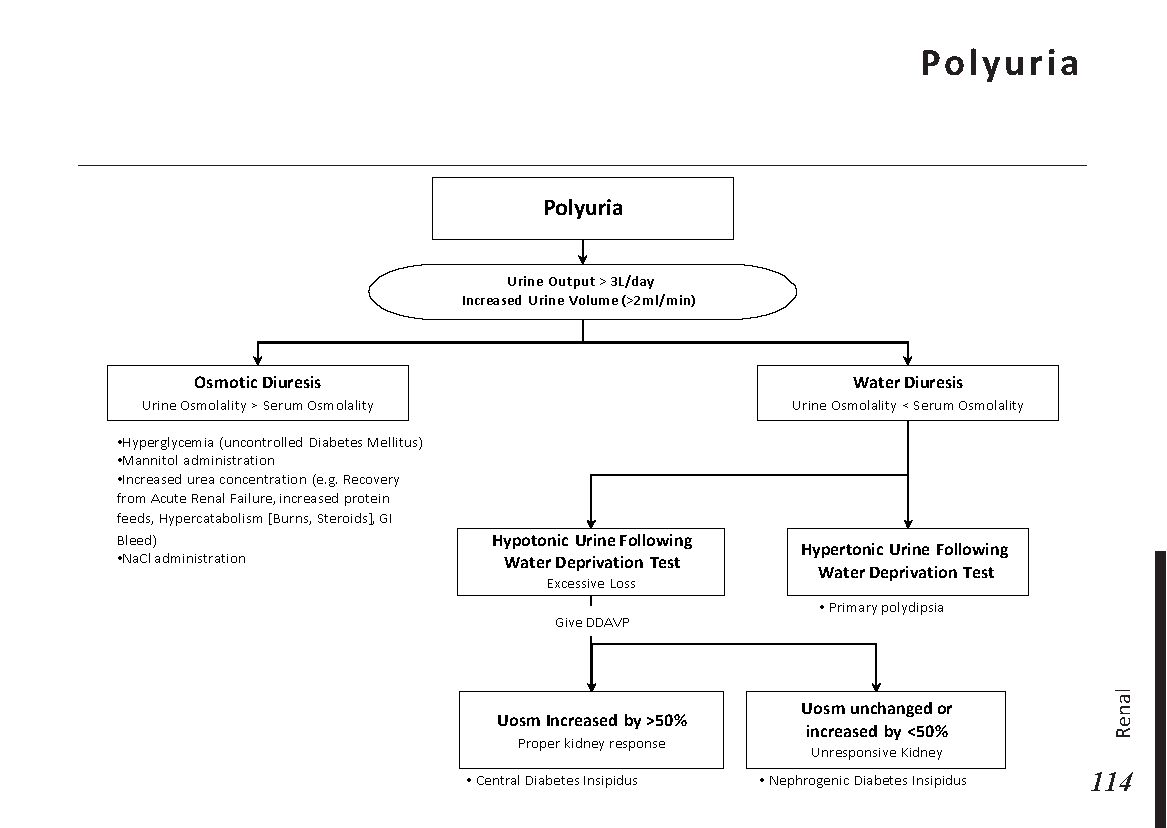
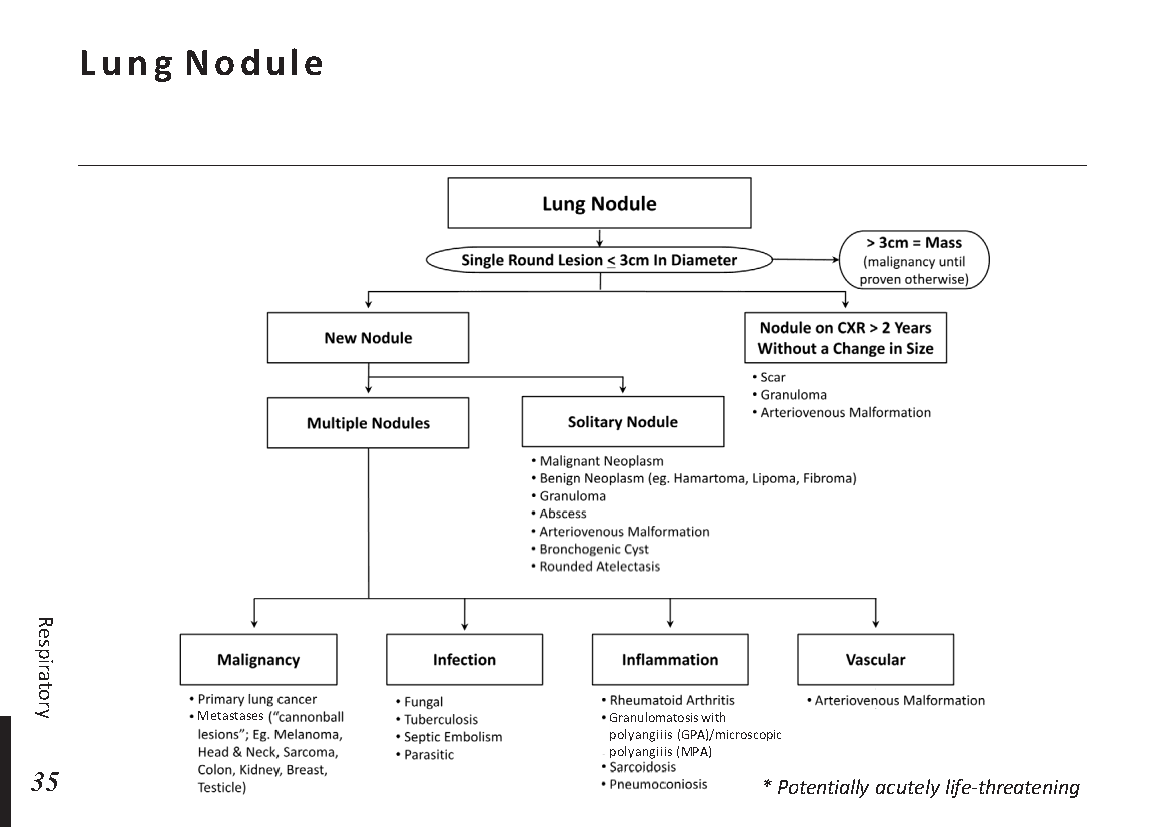
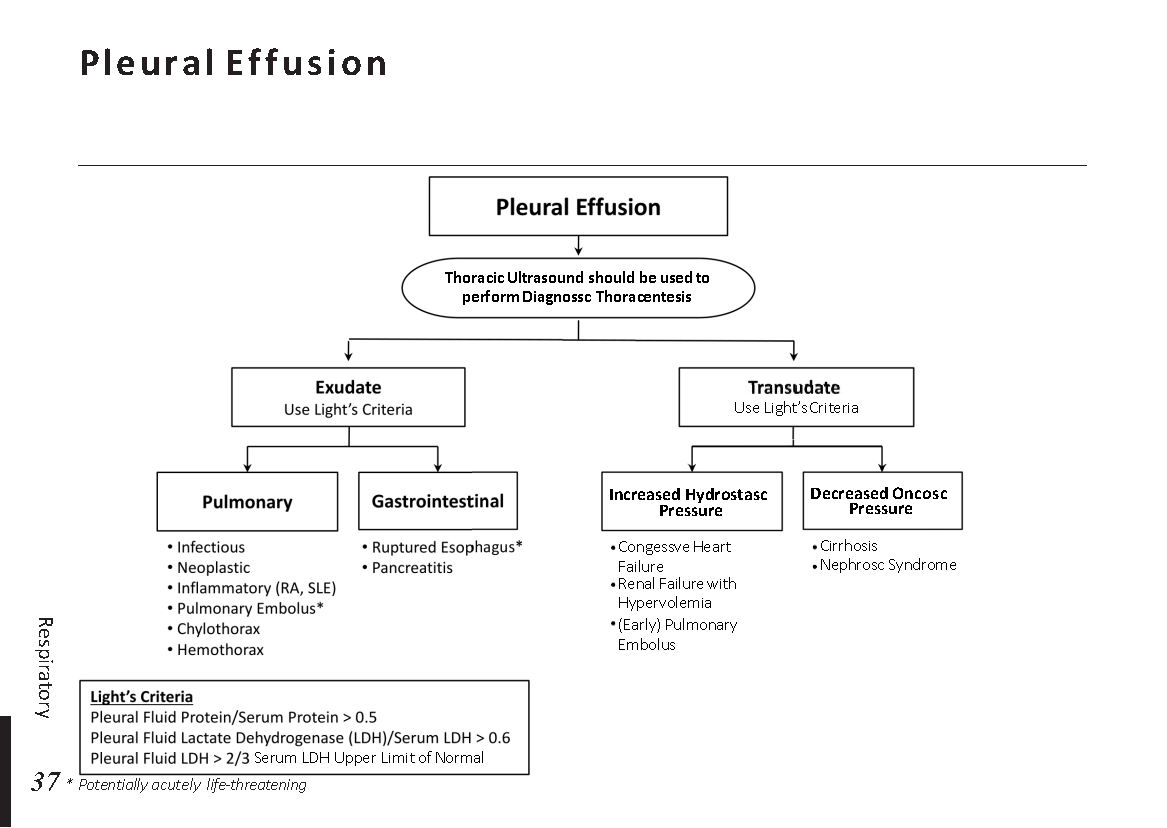
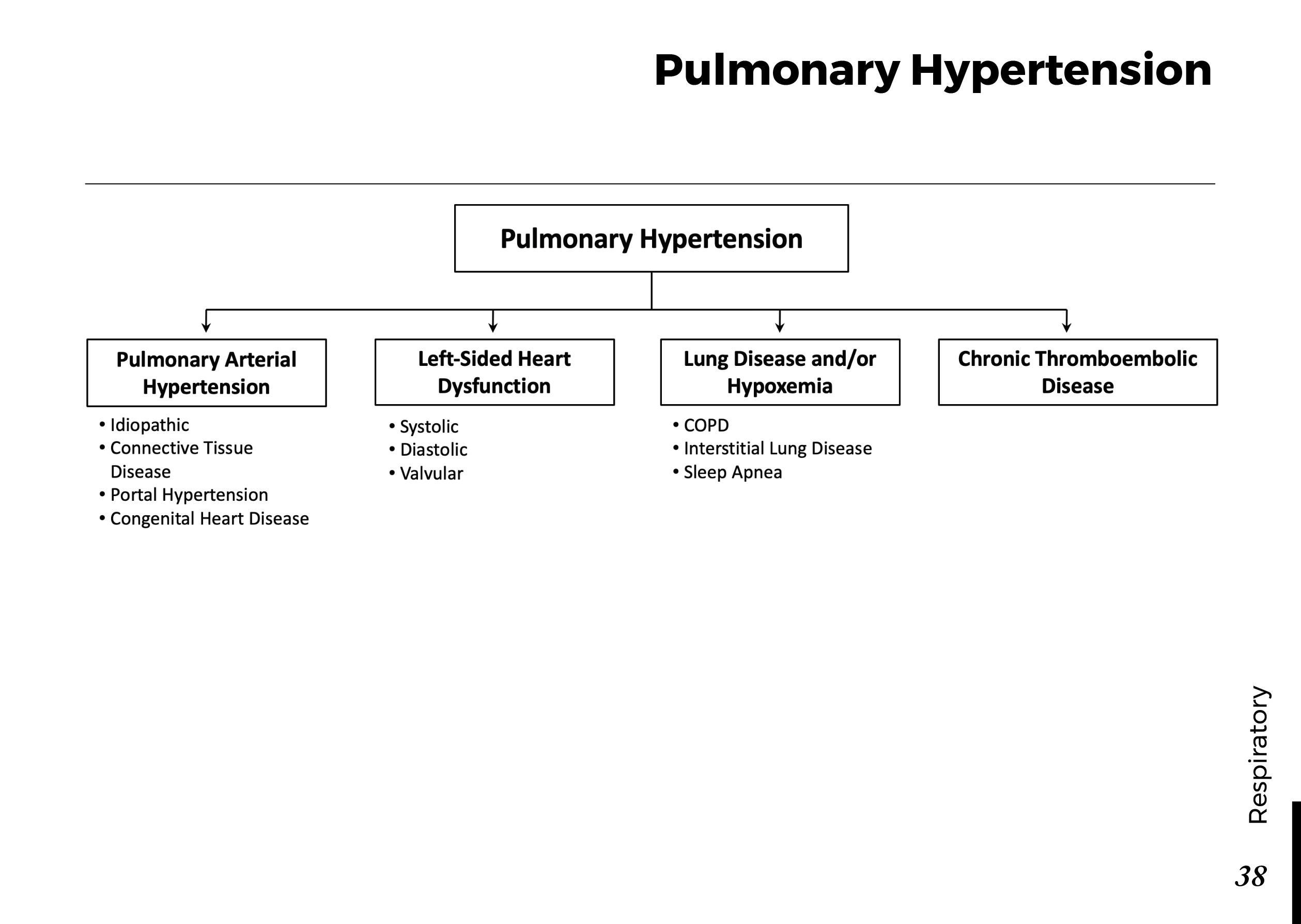
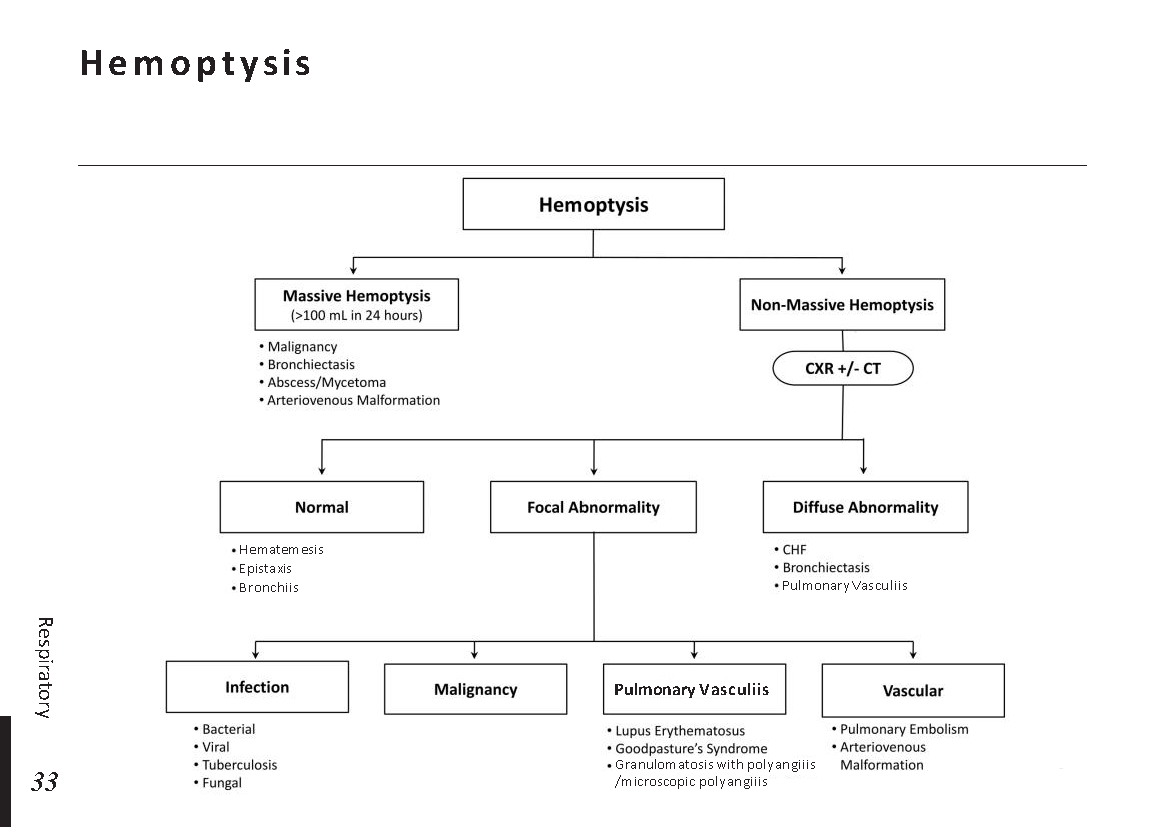
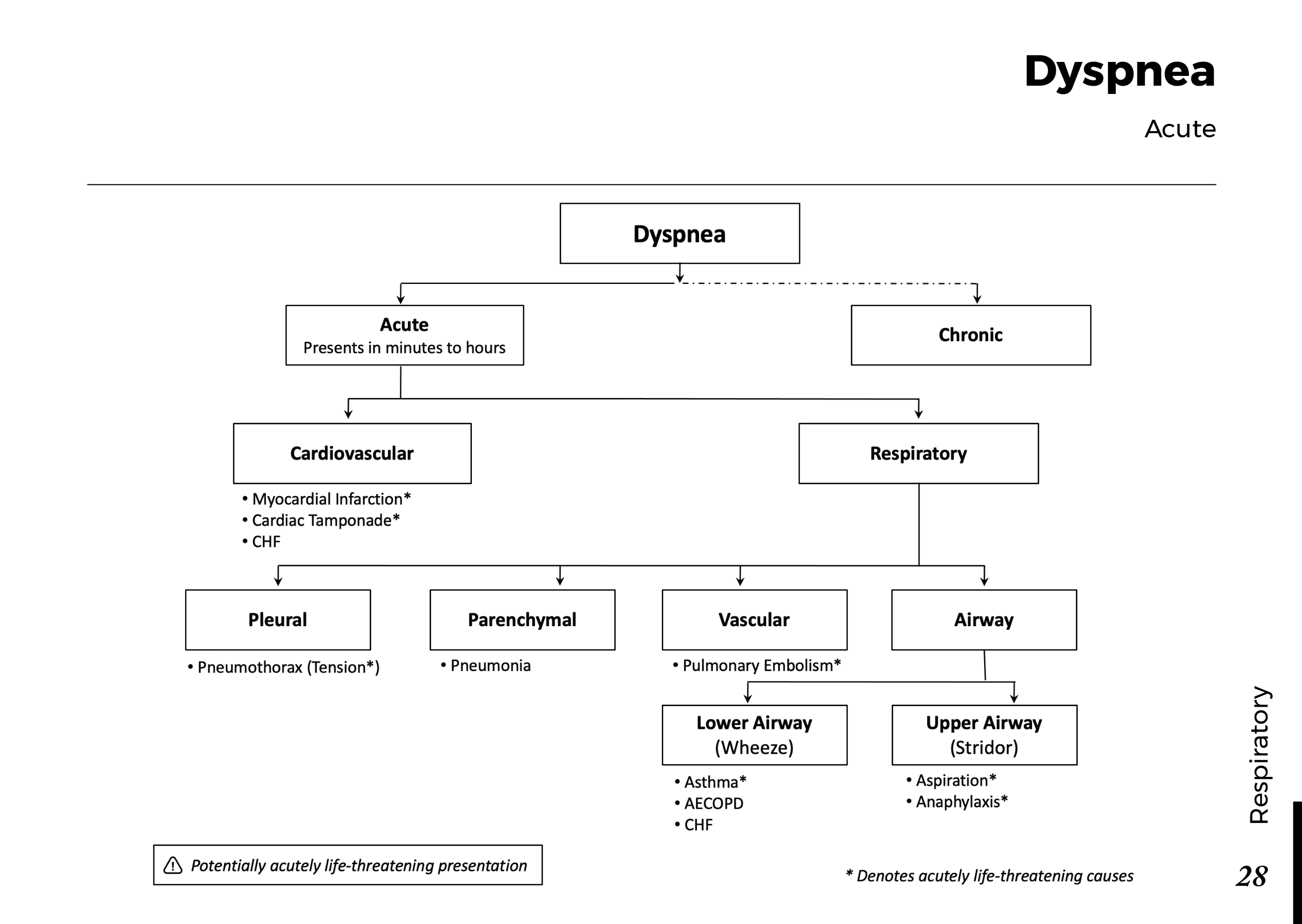
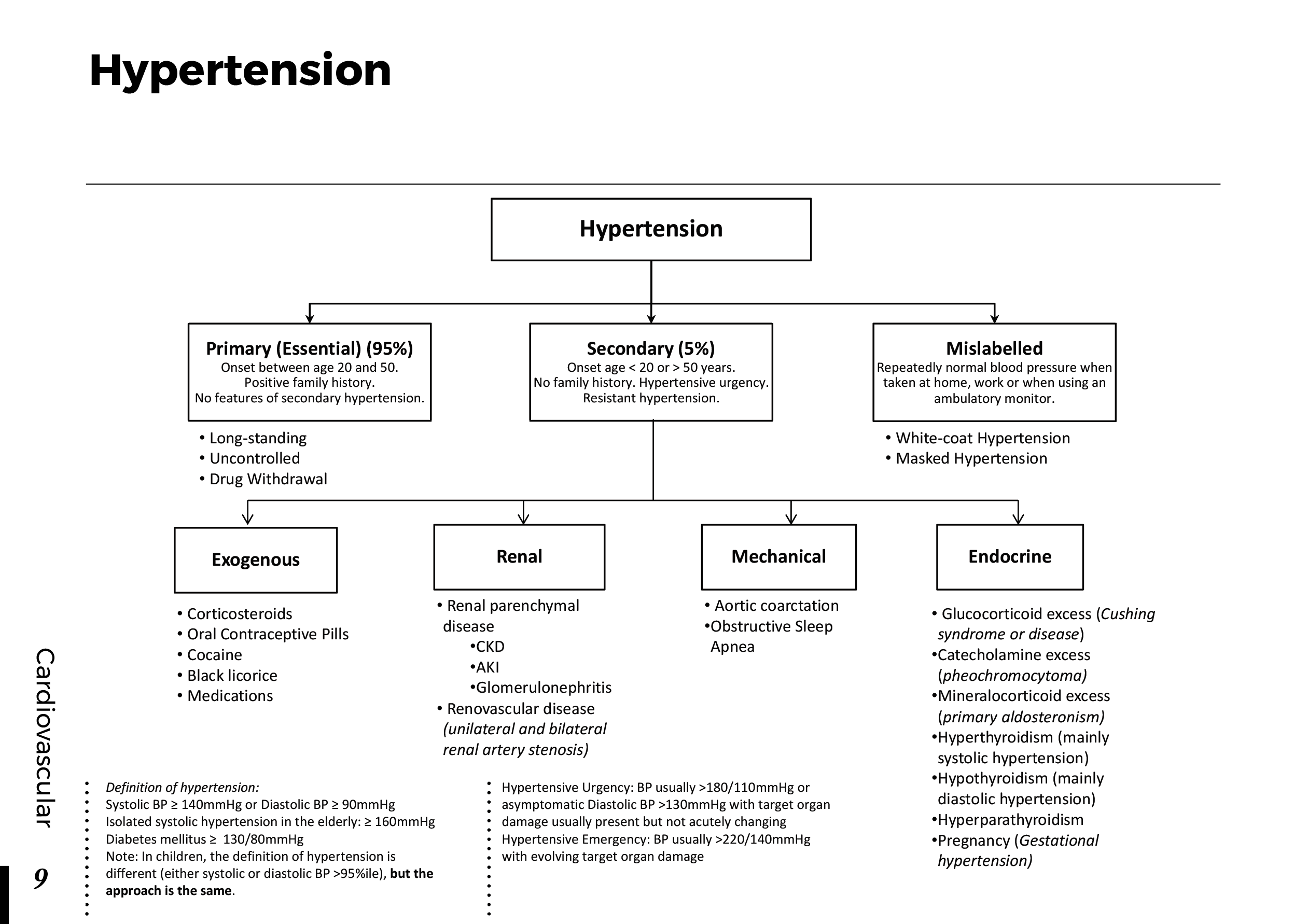
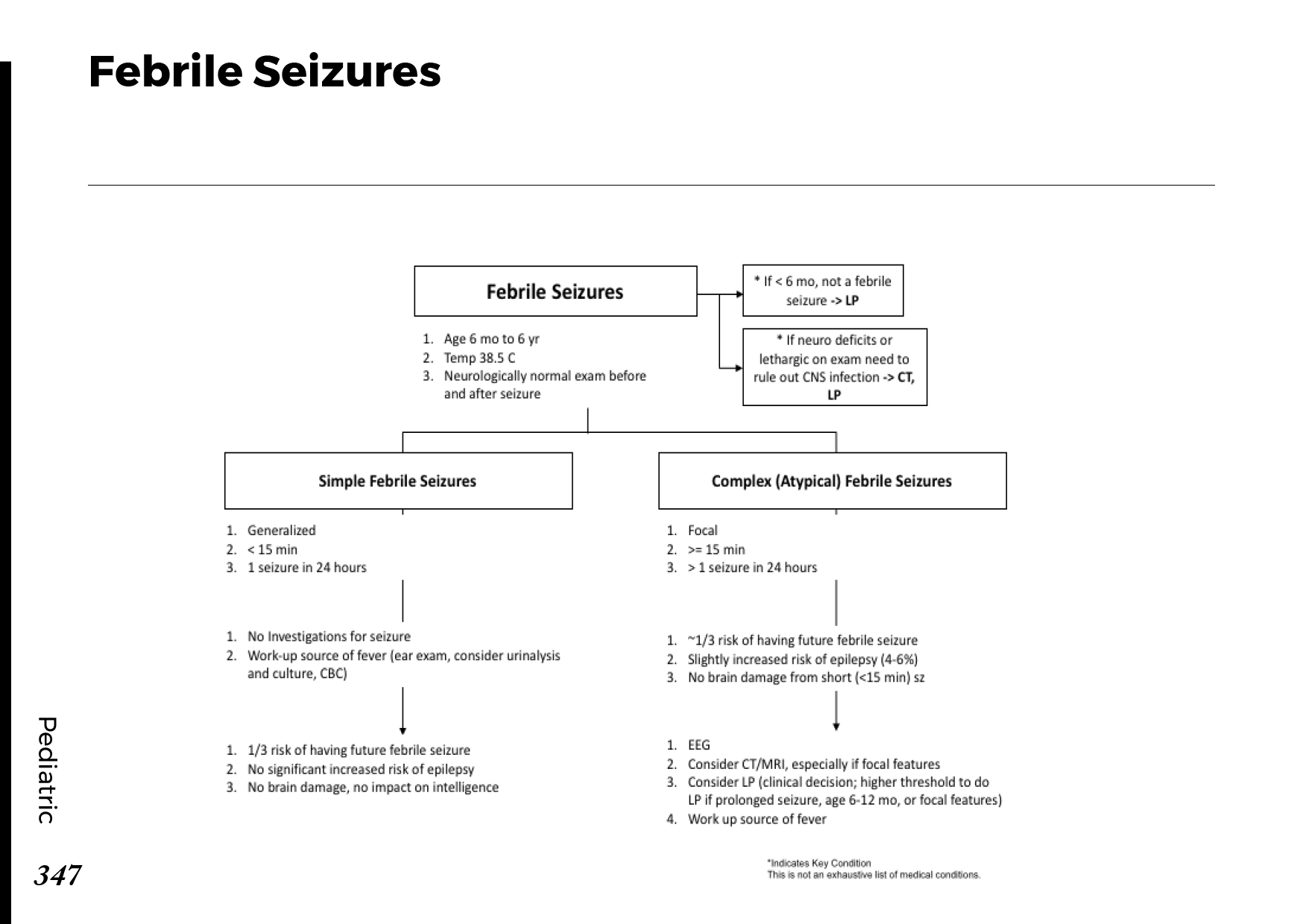
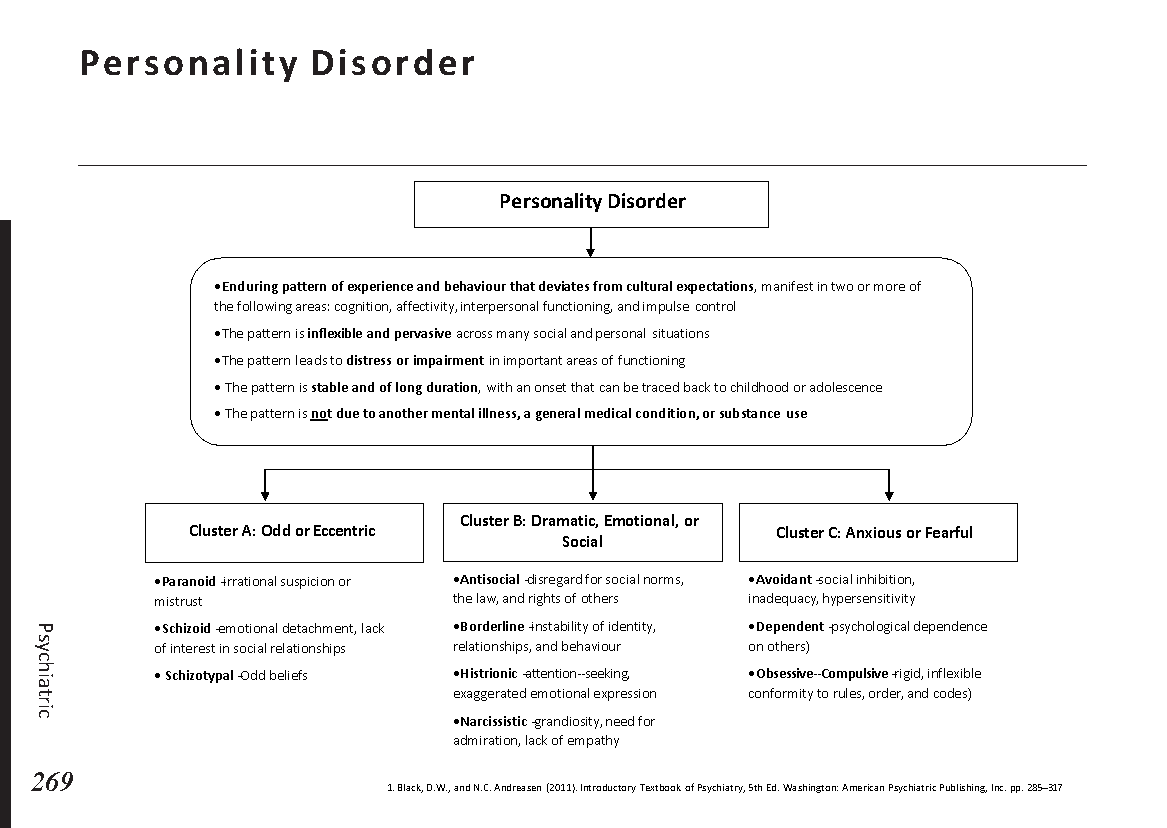
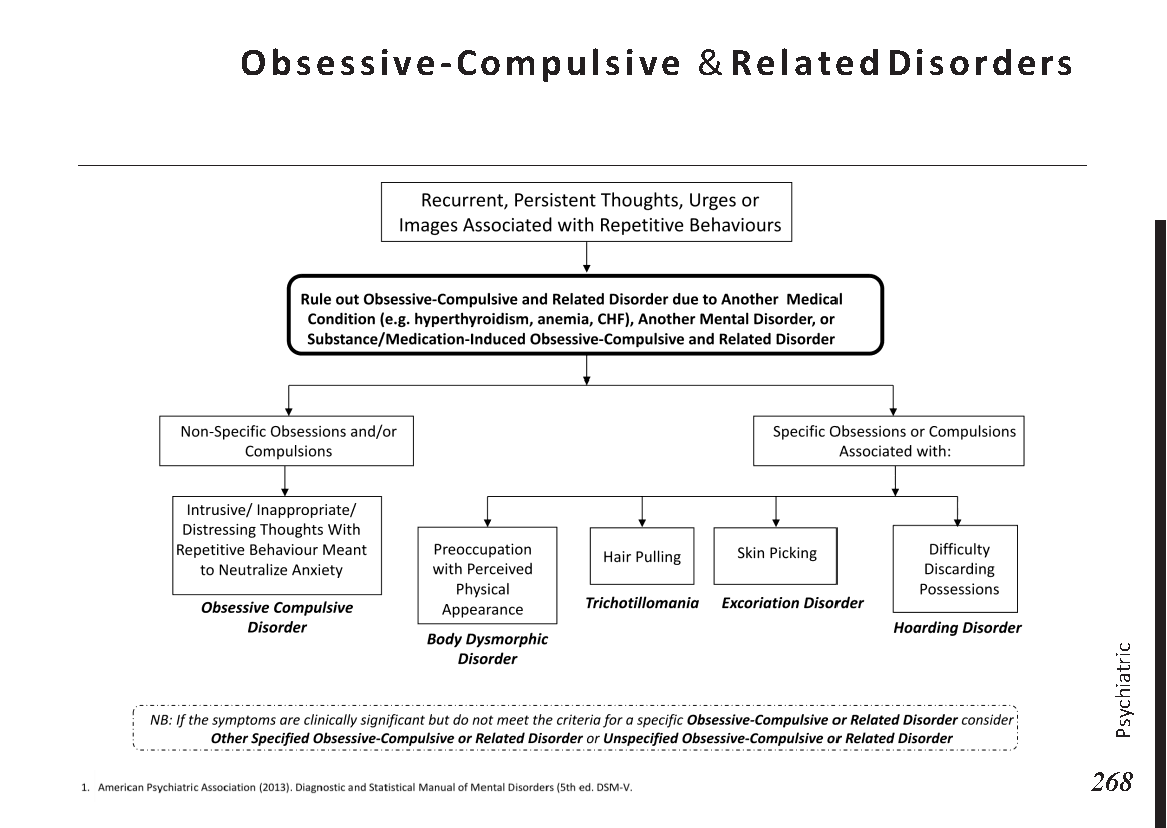
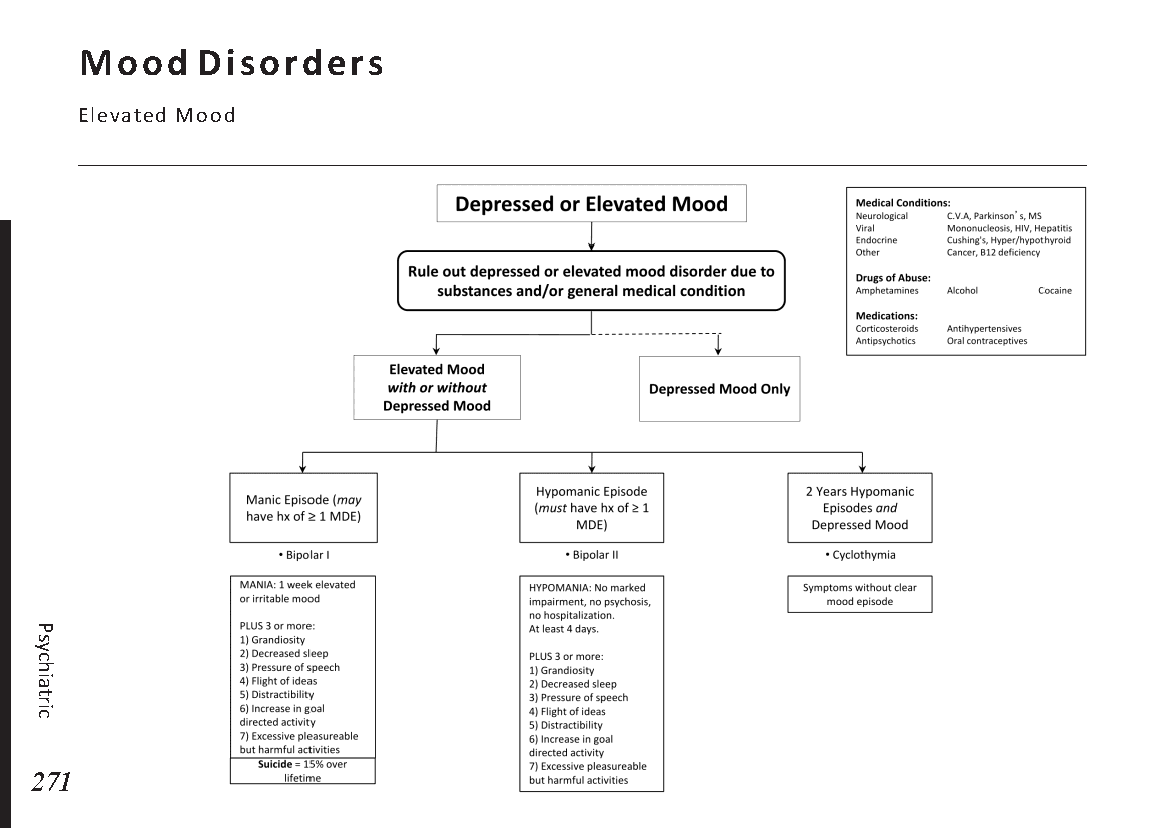
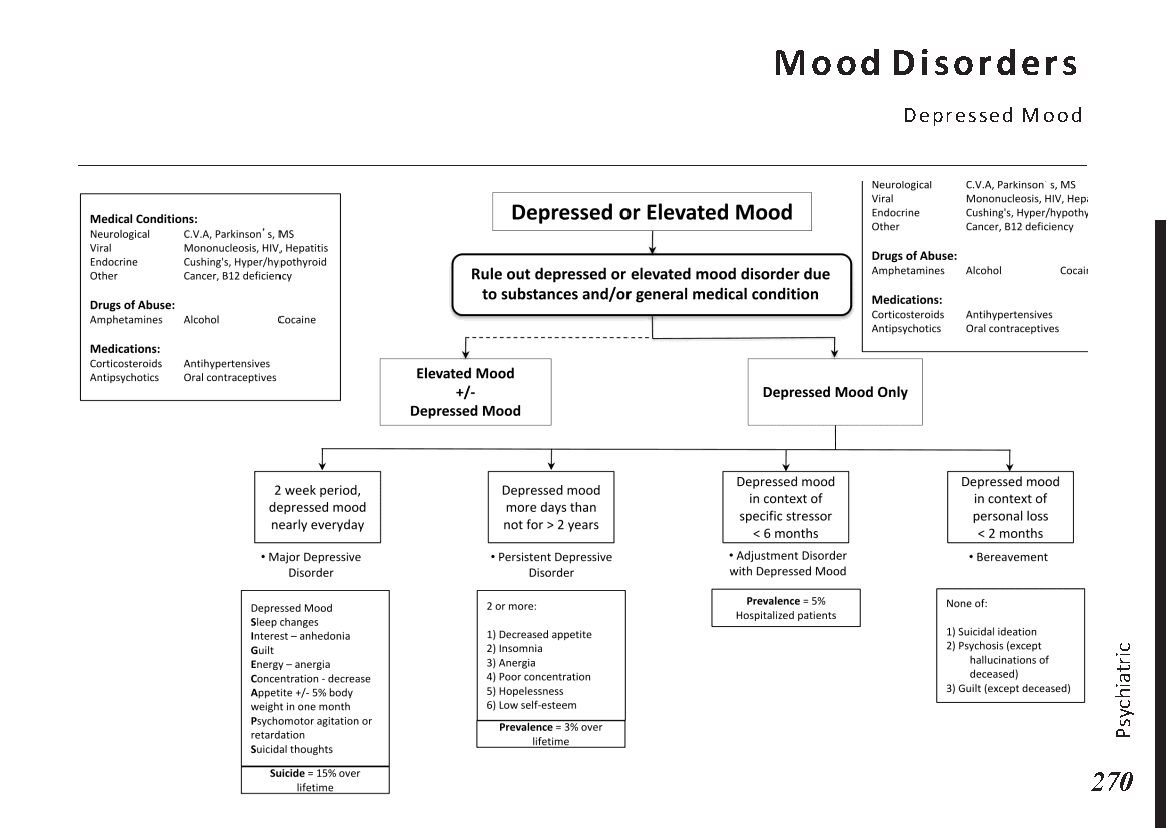
Peripheral neuropathy is often idiopathic but can be caused by a wide variety of toxic and metabolic disorders that impair axonal function. Common causes include diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, vitamin B12 deficiency, and medications (eg, cisplatin). signs and symptoms can vary. Treatment for neuropathy in legs and feet is vital to improve quality of life of the patient.
What is Peripheral neuropathy?
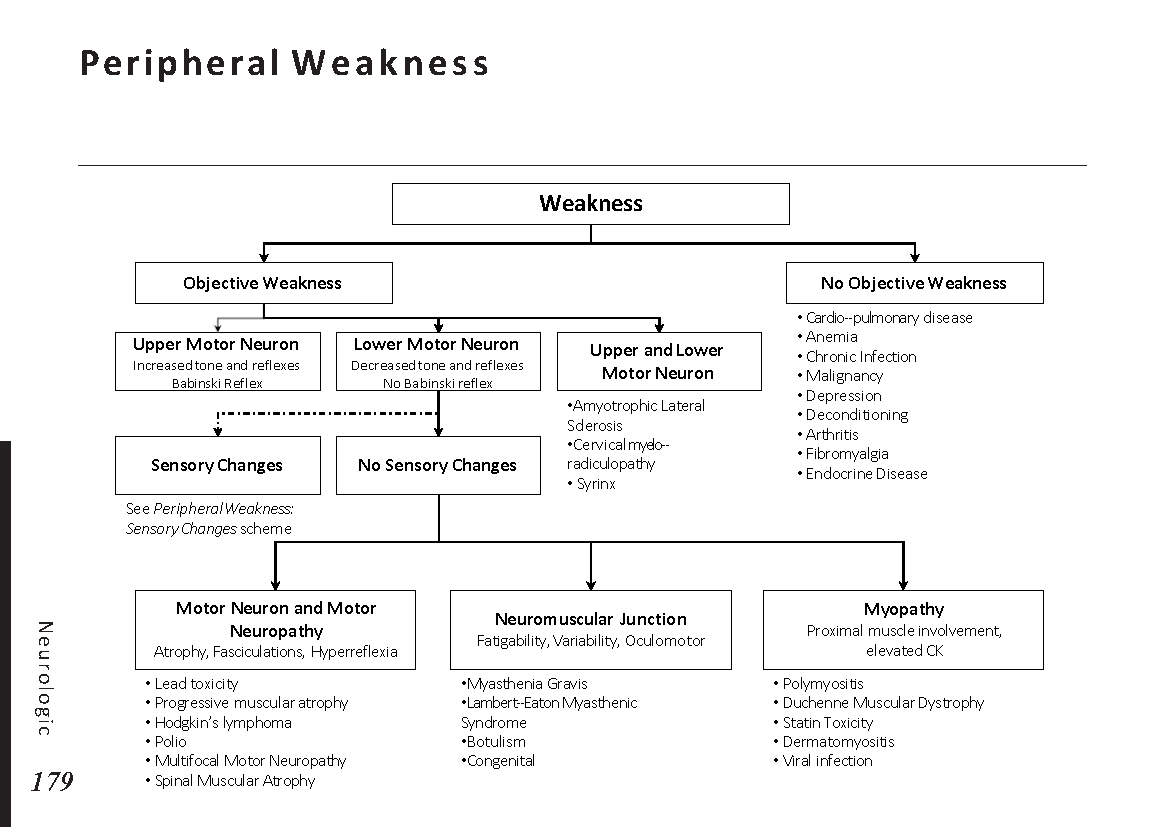
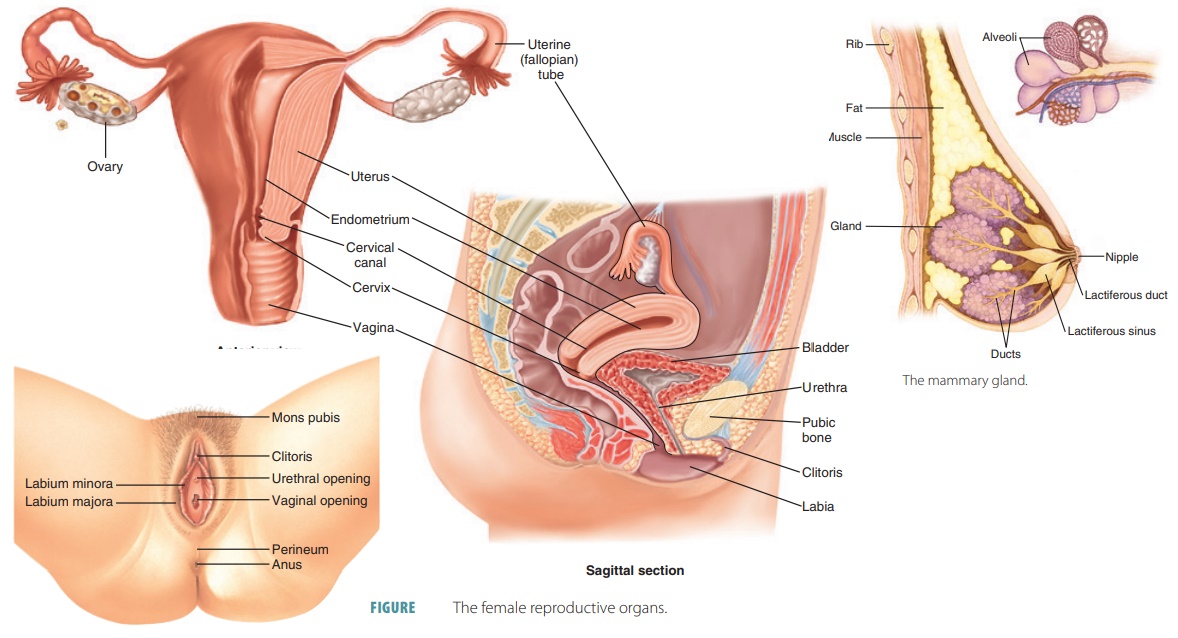
Peripheral neuropathy, which is brought on by injury to peripheral nerves (nerves outside the brain and spinal cord), frequently results in weakness, numbness, and pain, generally in the hands and feet. Other areas and bodily processes, such as digestion, urine, and circulation, may also be impacted.
Traumatic injuries, infections, metabolic issues, genetic reasons, and exposure to toxins are all potential causes of peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes is one of the most typical causes.
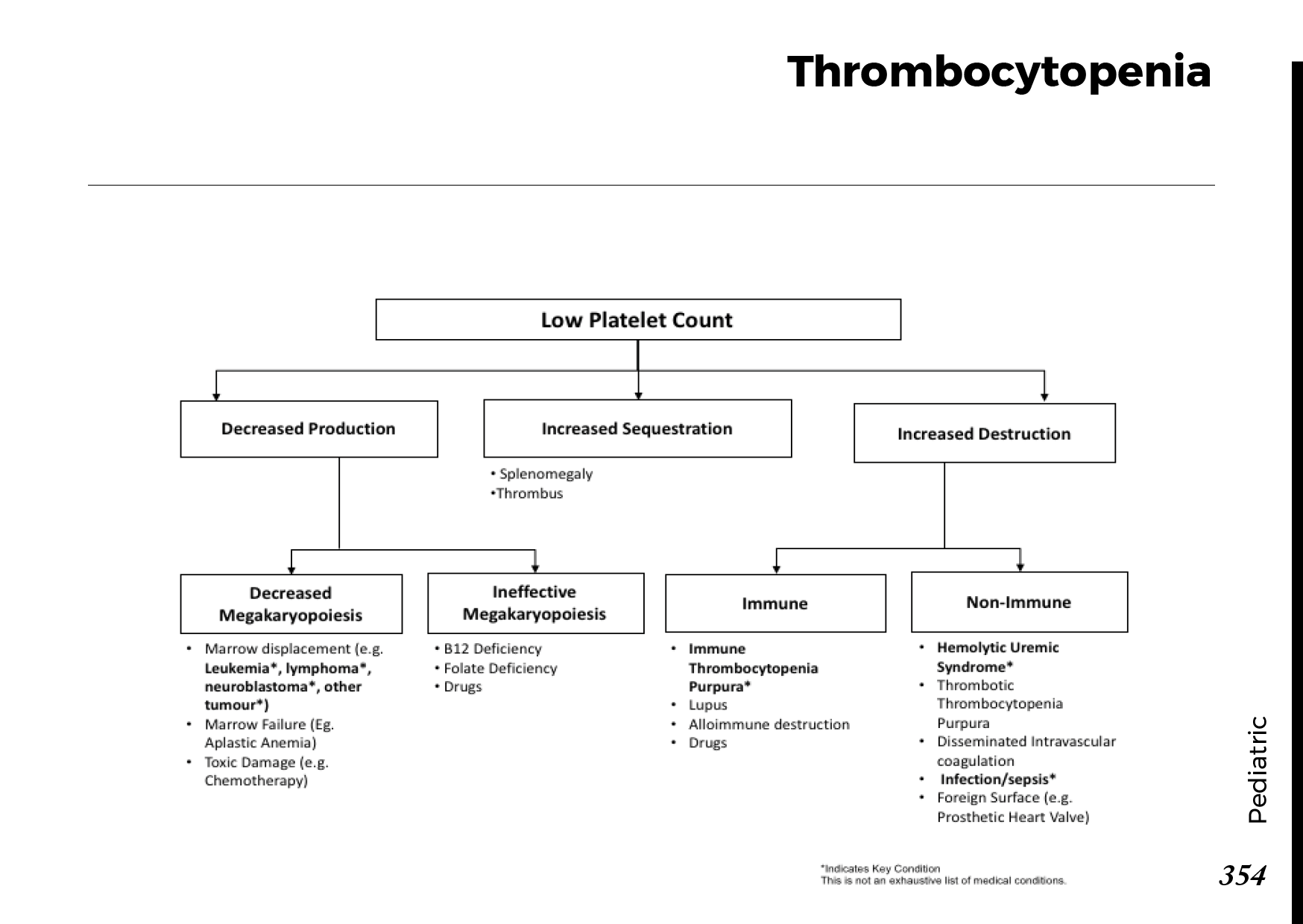
Symptoms indicating treatment for neuropathy in legs and feet
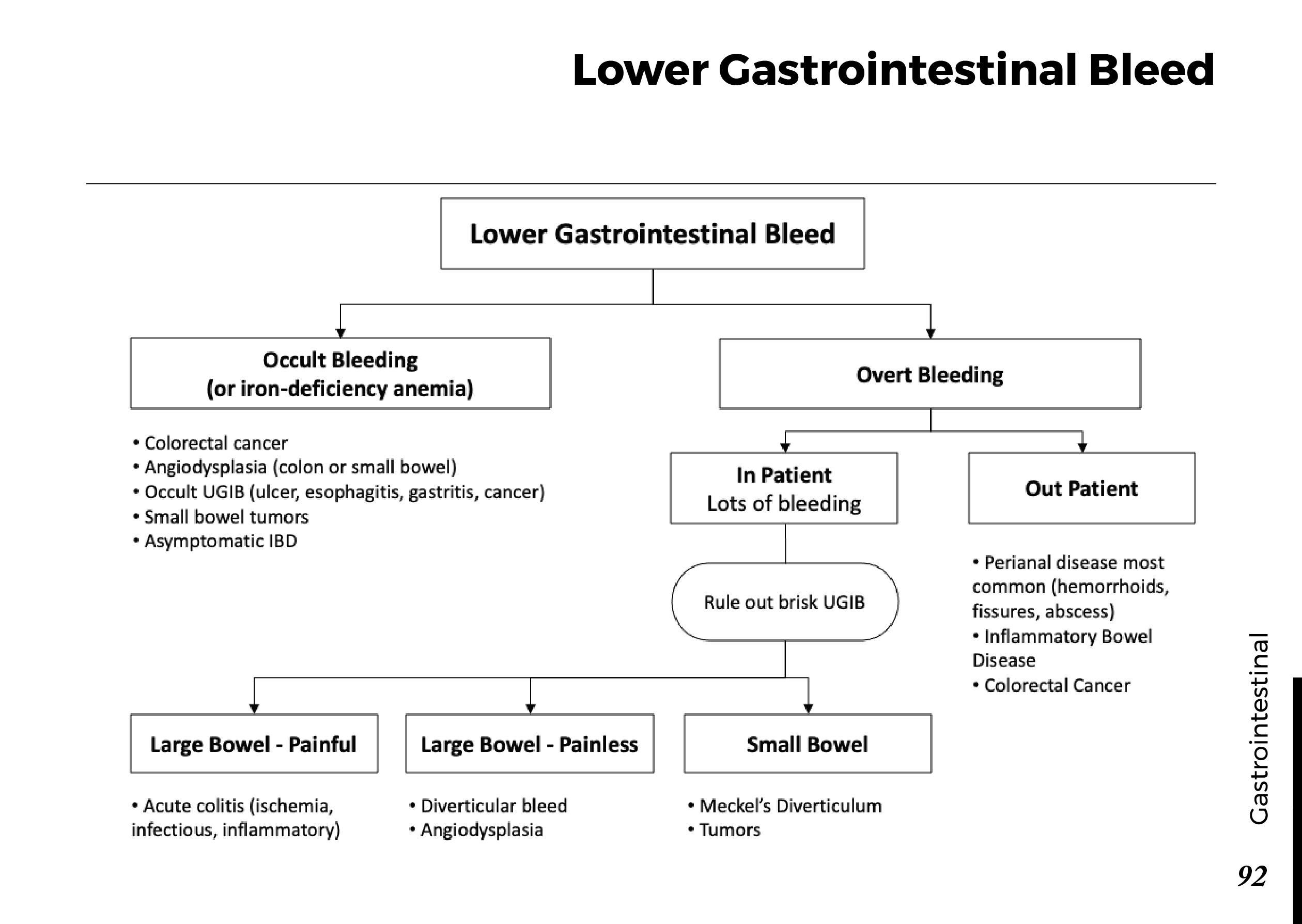
Peripheral neuropathy symptoms and signs could include:
- Gradual onset of numbness, prickling or tingling in your feet or hands, which can spread upward into your legs and arms
- Sharp, jabbing, throbbing or burning pain
- Extreme sensitivity to touch
- Pain during activities that shouldn’t cause pain, such as pain in your feet when putting weight on them or when they’re under a blanket
- Lack of coordination and falling
- Muscle weakness
- Feeling as if you’re wearing gloves or socks when you’re not
- Paralysis if motor nerves are affected
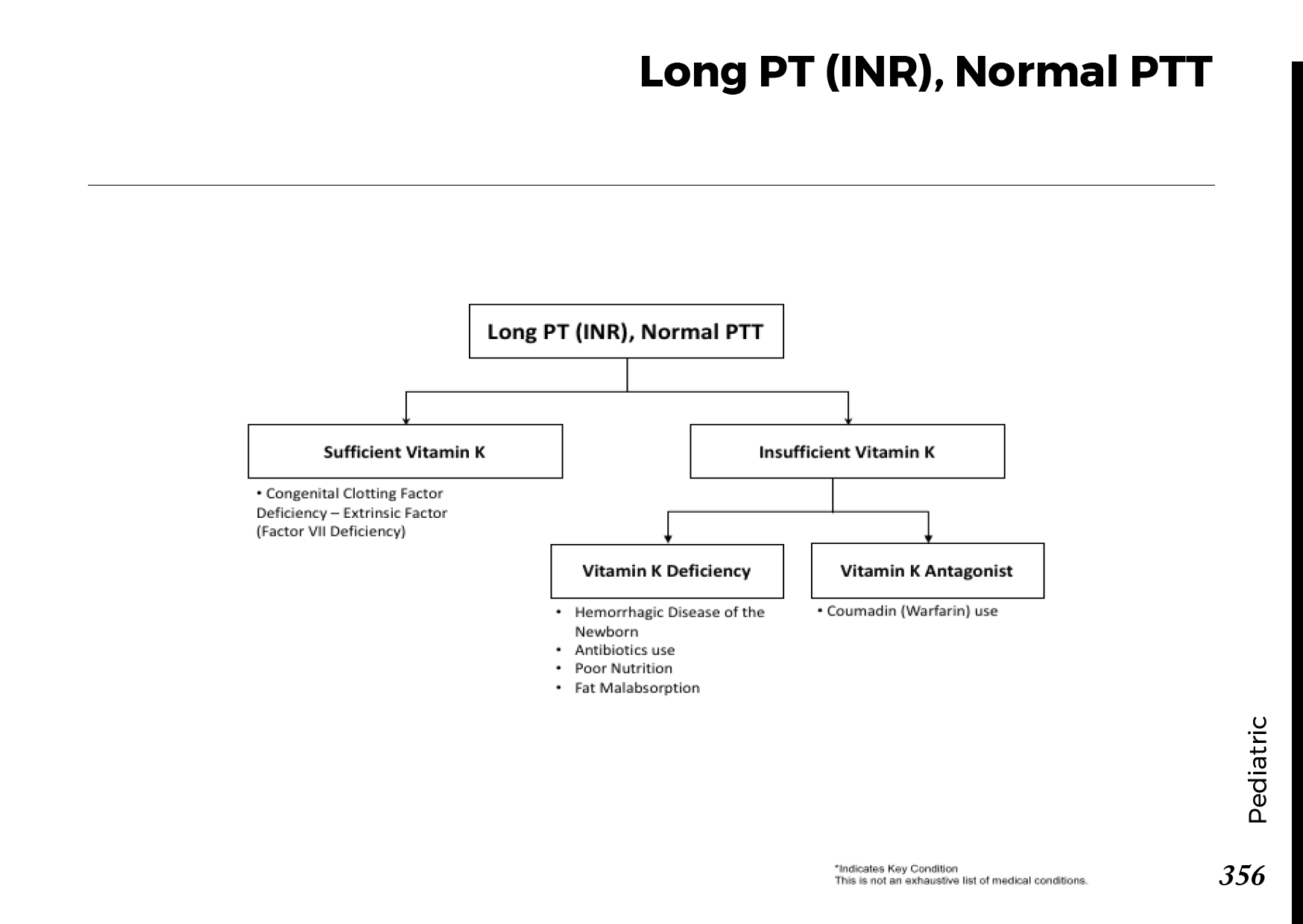
Diagnosis and tests
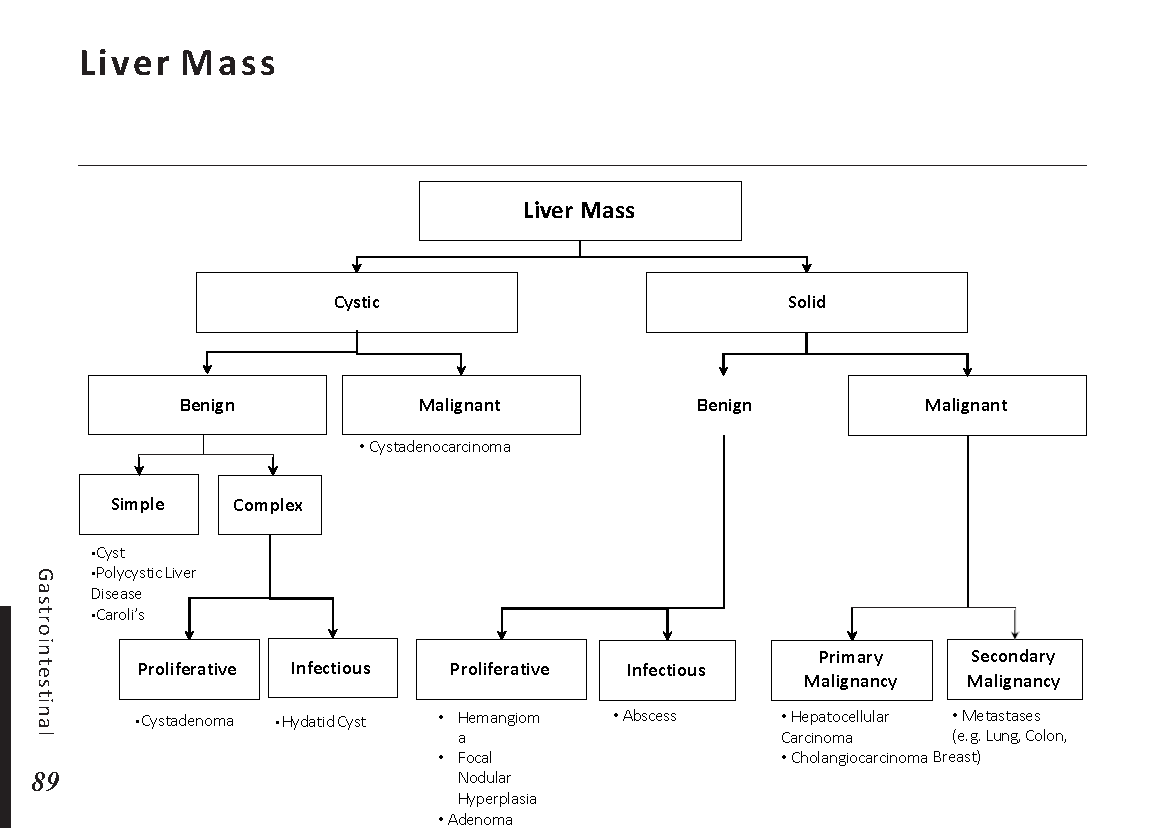
There are numerous possible causes of peripheral neuropathy. Diagnosis typically calls for:
– complete medical history. Your doctor will analyze your medical history, taking into account your symptoms, way of life, exposure to chemicals, drinking patterns, and any family members who have had neurological (or nervous system) disorders.
– neurological assessment. Your doctor may examine your posture and coordination in addition to your tendon reflexes, muscle strength, and muscle tone.
– blood tests. These can pick up signs of illnesses that can cause peripheral neuropathy, including vitamin deficiencies, diabetes, aberrant immunological function, and others.
– imaging studies. CT or MRI scans can check for cancers, herniated disks, pinched (compressed) nerves, blood vessel abnormalities, and other conditions affecting the bones and blood vessels.
– testing of nerve function. Your muscles’ electrical activity is captured by electromyography (EMG), which can identify nerve damage. To record electrical activity as the muscle contracts, a tiny needle (electrode) is placed into the muscle.
– further tests for nerve function. A sweat test, which gauges your body’s sweat production, an autonomic reflex screen that documents how the autonomic nerve fibers function, and sensory tests that capture your perception of touch, vibration, cooling, and heat are some examples of these.
– nerve biopsy. This is taking out a short piece of a nerve, typically a sensory nerve, to check for anomalies.
– skin biopsy To check for a decrease in nerve endings, your doctor takes a little piece of skin off.
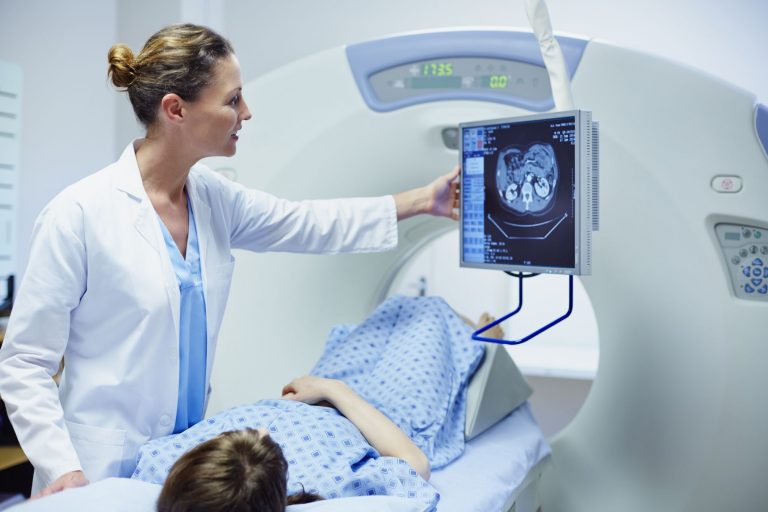
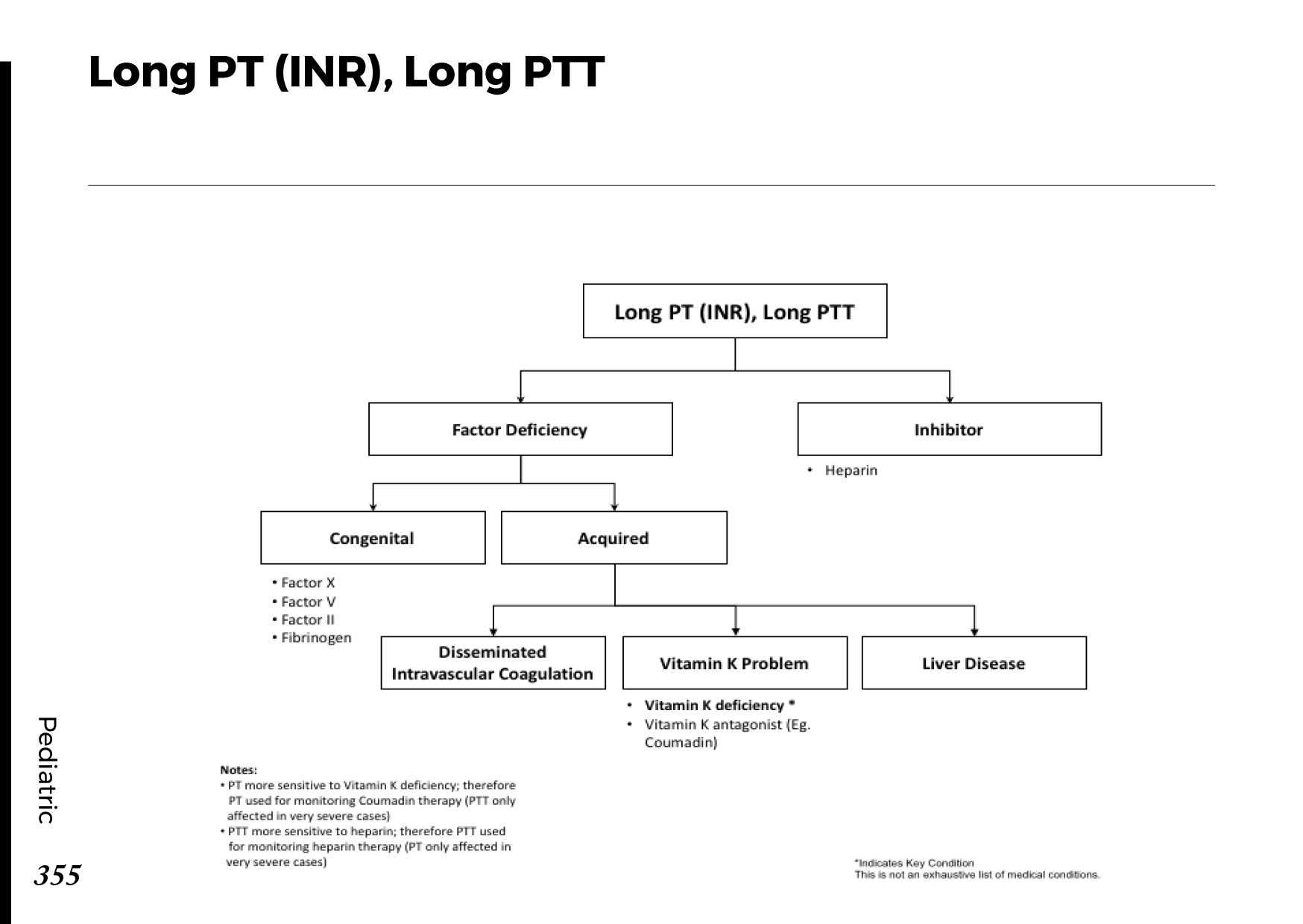
Treatment for neuropathy in legs and feet
Goals of treatment include symptom relief and management of the underlying illness causing your neuropathy. Your doctor might advise watchful waiting to see if your neuropathy gets better if your lab results show no underlying problem.
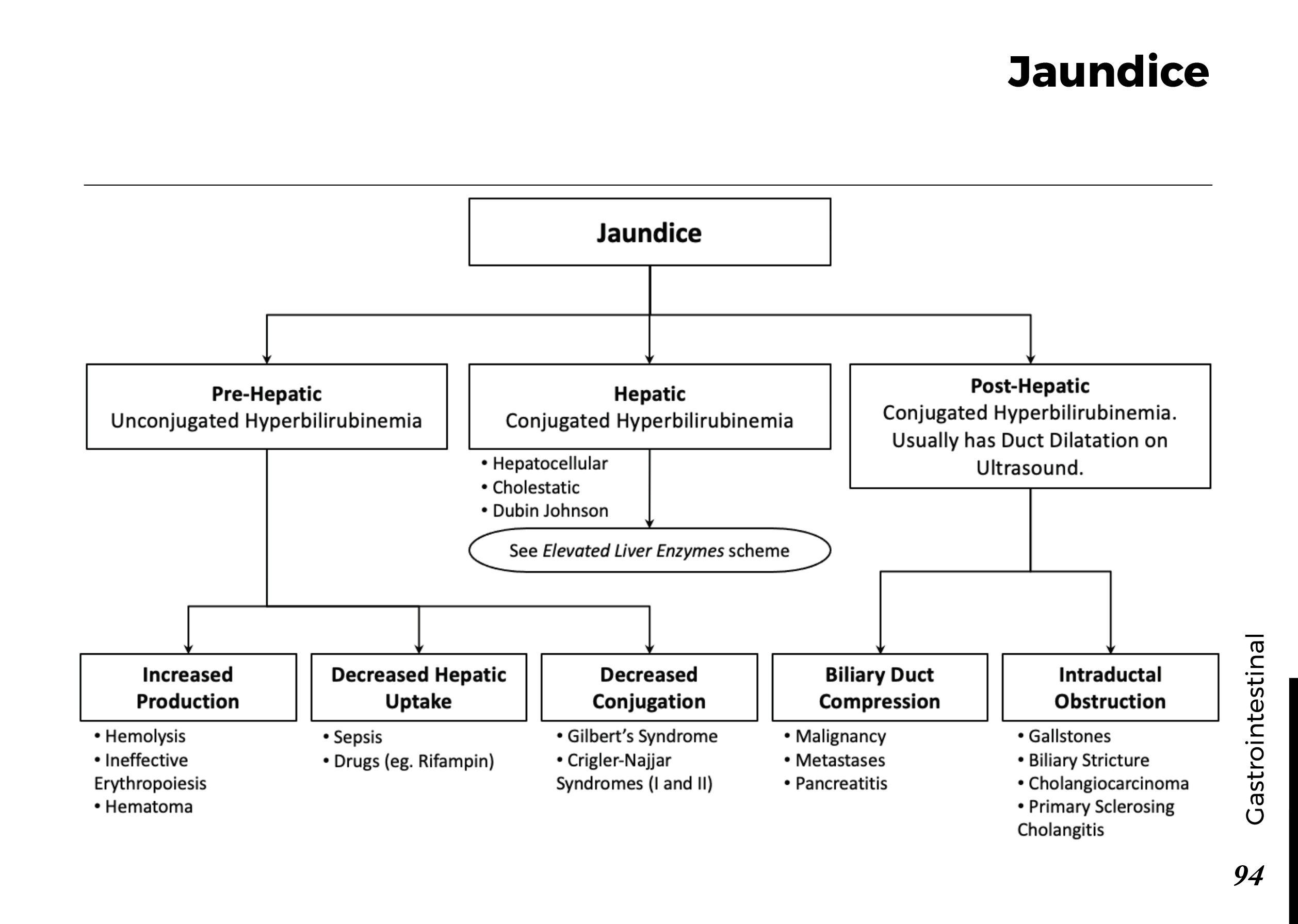
Medications
– Pain relievers. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines, for example, are over-the-counter painkillers that can treat moderate symptoms. Your doctor might recommend painkillers if you have more severe symptoms.
Opioid medications like tramadol (Conzip, Ultram, etc.) or oxycodone (Oxycontin, Roxicodone, etc.) can cause dependence and addiction, hence these medications are typically not recommended unless all other therapies have failed.
– anti-seizure drugs. Pregabalin (Lyrica) and gabapentin (Gralise, Neurontin, Horizant), drugs designed to treat epilepsy, may help with nerve pain. Drowsiness and lightheadedness are possible side effects.
– topical Treatment. Peripheral neuropathy symptoms can be slightly improved by using capsaicin lotion, which contains a compound found in hot peppers. Wherever you put the cream, you can have skin burning and irritation, although this normally subsides with time. However, some people find it intolerable.
Another skin-applied treatment that may provide pain relief is lidocaine patches. Drowsiness, vertigo, and numbness at the patch’s location are possible side effects.
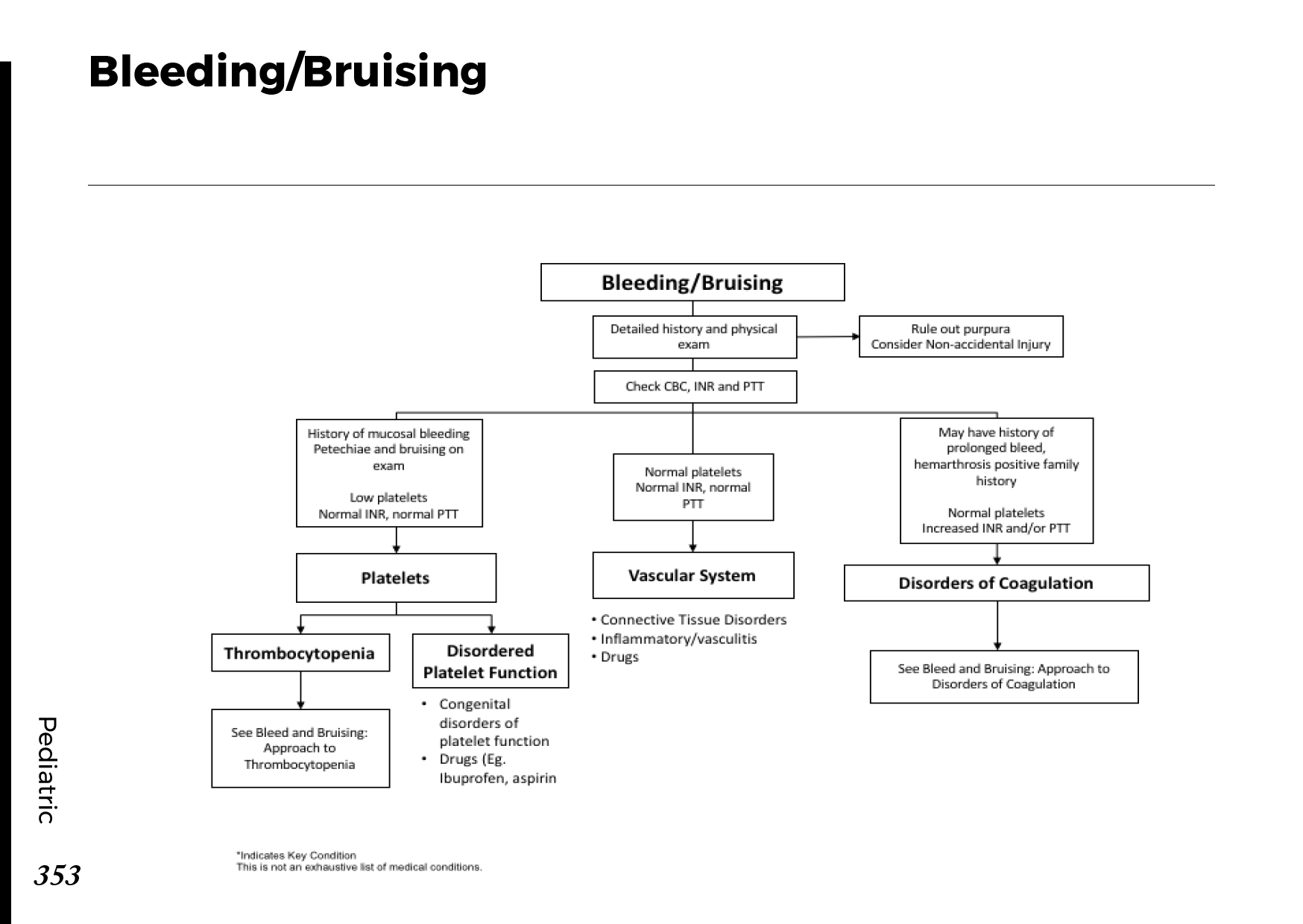
Therapies and Procedures
– electrical nerve stimulation transcutaneously (TENS). Various frequencies of a mild electric current are delivered to the skin through electrodes. For roughly a month, TENS should be used for 30 minutes per day.
– Intravenous immune globulin and plasma exchange. These methods, which aid in reducing immune system activity, may be advantageous for those who suffer from specific inflammatory disorders.
Plasma exchange entails drawing blood from you, purifying it of antibodies and other proteins, and then reintroducing it to your body. Immune globulin treatment involves administering large amounts of antibodies-producing proteins (immunoglobulins).
– Physical therapy might help you move better if you have weak muscles. You might also require wheelchairs, canes, walker, or foot or hand braces.
– Surgery. You may require surgery to relieve the strain if your neuropathies are brought on by pressure on your nerves, such as pressure from tumors.
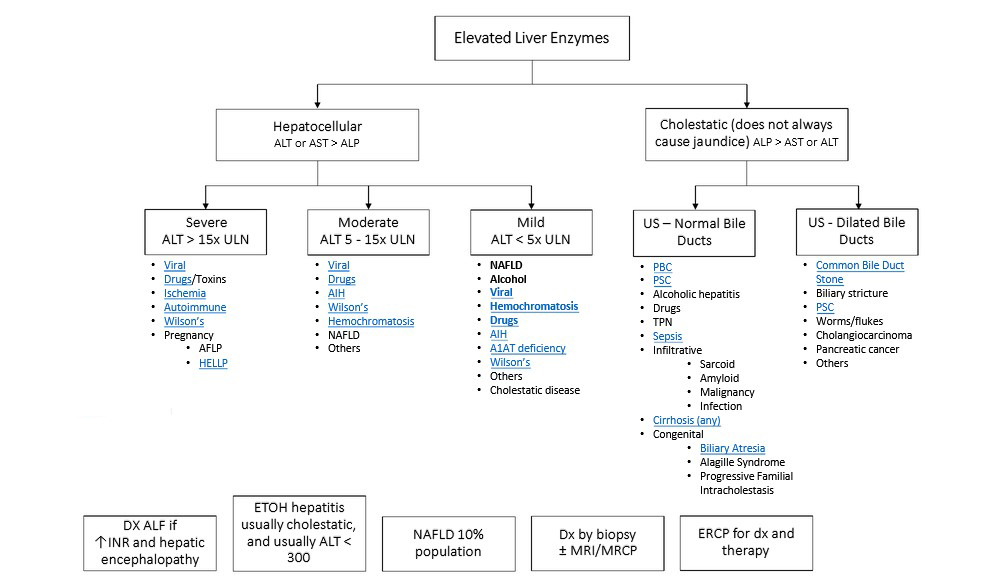
Natural remedies
– Cayenne pepper: Capsaicin, the component in hot peppers that gives them their spiciness, may be found in cayenne pepper. It can also be used in topical creams to alleviate pain since it diffuses pain signals throughout the body, reducing its severity. You can add cayenne pepper to your diet, or if you can’t take the heat, you can use ointments or pills that contain capsaicin.
– Warm baths: Taking a warm bath can be calming and alleviate general aches and pains even if it is not a cure for neuropathy in your legs and feet. However, warm water can also improve blood flow and lessen pain that might be connected to numbness if you have neuropathic pain. Make sure your bathwater is not too hot if your sensory nerves are affected by your condition and you are not sensitive to temperature.
– Acupuncture : Acupuncture stimulates pressure points with needles to encourage the body’s own healing processes. The method causes the nervous system to release chemicals into the body that can alter how painful you feel and how tolerable you are to it. Acupuncture’s ability to regulate your energy can also help your emotional health.
Article writer
This article was written by Hashem Khdour, Medical Doctor and the founder of Medicogenic medicine learning & health website

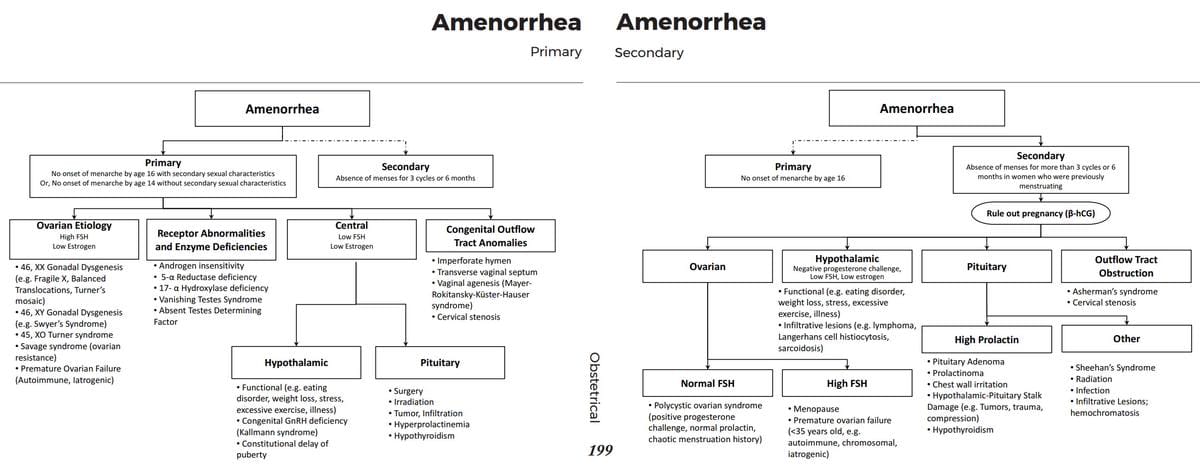
 Menstrual cycle physiology:
Menstrual cycle physiology: