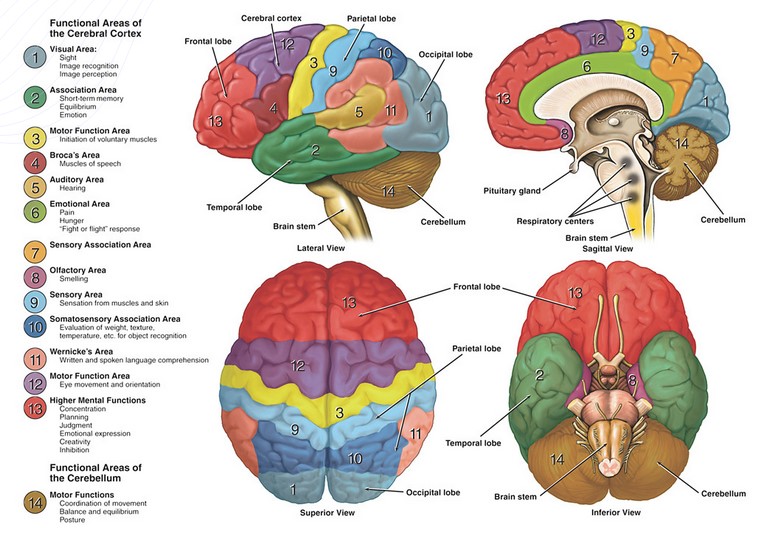
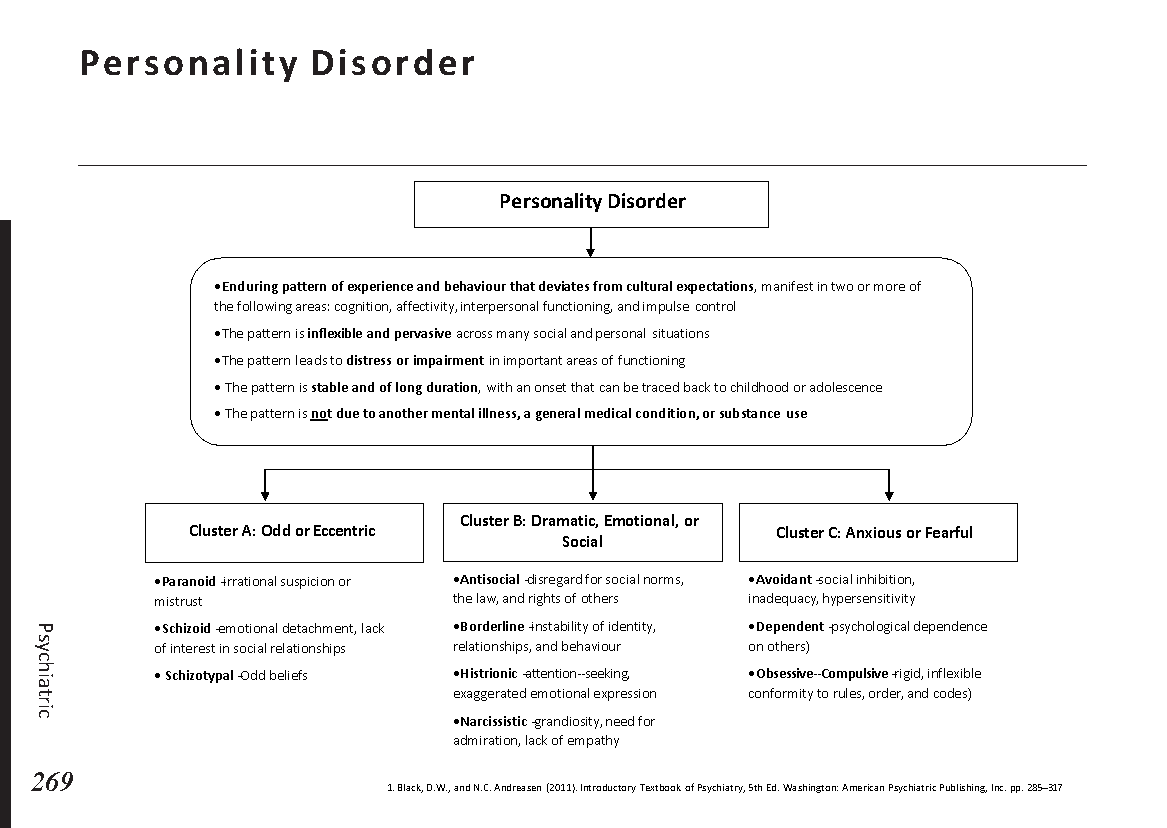
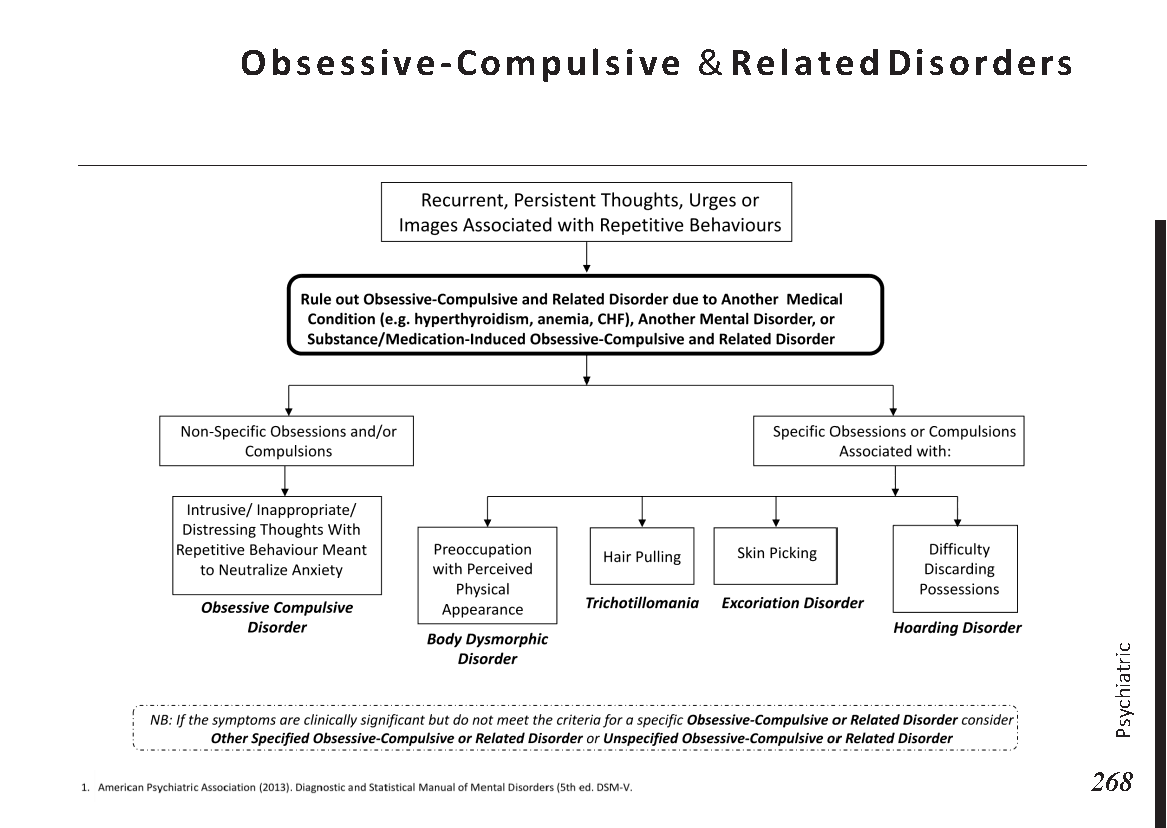
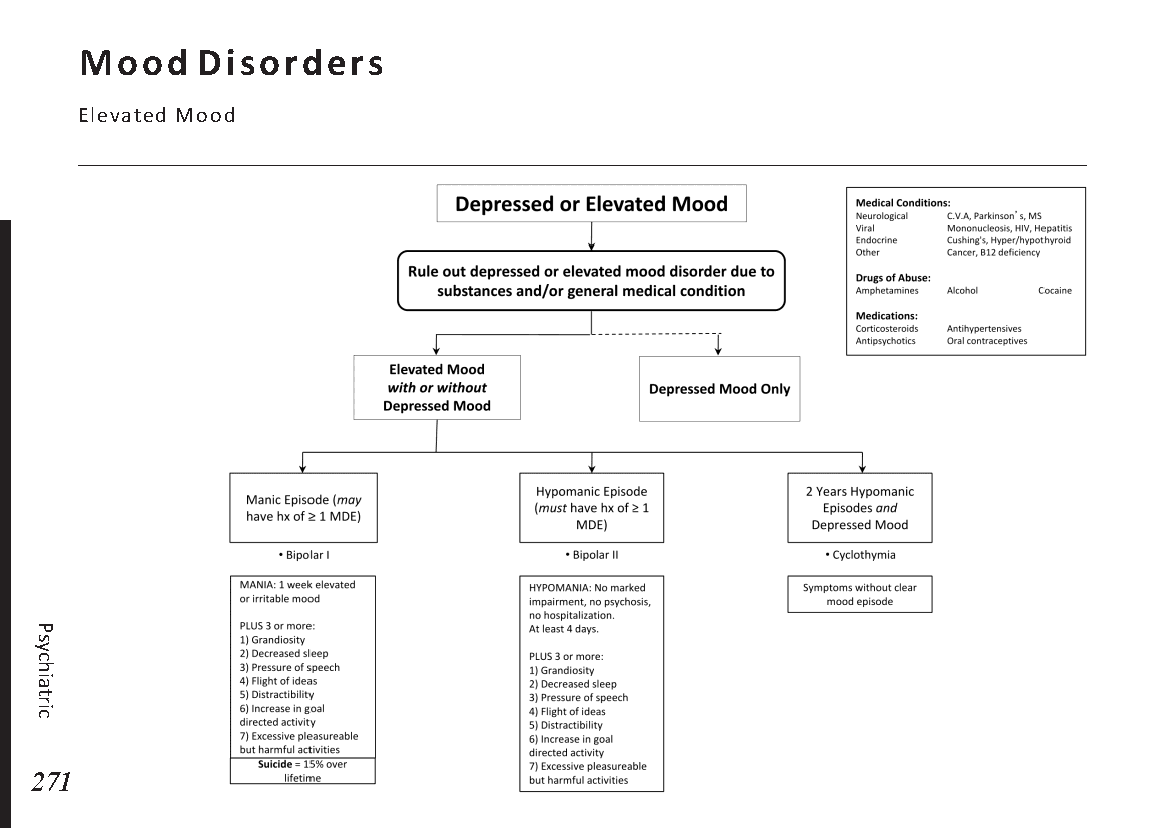
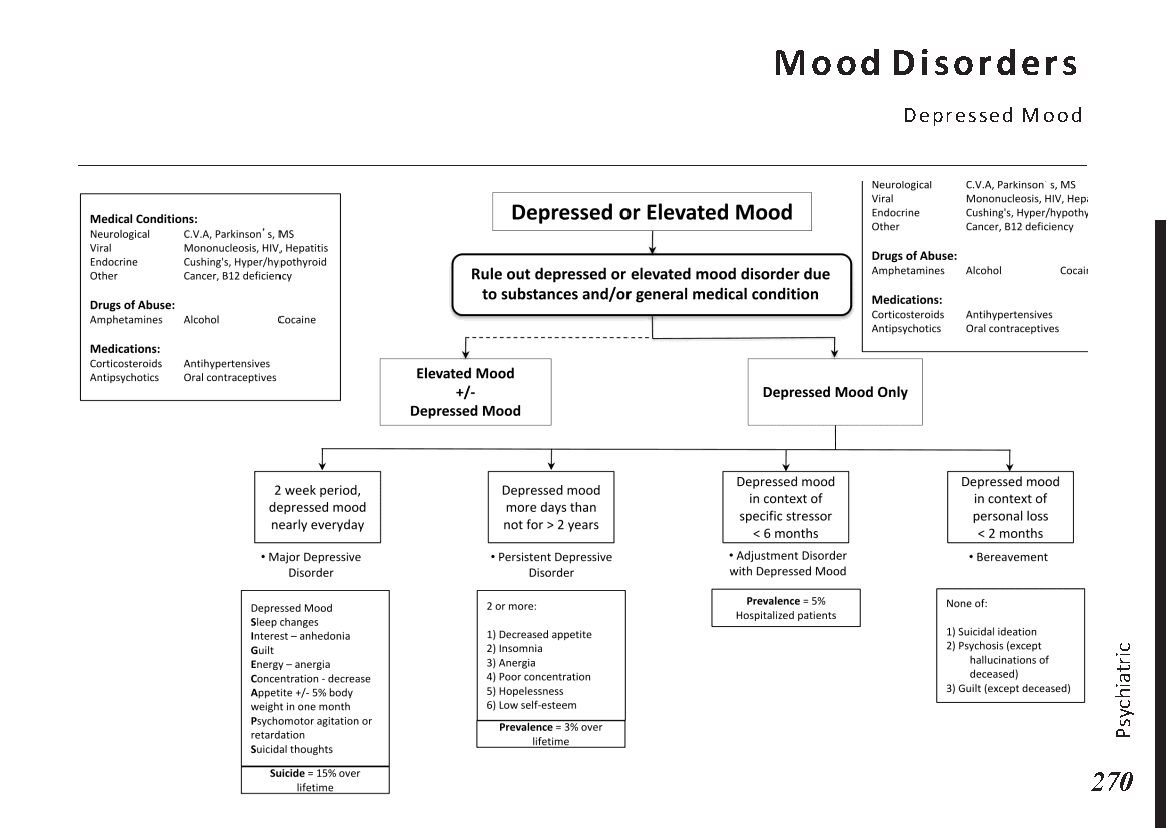
Introduction
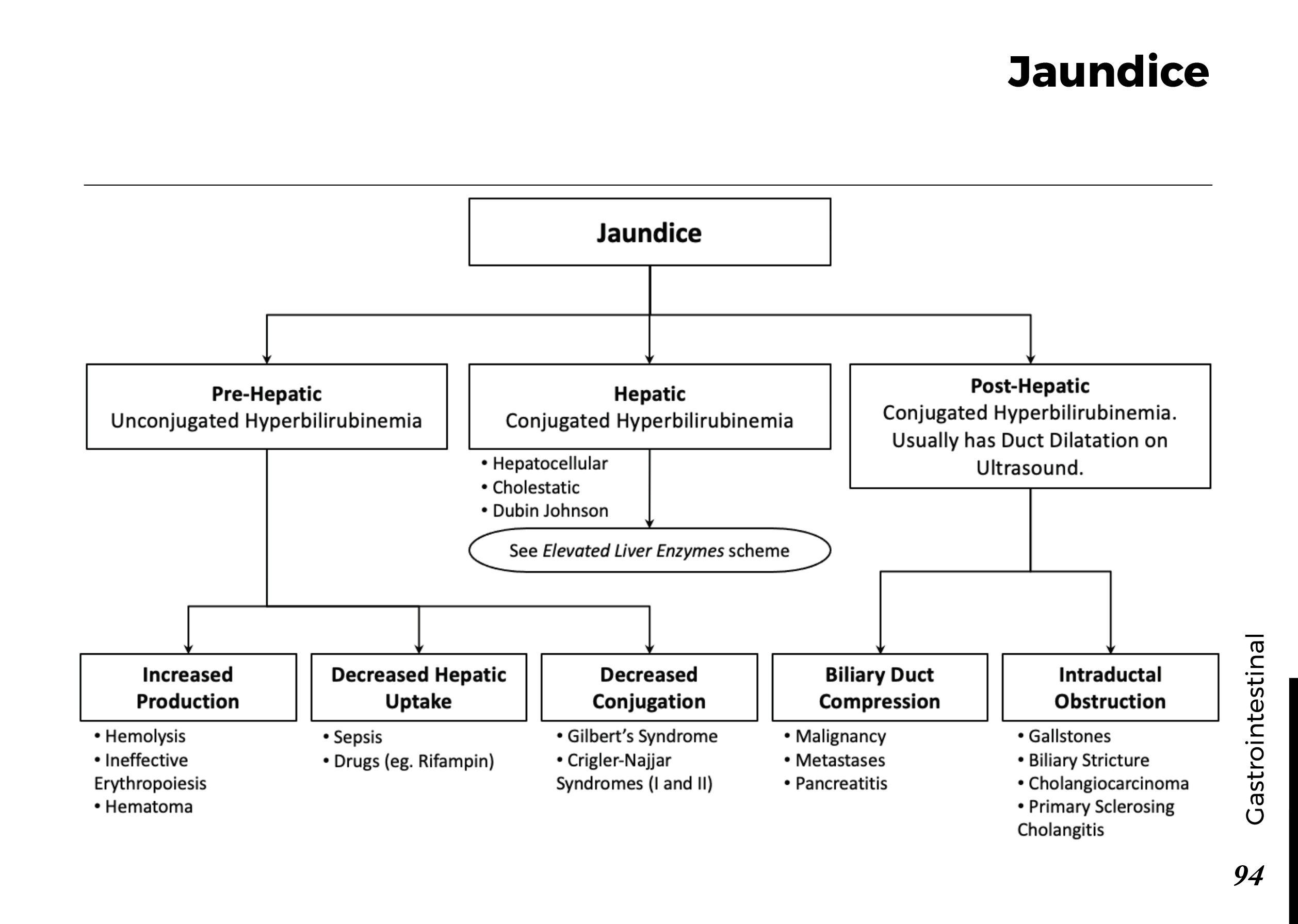
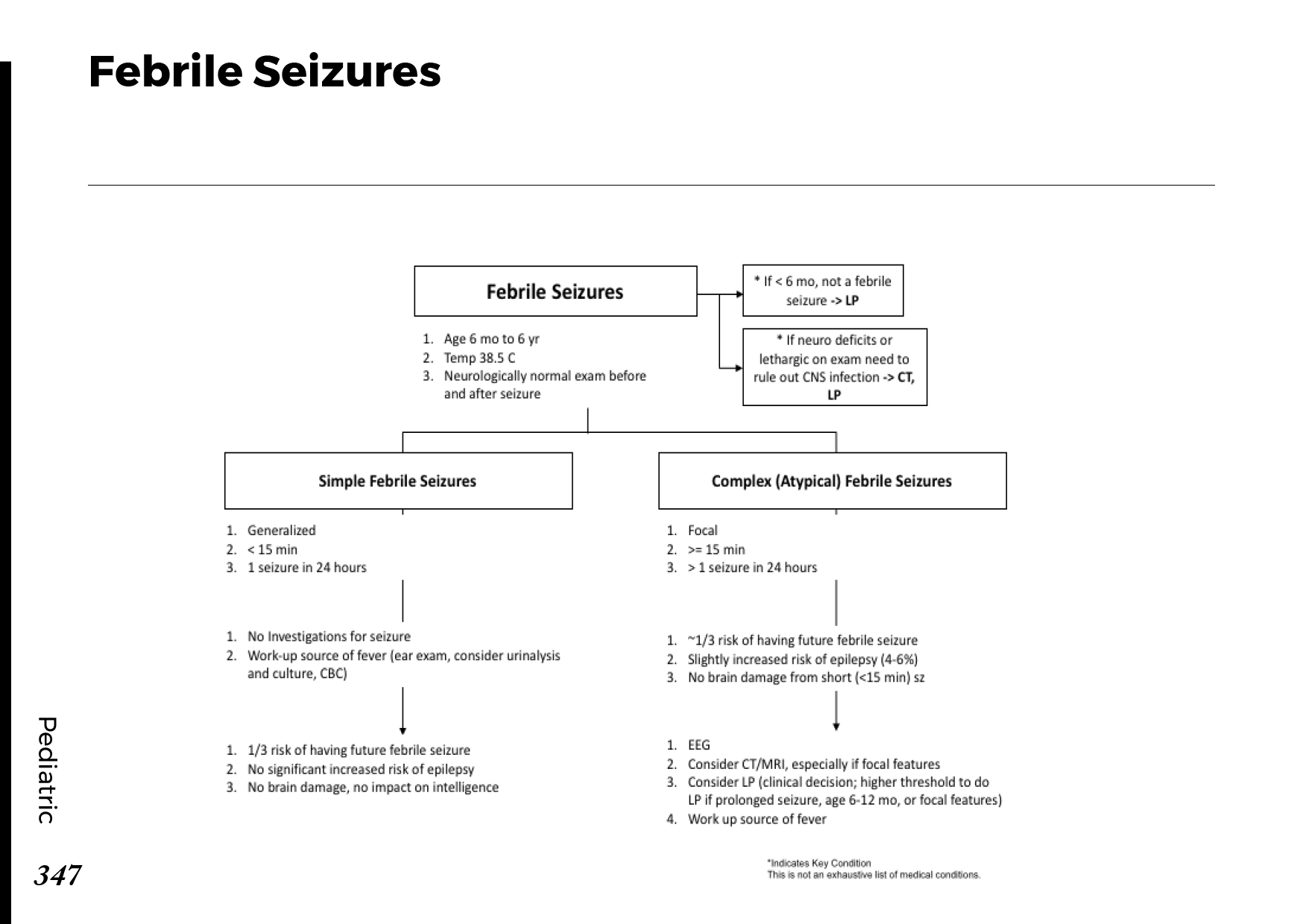
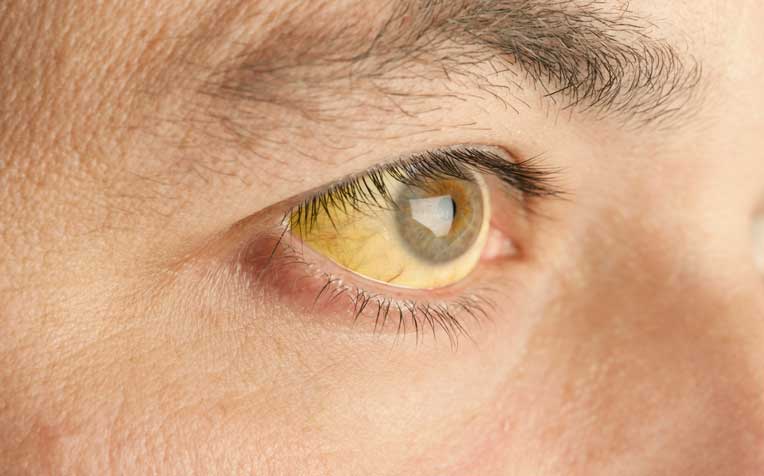
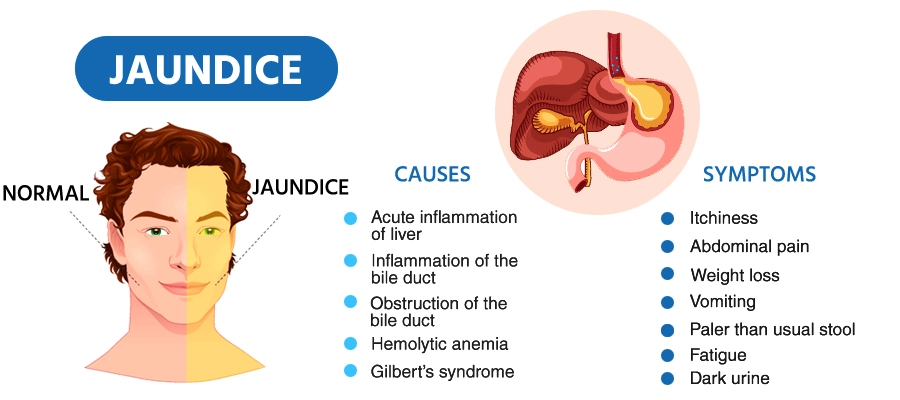
Obstructive jaundice is a serious medical condition that can lead to yellowing of the skin and eyes. In this post, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options for obstructive jaundice. Whether you or someone you know is dealing with this condition, it’s crucial to gain insights into its nature and seek timely medical attention for effective management.
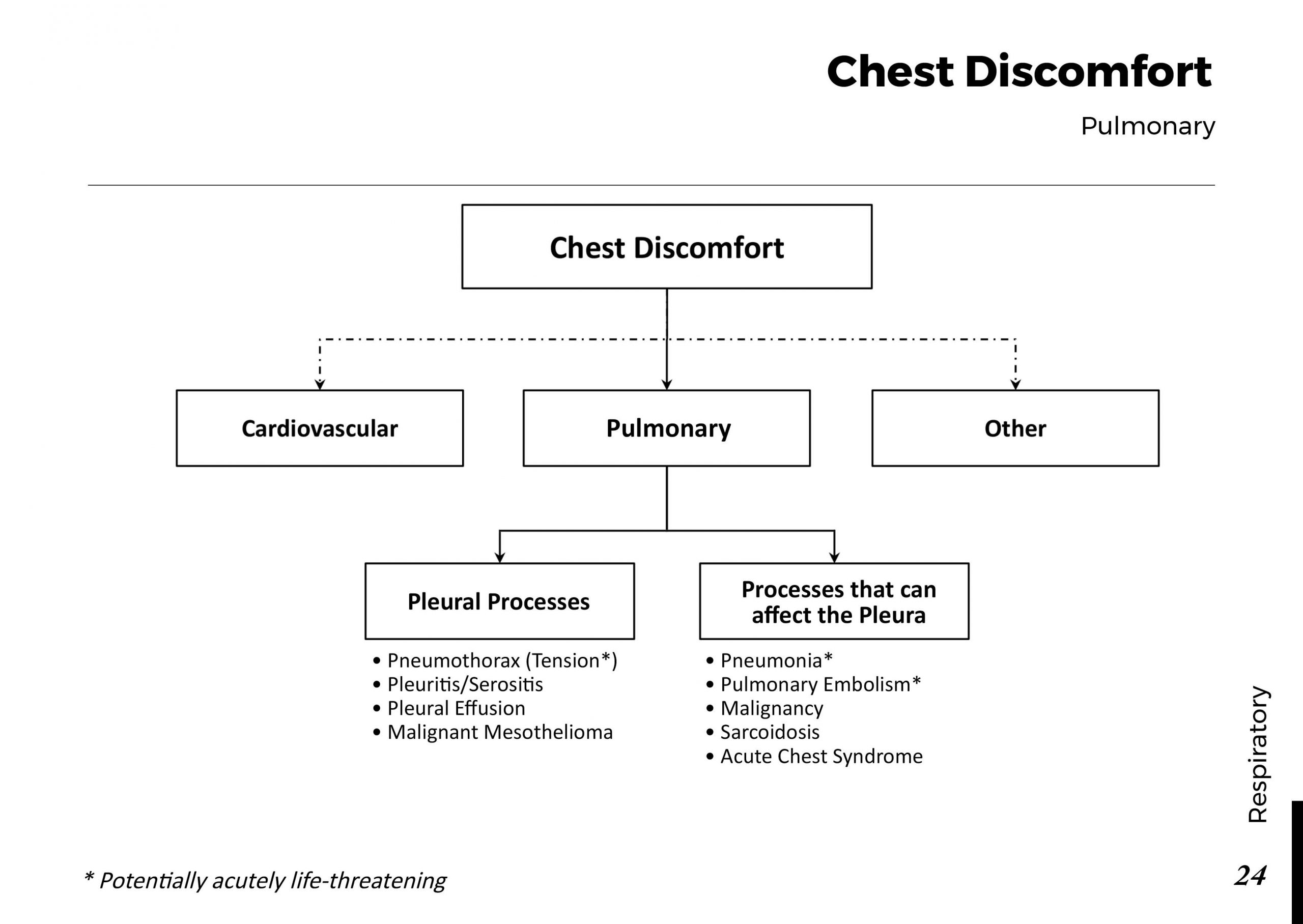
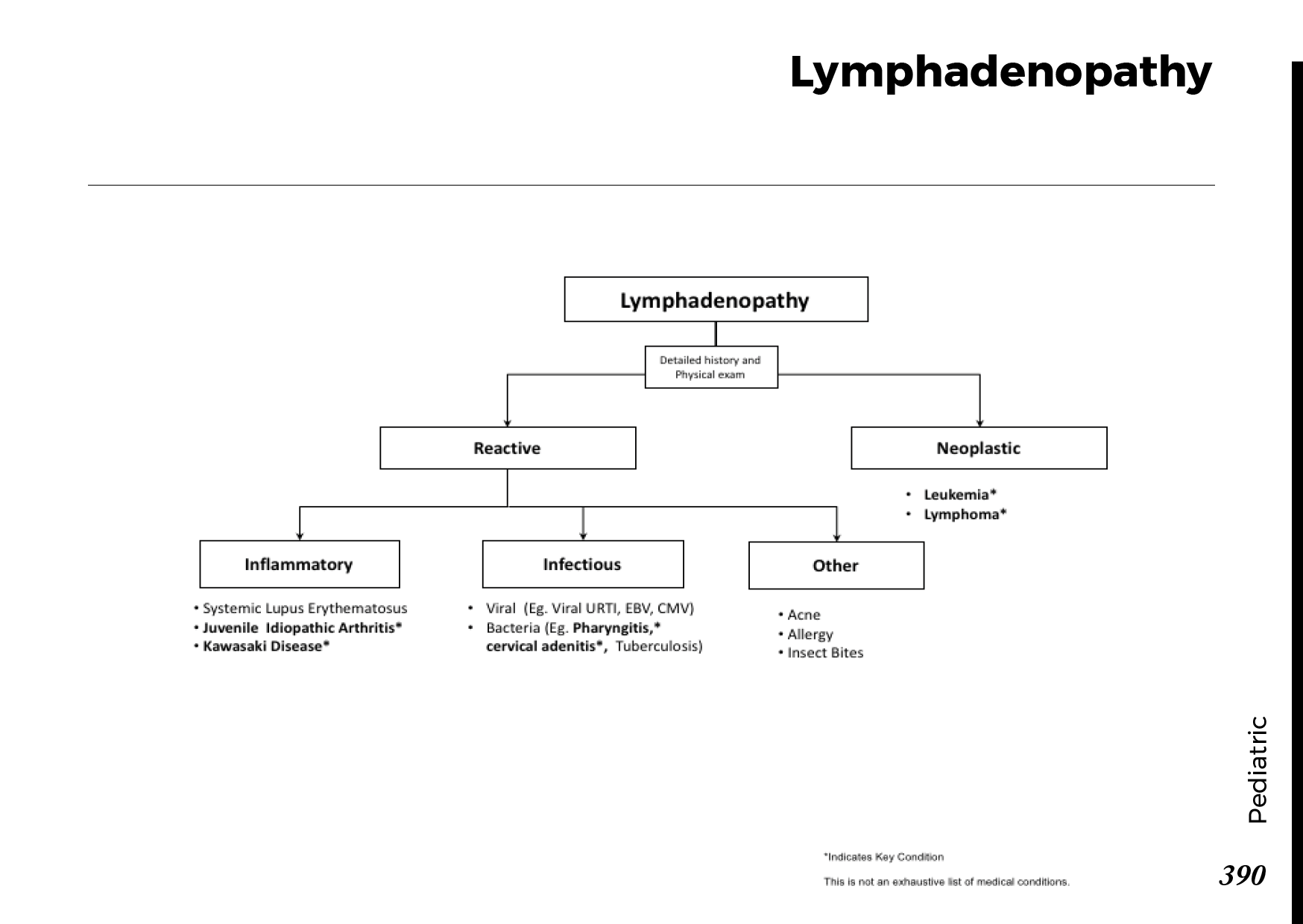
Understanding Obstructive Jaundice:
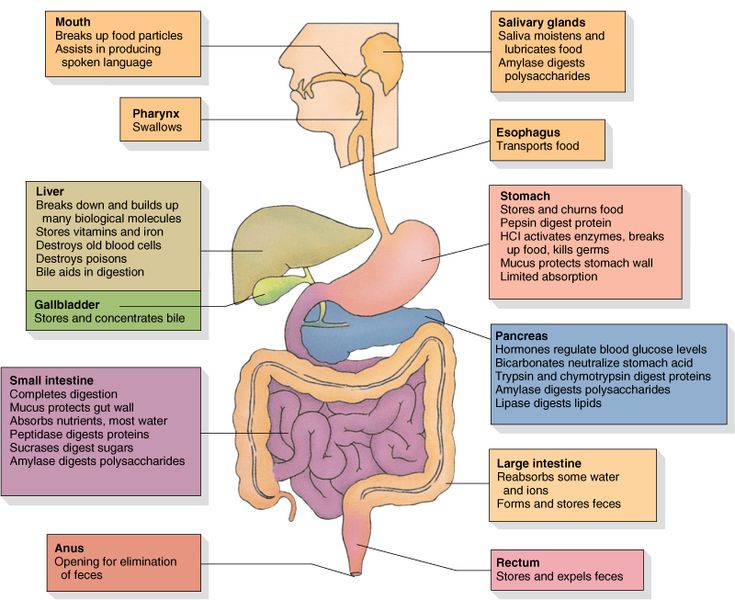
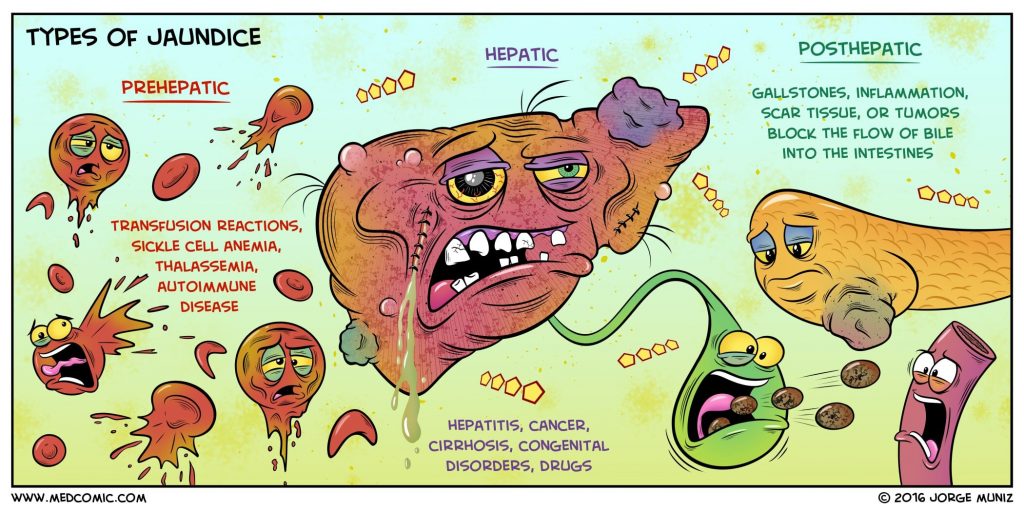
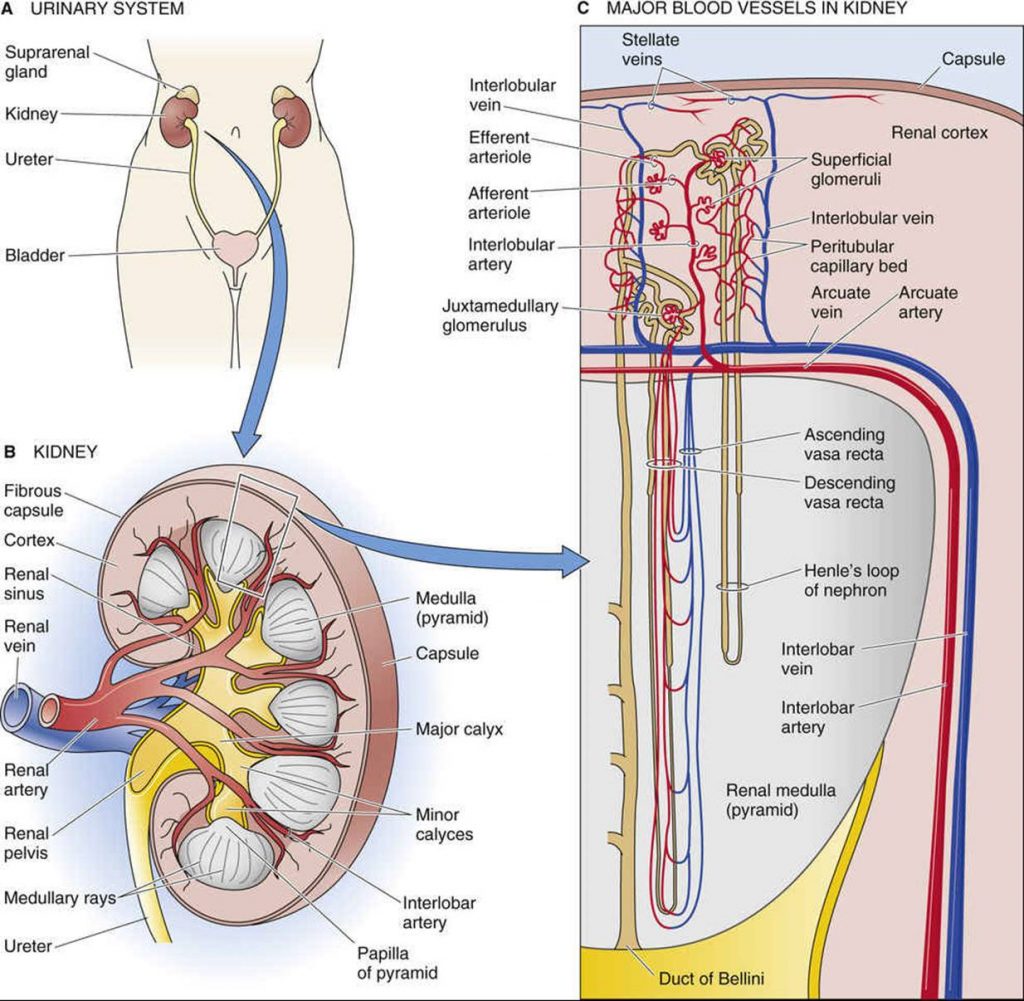
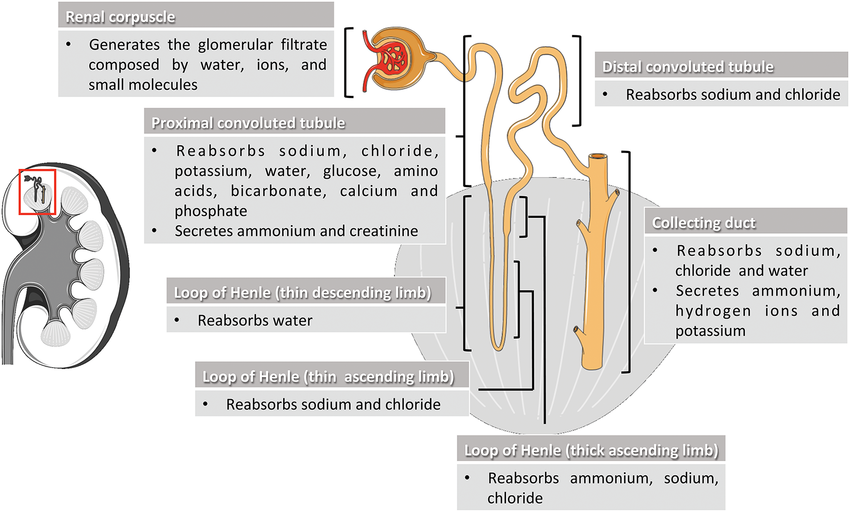
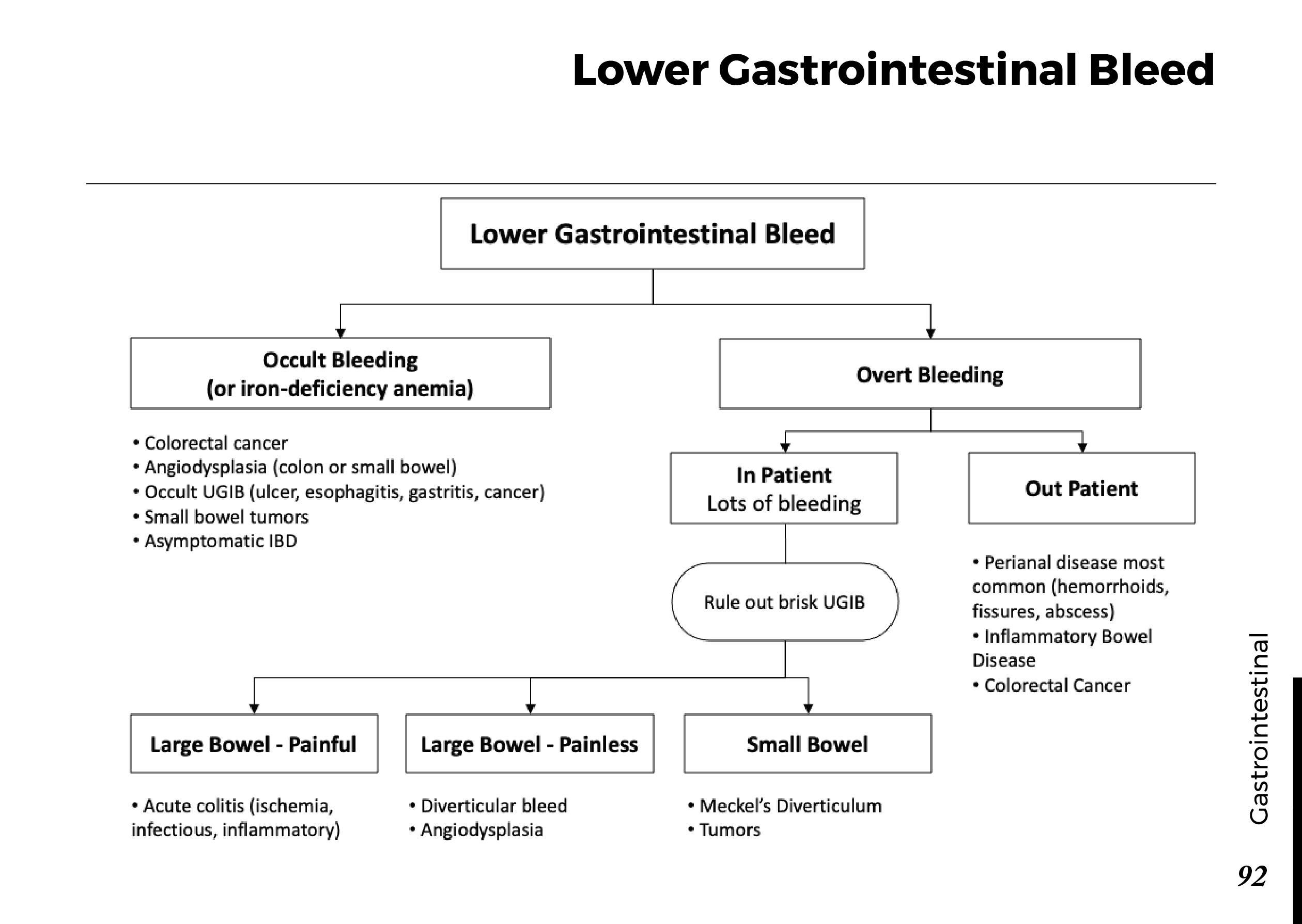
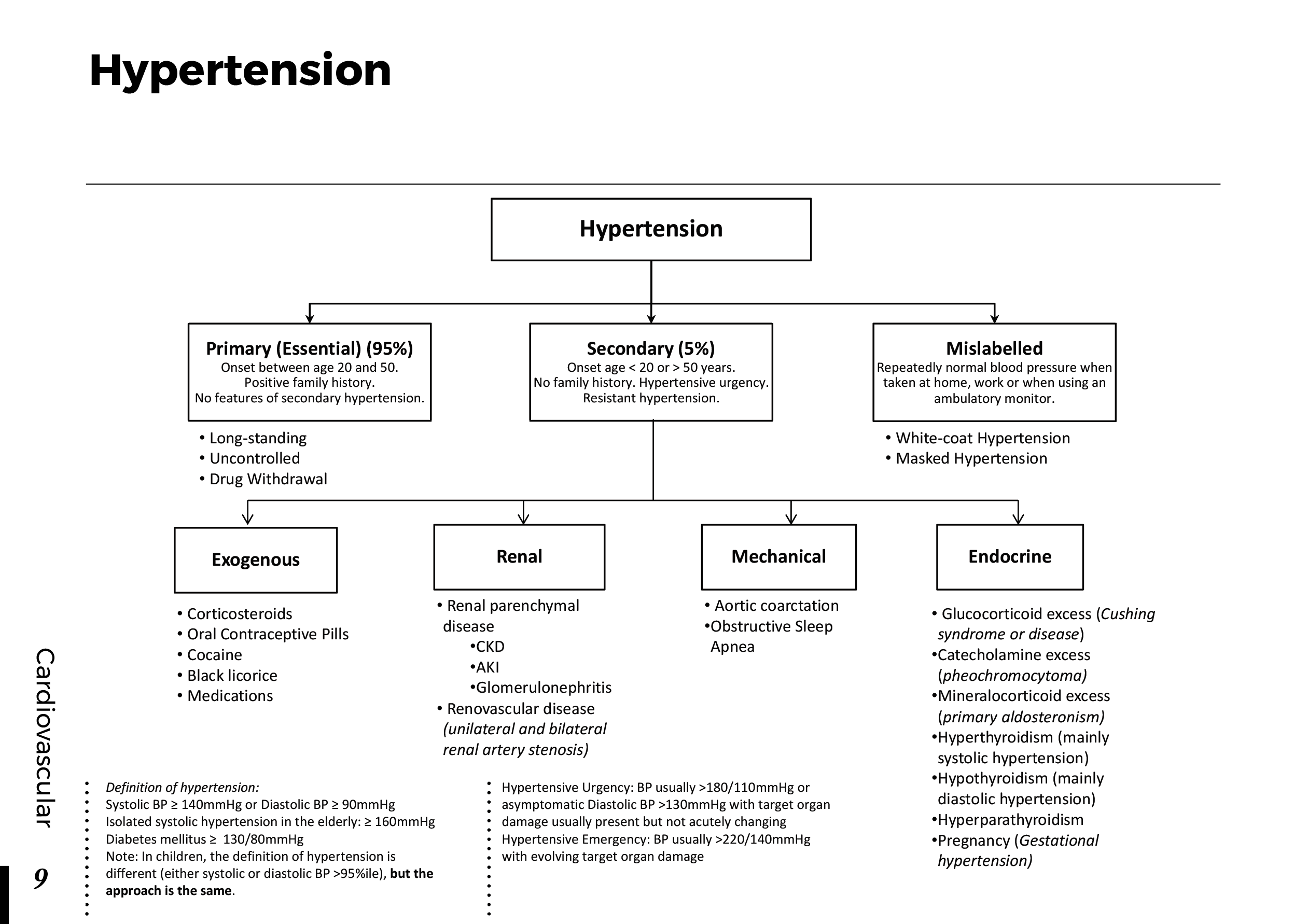
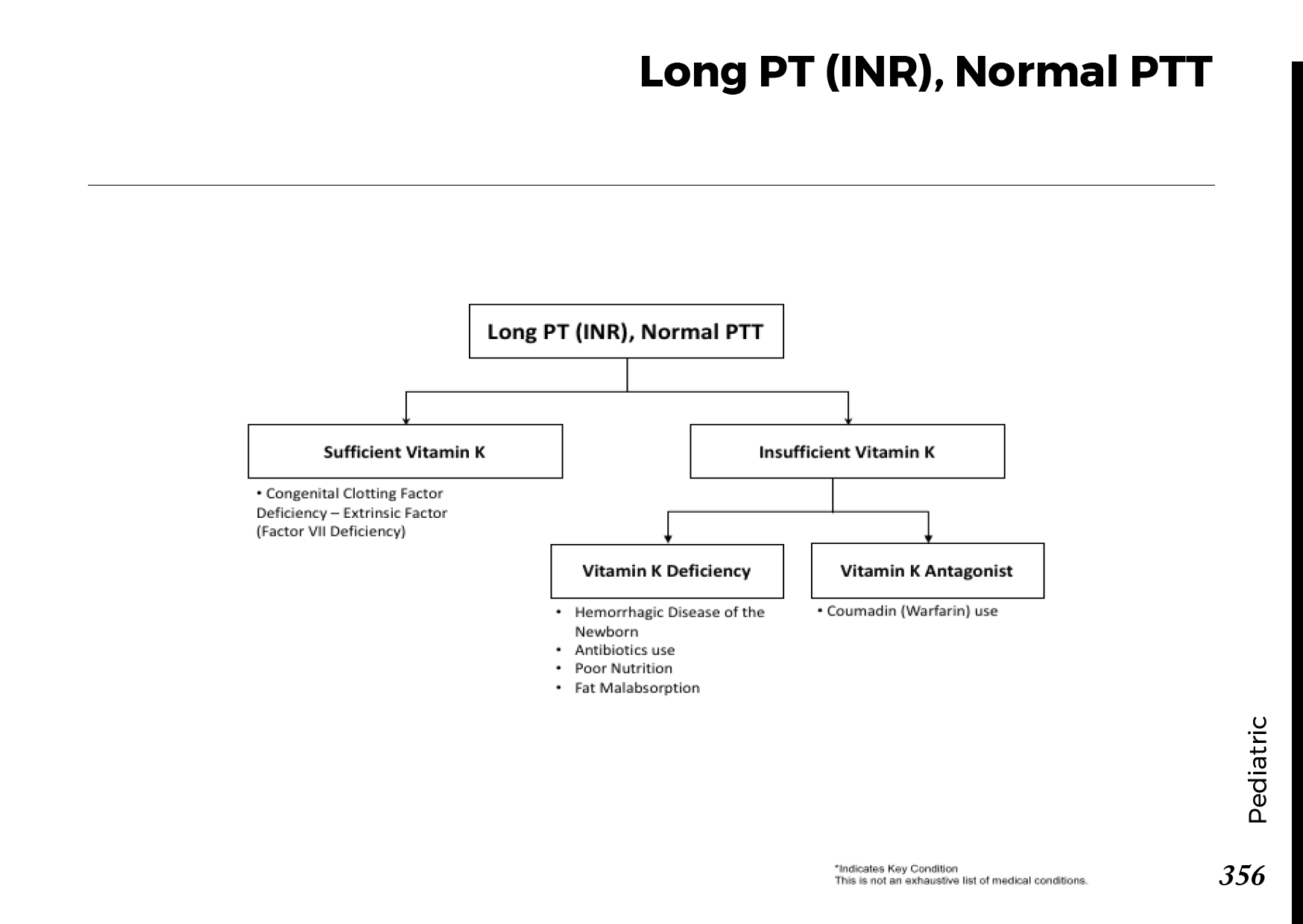
Obstructive jaundice occurs when there is an obstruction in the bile ducts, preventing the normal flow of bile from the liver to the small intestine. Bile contains bilirubin, a yellow pigment produced during the breakdown of red blood cells. When the flow of bile is blocked, bilirubin accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to the characteristic yellowing of the skin and eyes.
Causes of Obstructive Jaundice:
Several factors can contribute to the development of obstructive jaundice:
Gallstones: Gallstones can obstruct the bile ducts and lead to jaundice.
Pancreatic Cancer: Tumors in the pancreas or surrounding areas can block bile flow.
Bile Duct Strictures: Narrowing or scarring of the bile ducts can impede bile movement.
Enlarged Lymph Nodes: Swollen lymph nodes can compress the bile ducts.
Liver Infections: Infections such as hepatitis can cause inflammation and blockages.
Symptoms of Obstructive Jaundice:
Recognizing the symptoms of obstructive jaundice is crucial for early diagnosis and treatment. Common signs include:
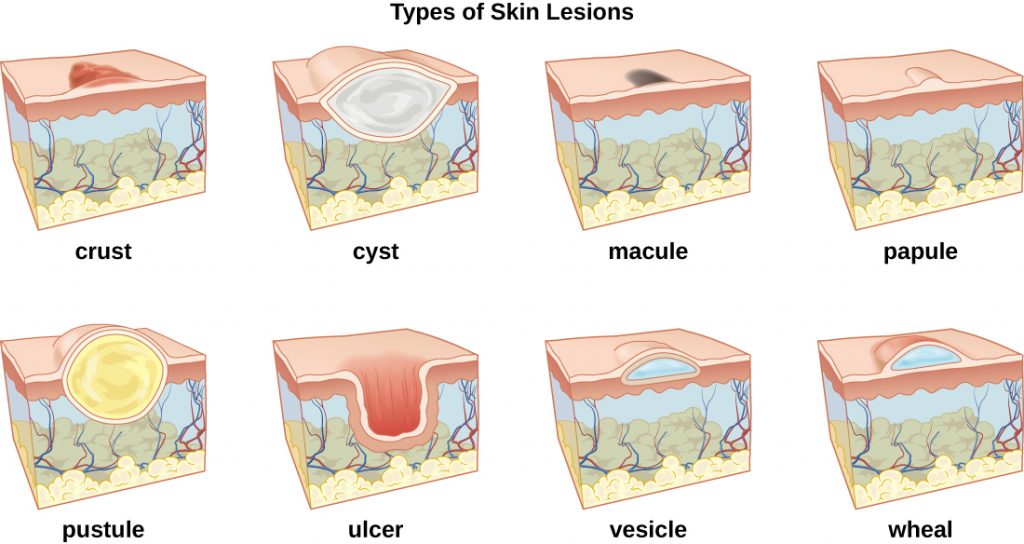
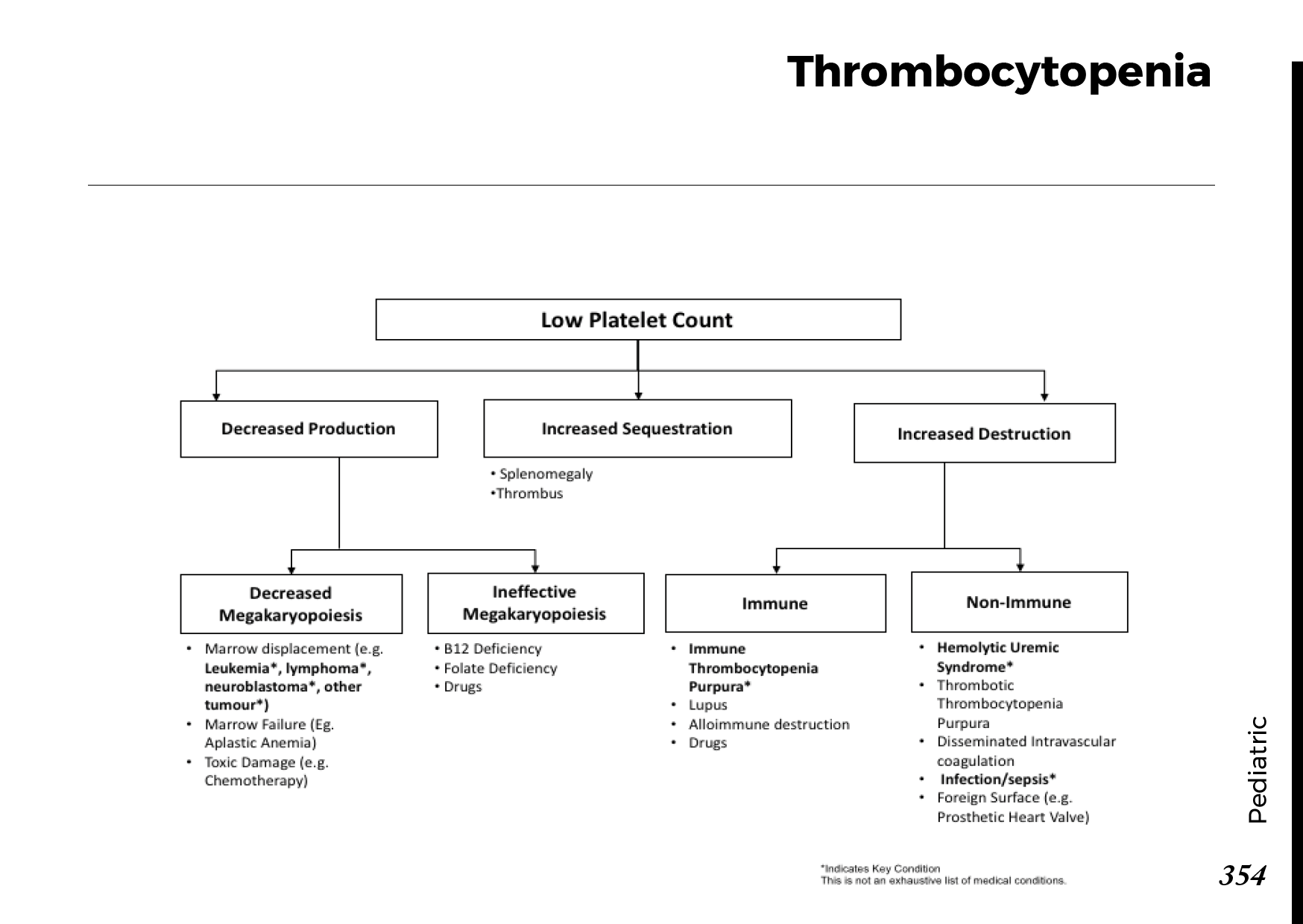
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Dark urine
- Pale stools
- Itchy skin
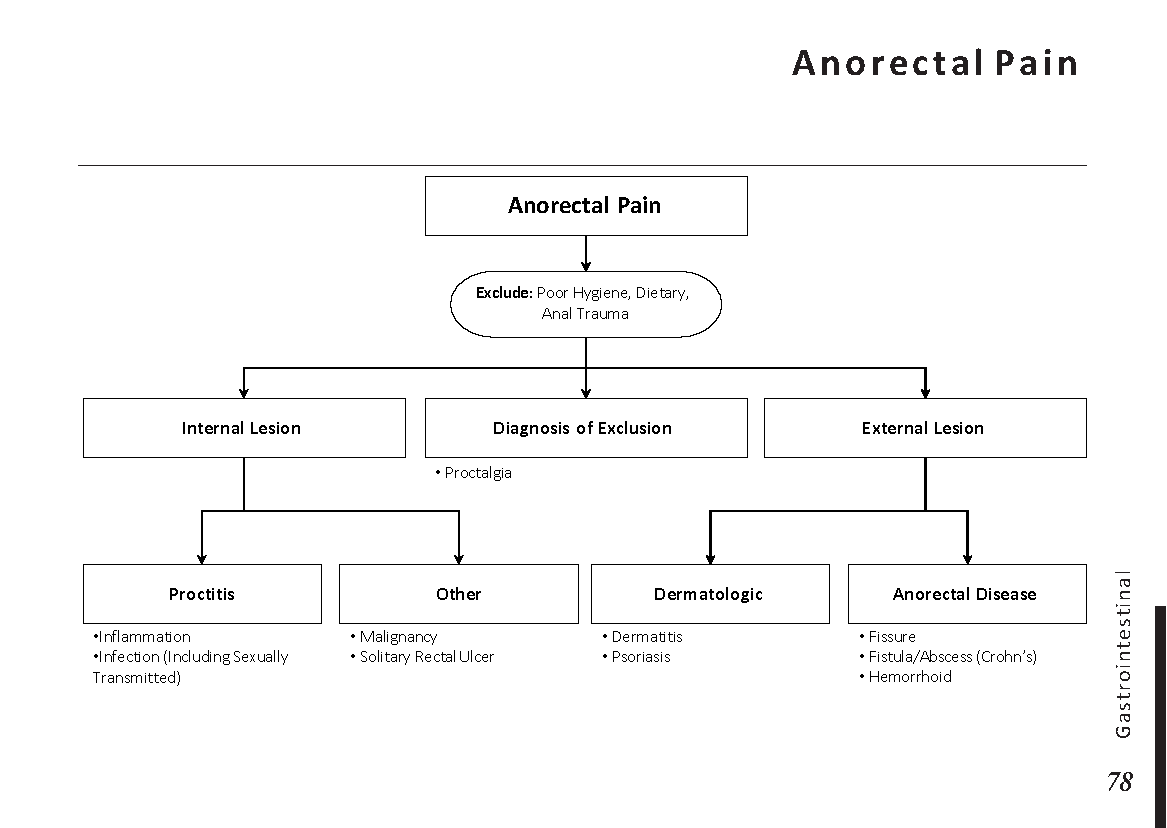
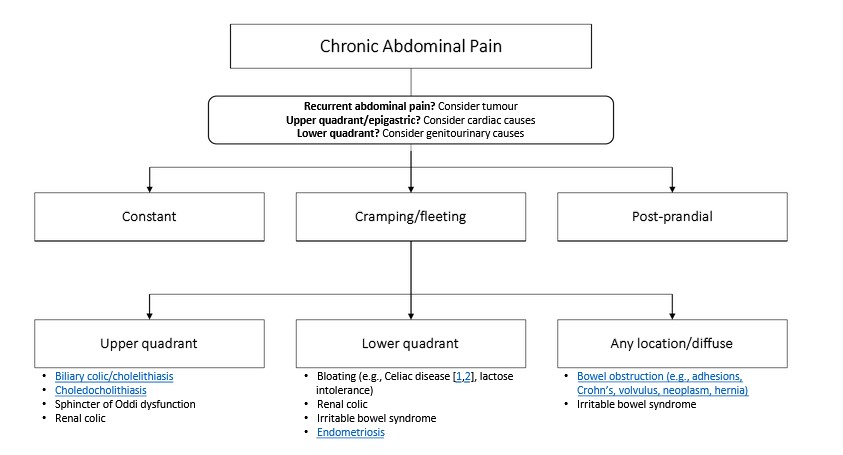
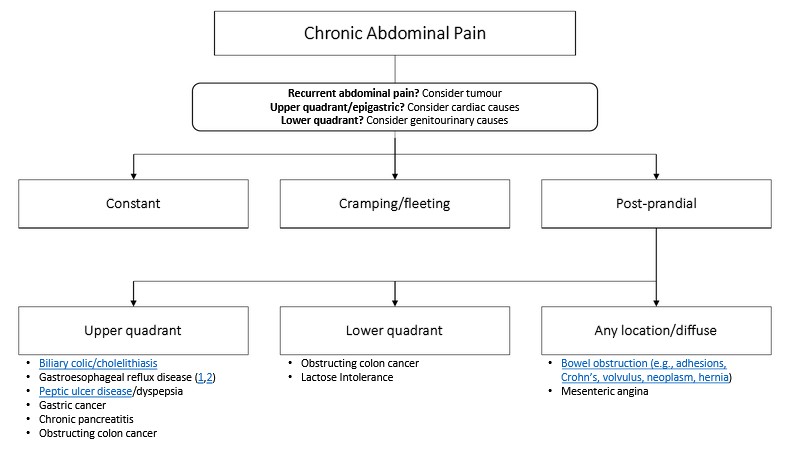
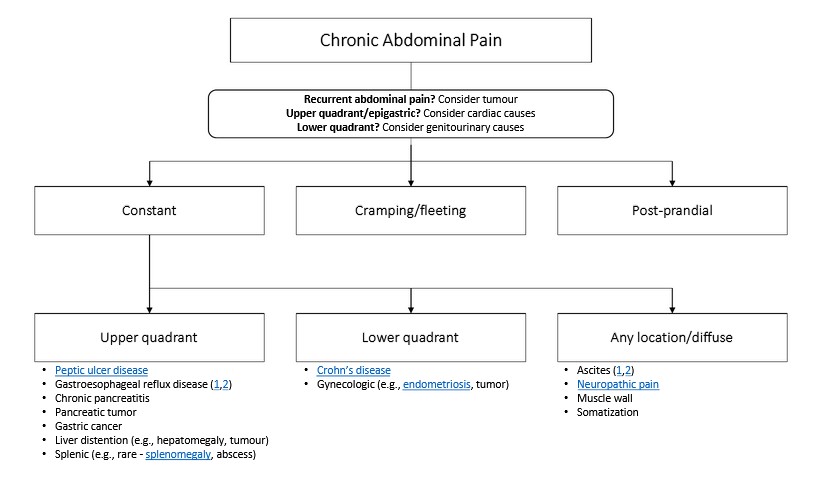
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Unintentional weight loss
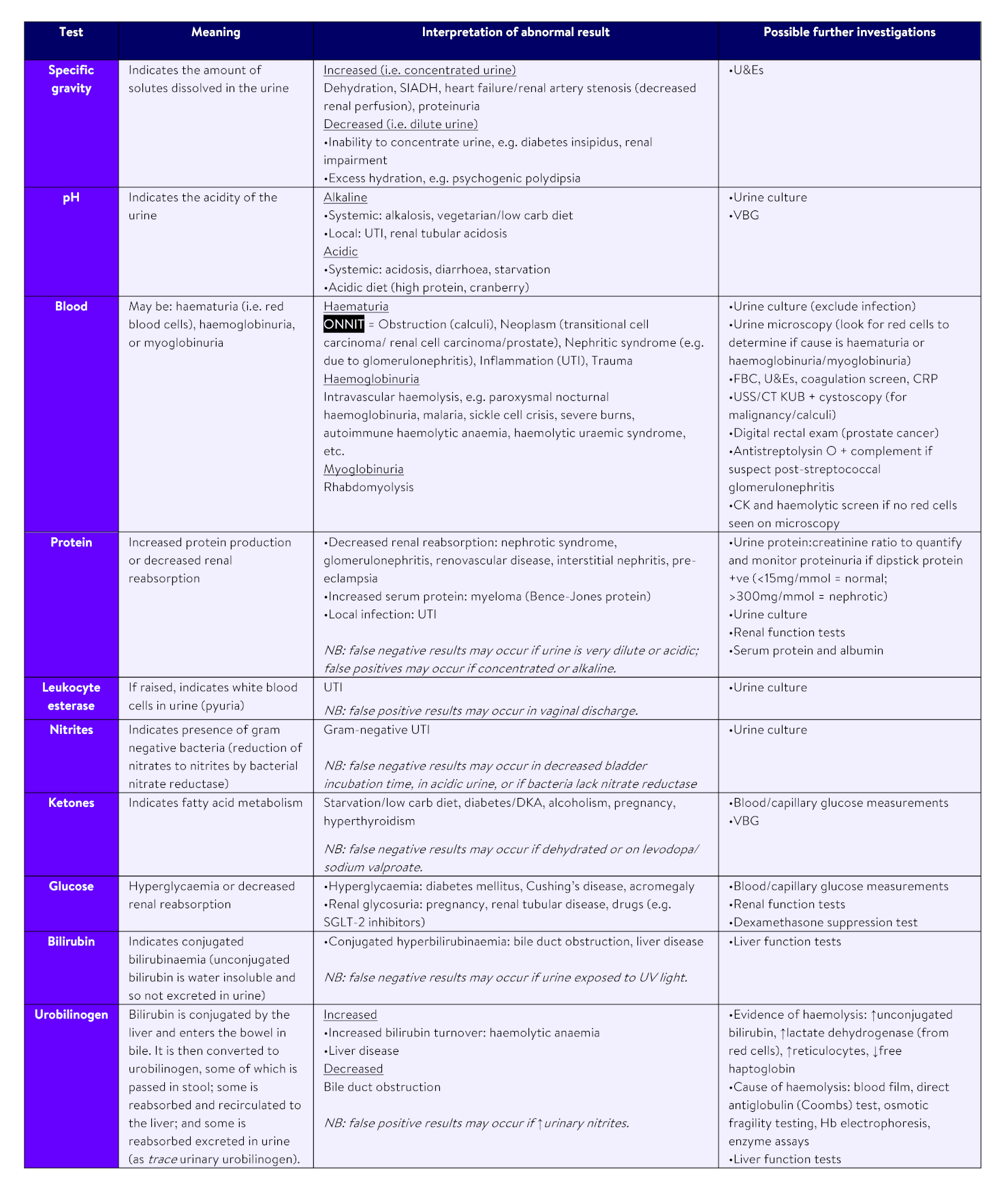
Diagnostic Procedures:
Medical professionals use various methods to diagnose obstructive jaundice, including:
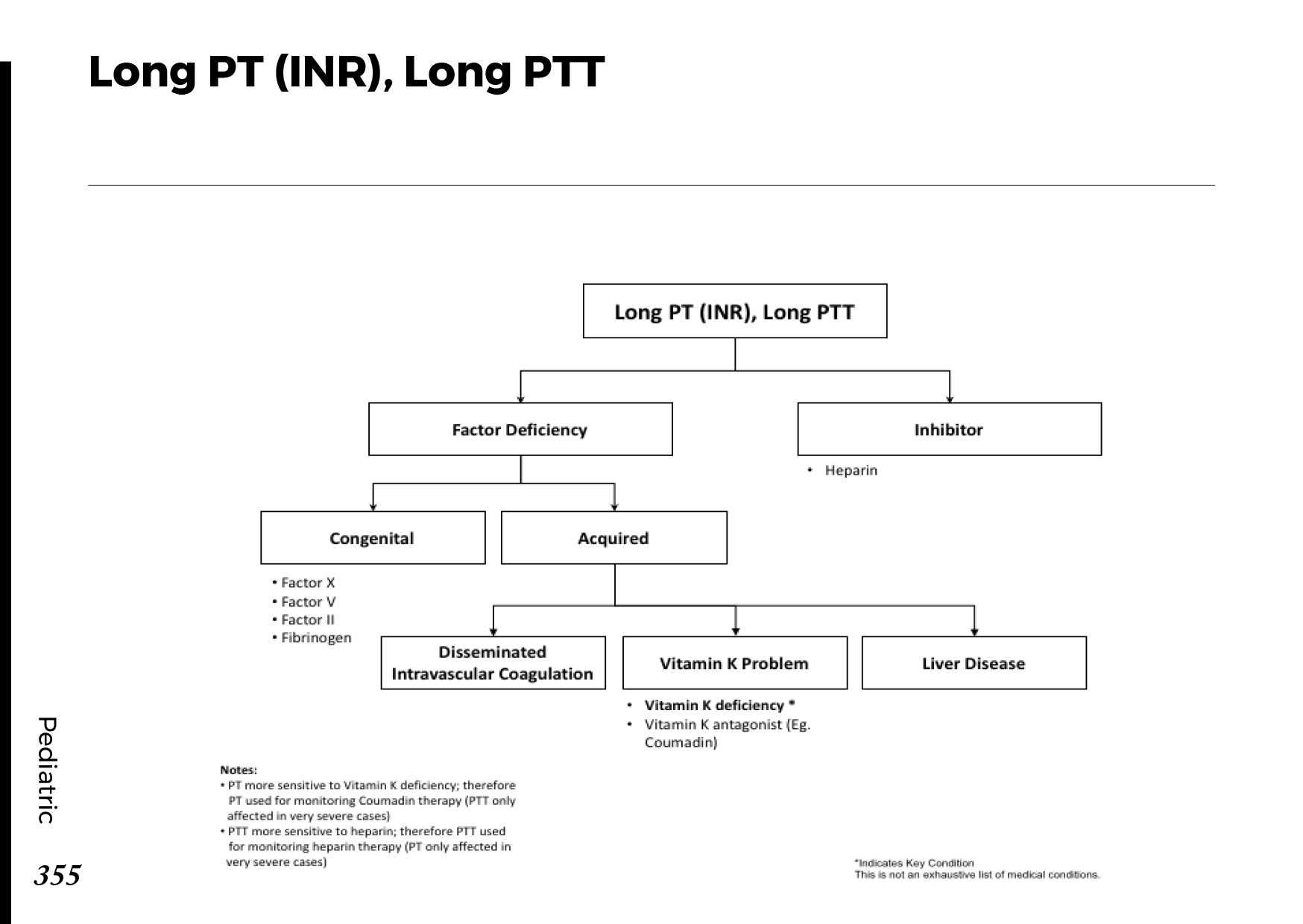
Blood Tests: These tests measure bilirubin levels and liver function.
Imaging Studies: Ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI can identify obstructions and assess the bile ducts.
Endoscopic Procedures: ERCP (Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography) allows visualization and treatment of blockages using a thin, flexible tube with a camera.
Treatment Options:
The approach to treating obstructive jaundice depends on the underlying cause. Treatment options may include:
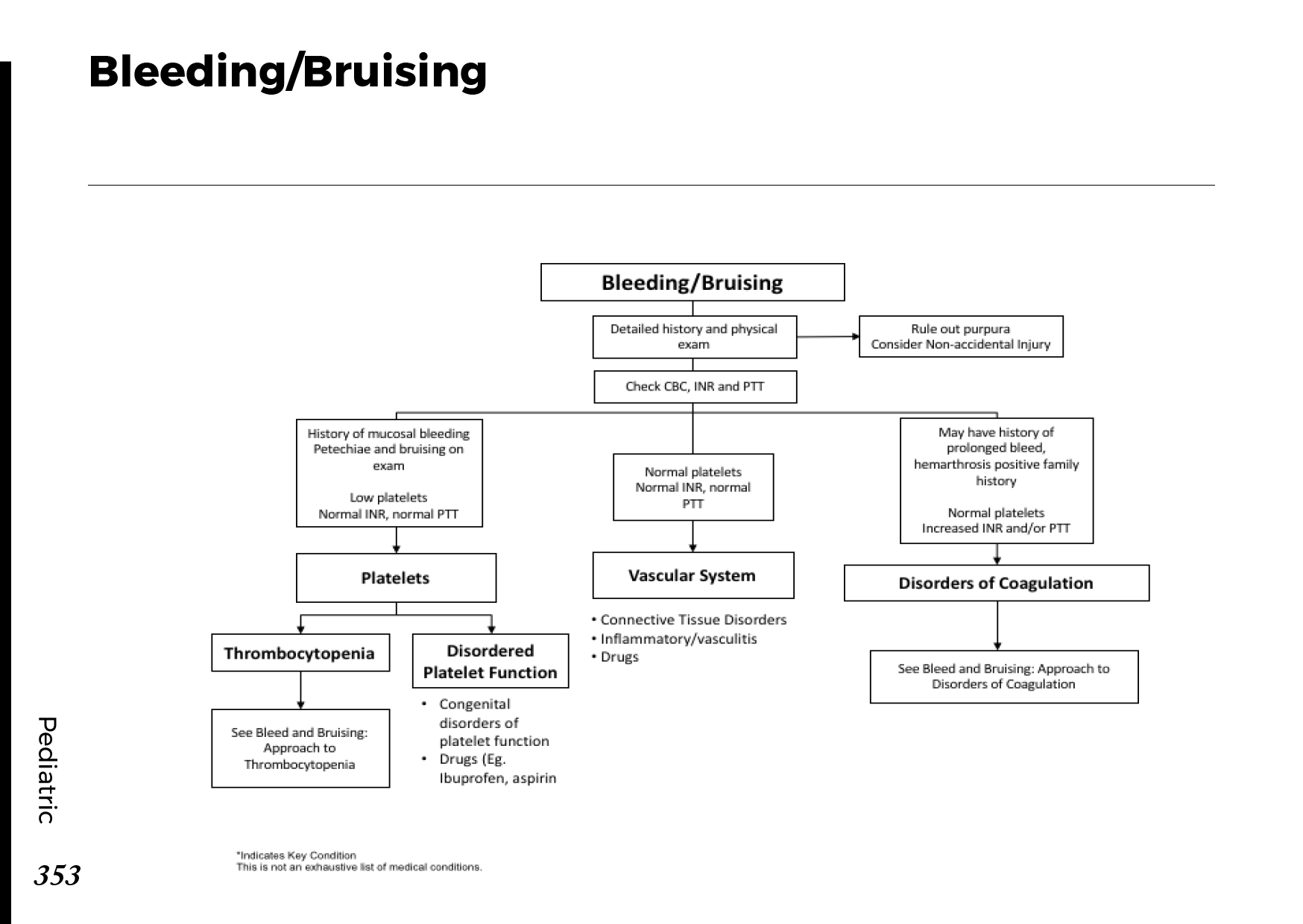
Surgery: Surgical procedures may be necessary to remove obstructions caused by tumors or gallstones.
Endoscopic Stenting: A stent can be placed to keep the bile ducts open and restore bile flow.
Biliary Drainage: A tube may be inserted to drain bile and relieve pressure.
Chemotherapy or Radiation: These treatments may be used for cases involving cancer.
Prevention and Lifestyle:
While not all cases of obstructive jaundice can be prevented, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of certain underlying causes. This includes:
Staying Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water can help prevent gallstones.
Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet low in saturated fats can support liver health.

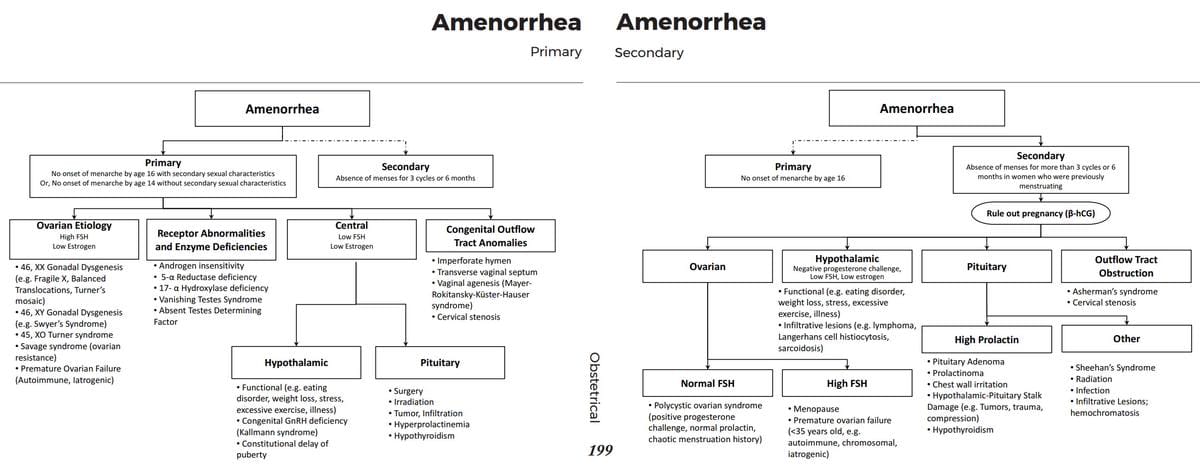
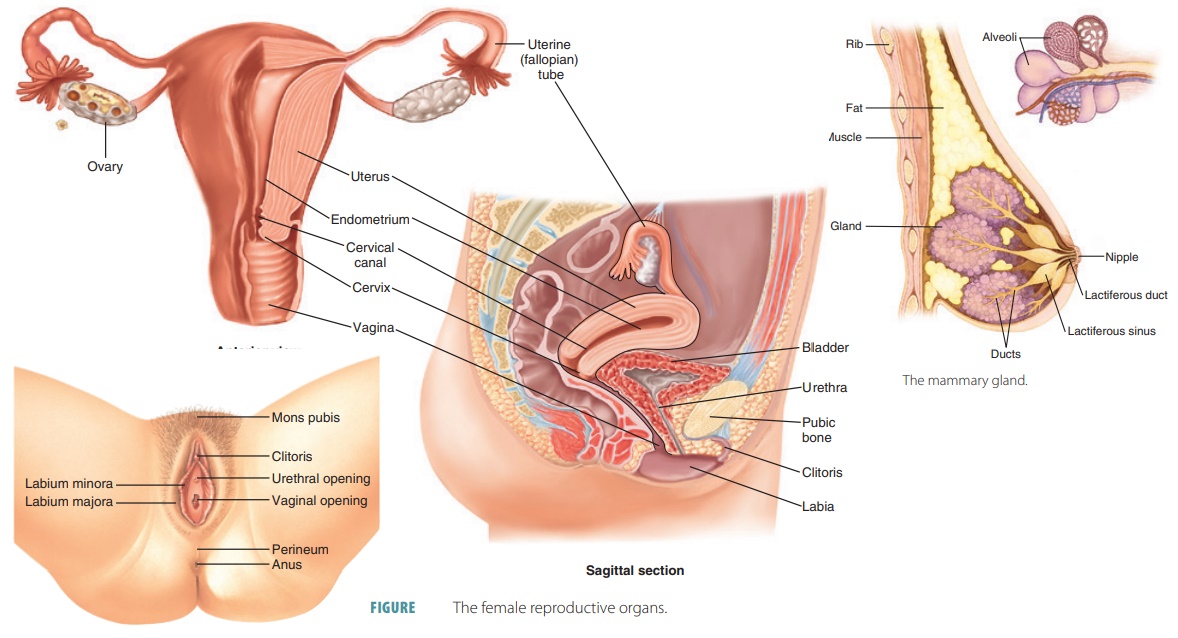
 Menstrual cycle physiology:
Menstrual cycle physiology: