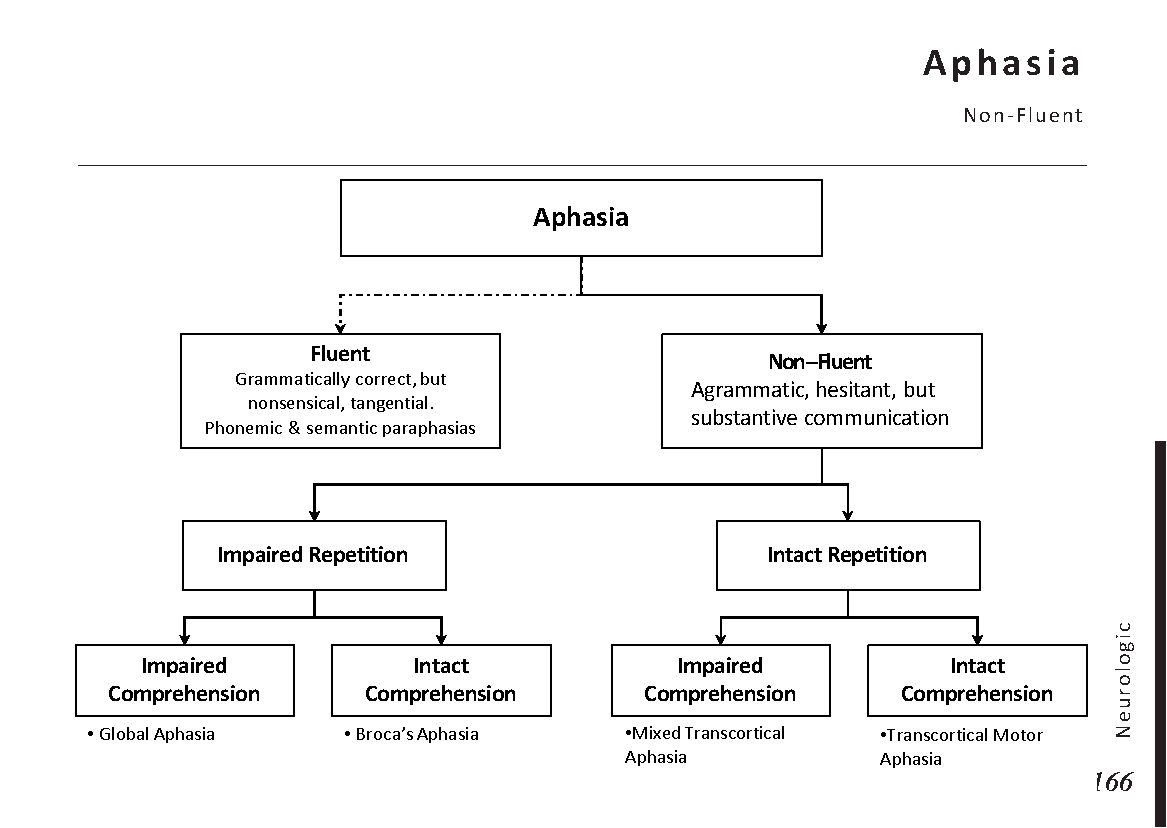
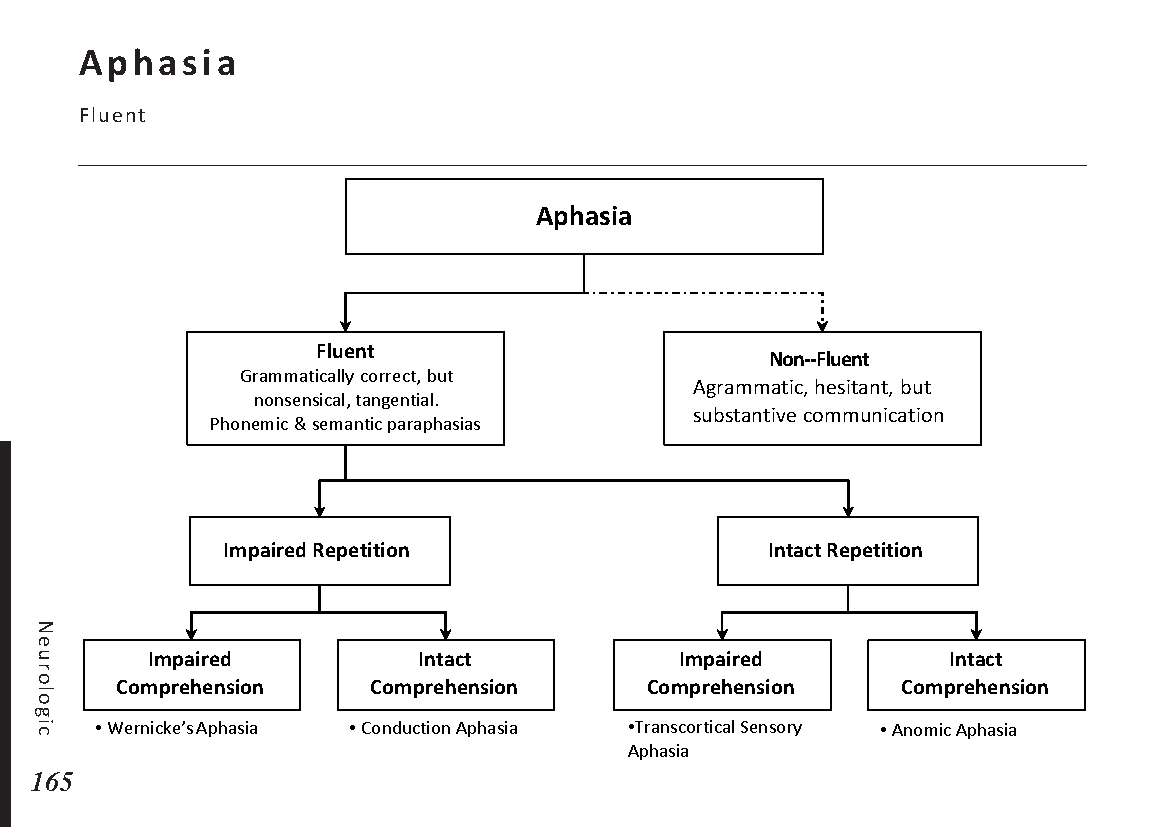
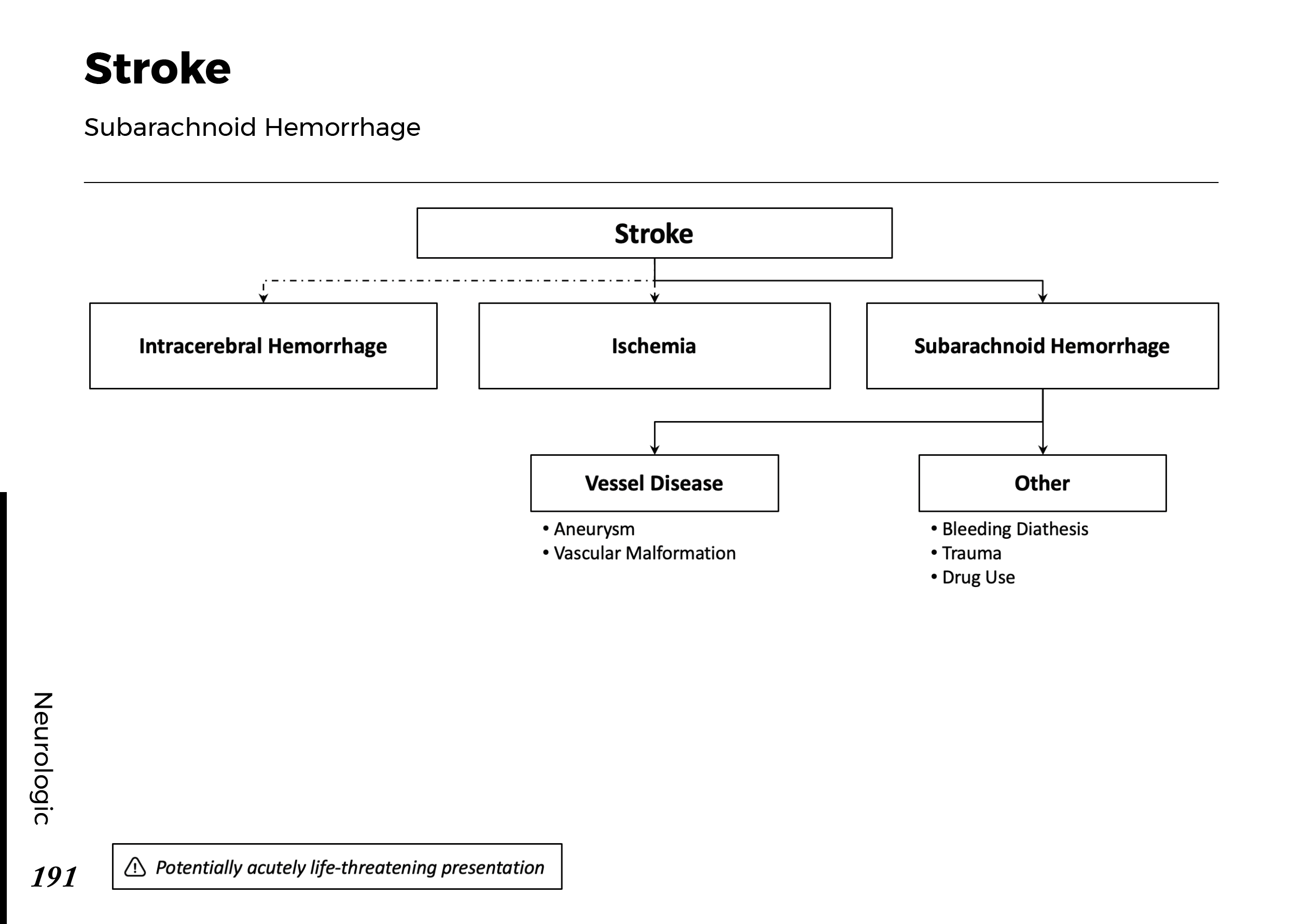
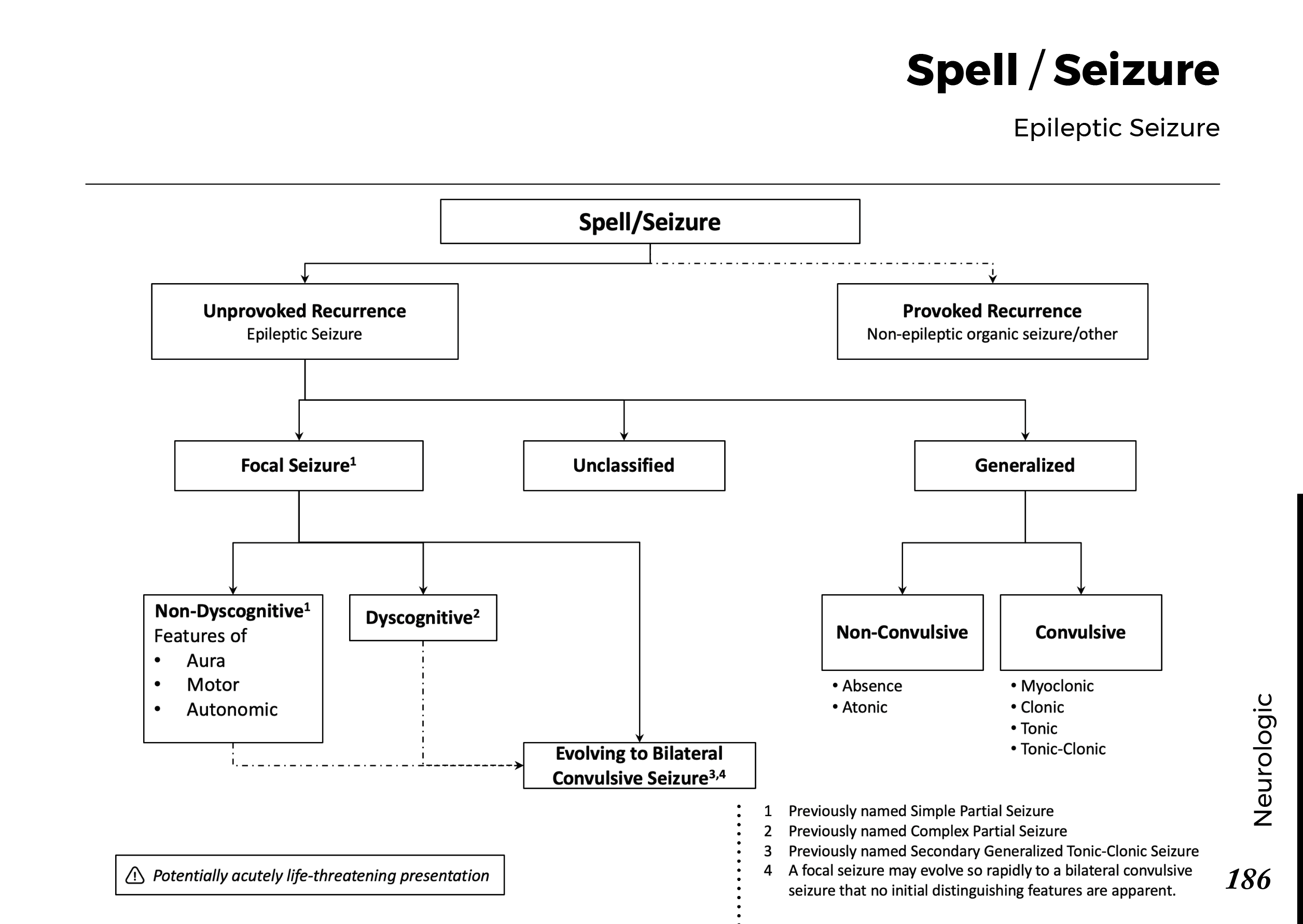
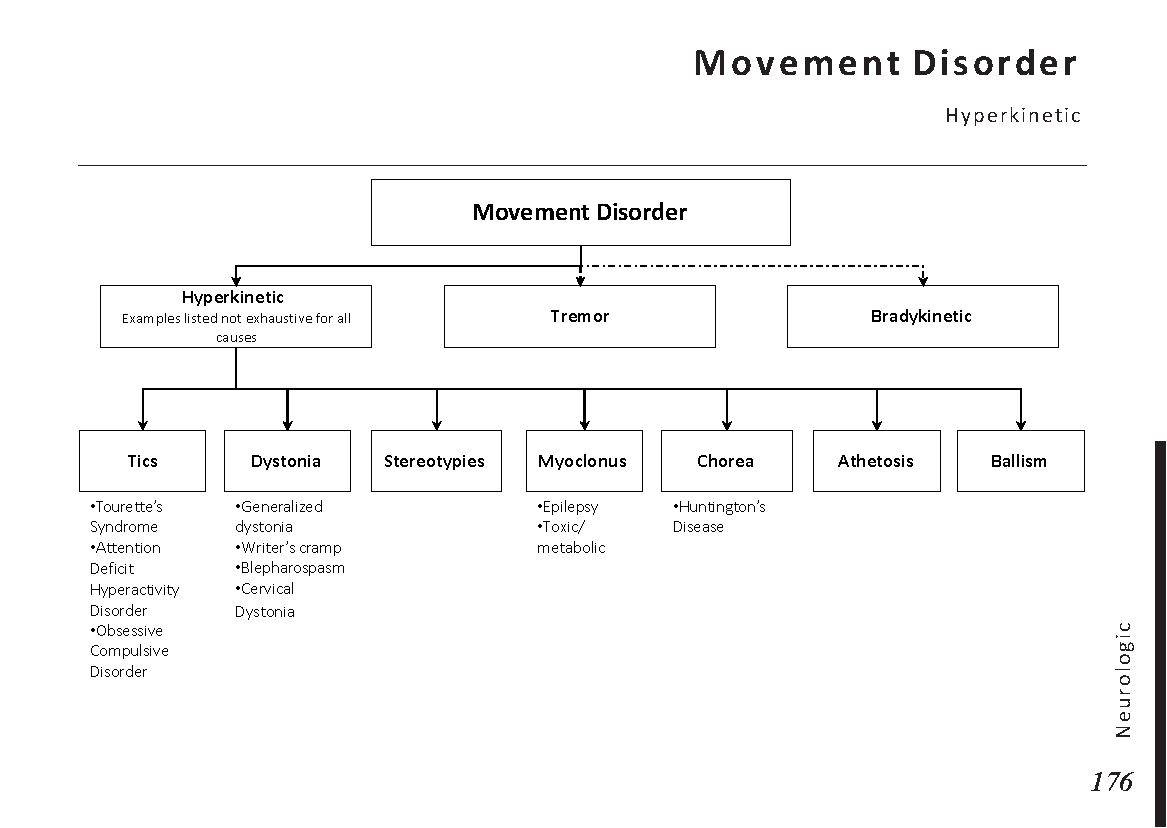
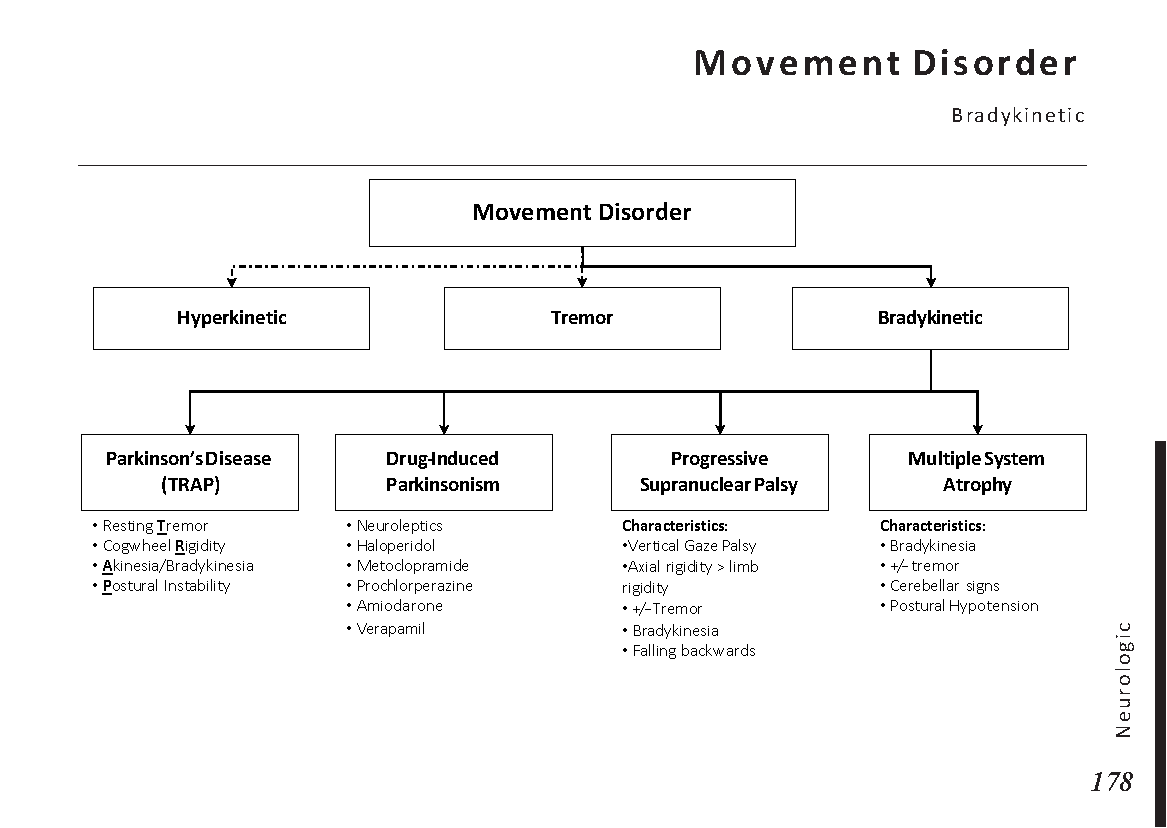
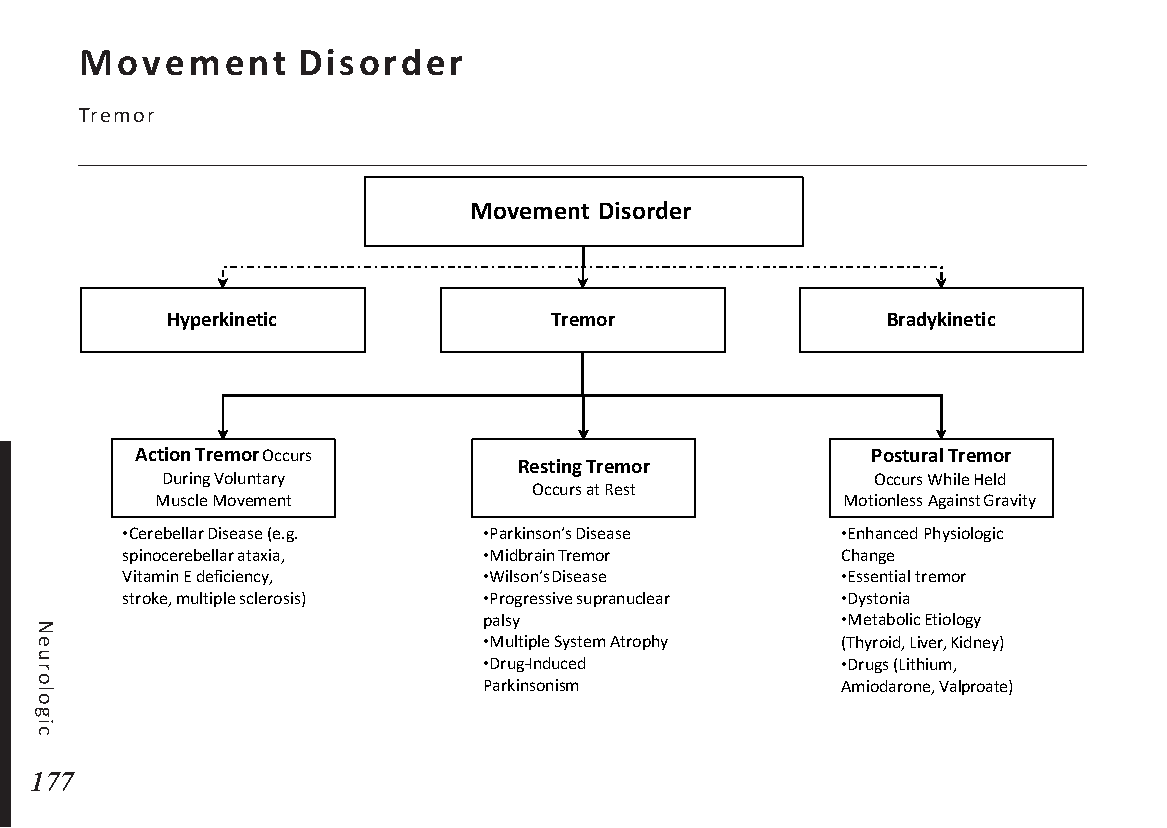
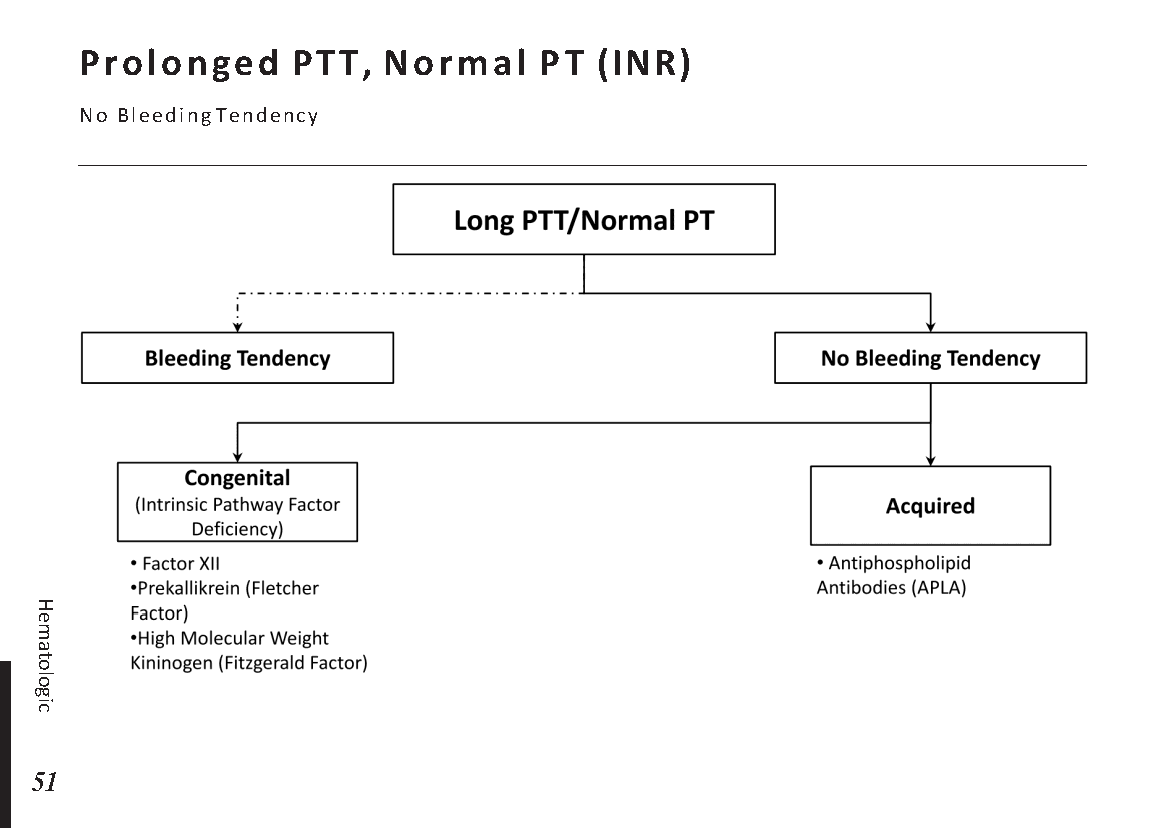
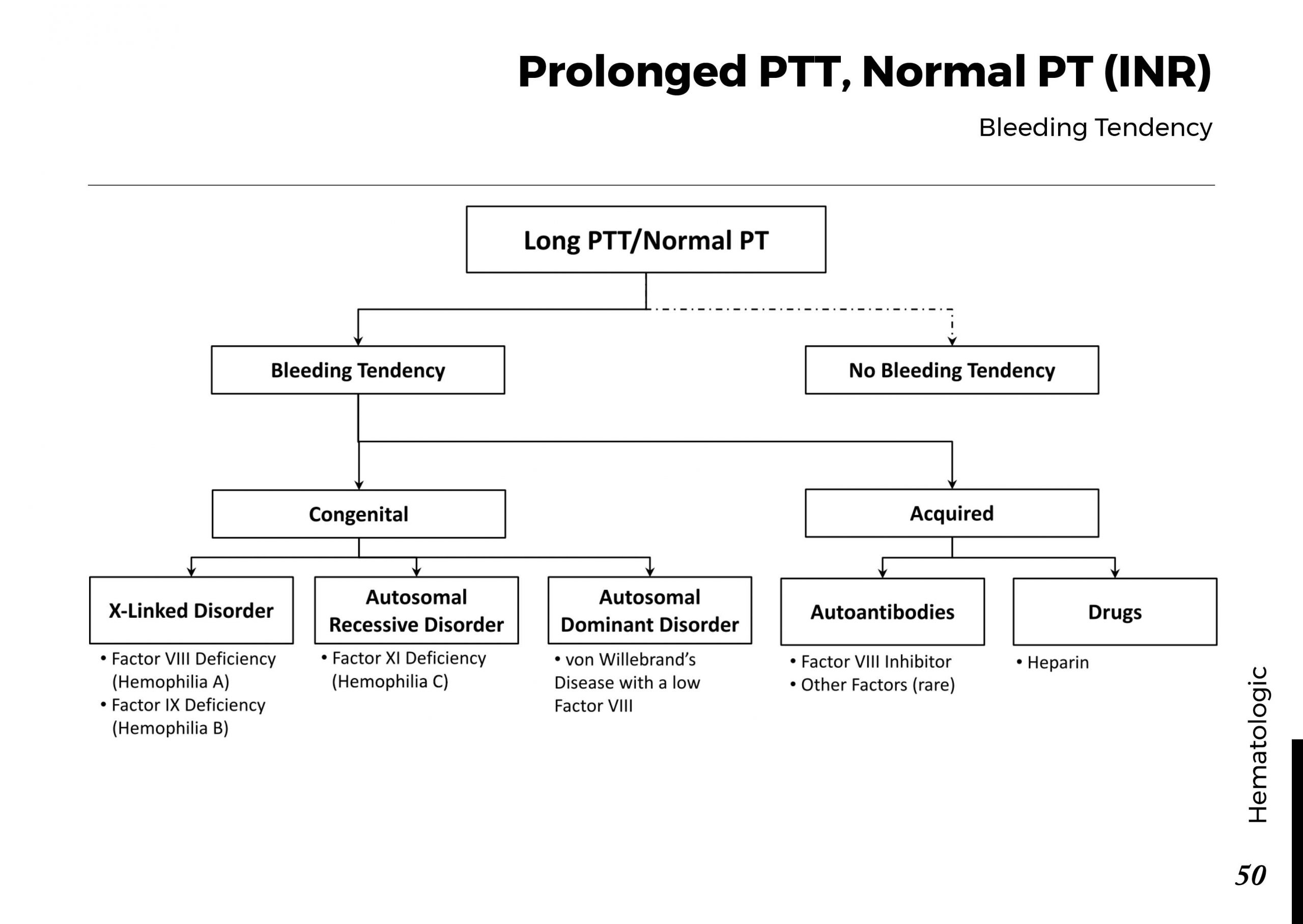
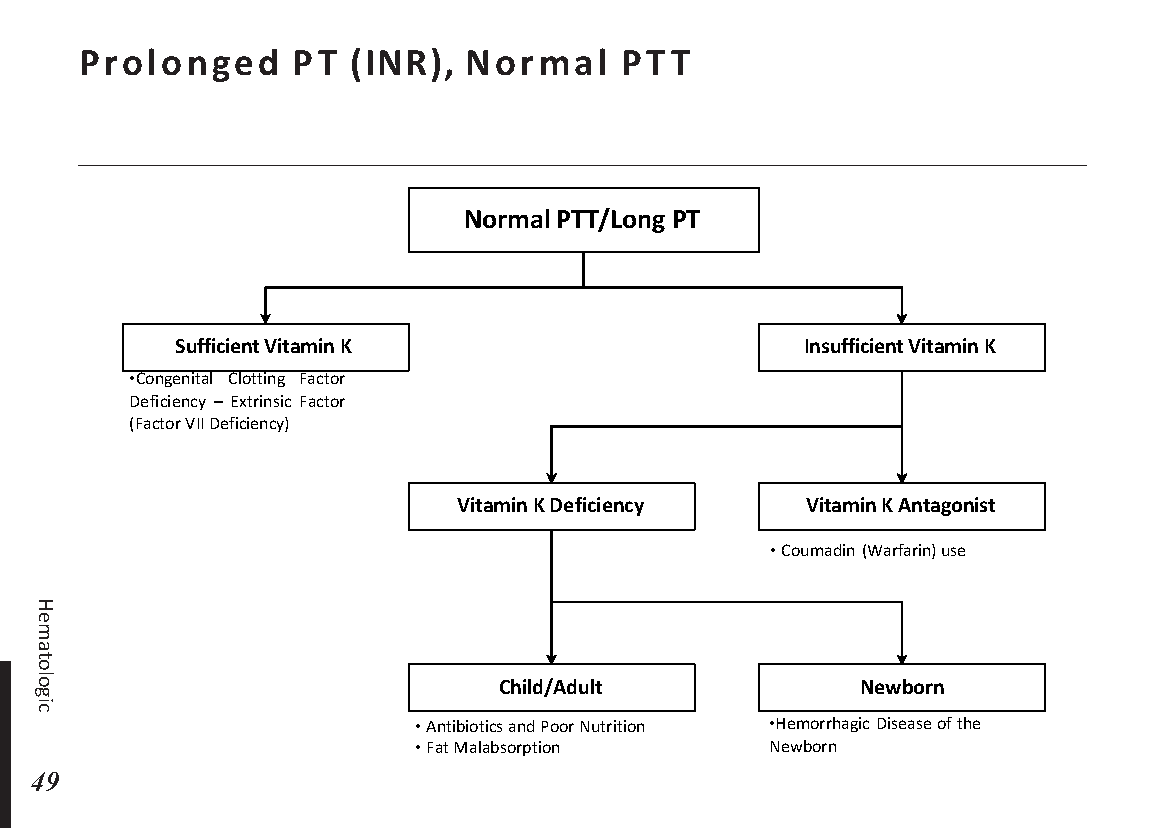
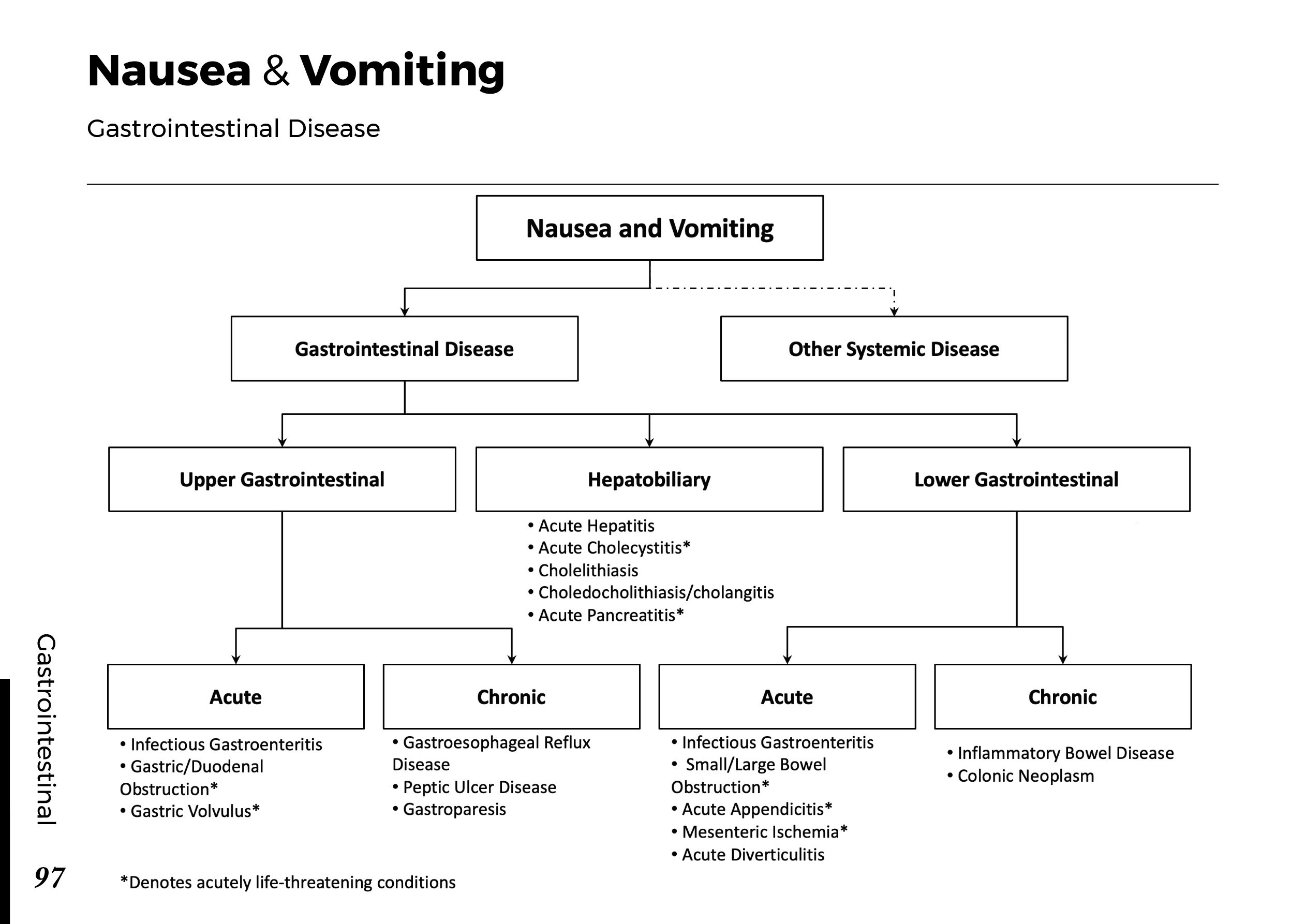
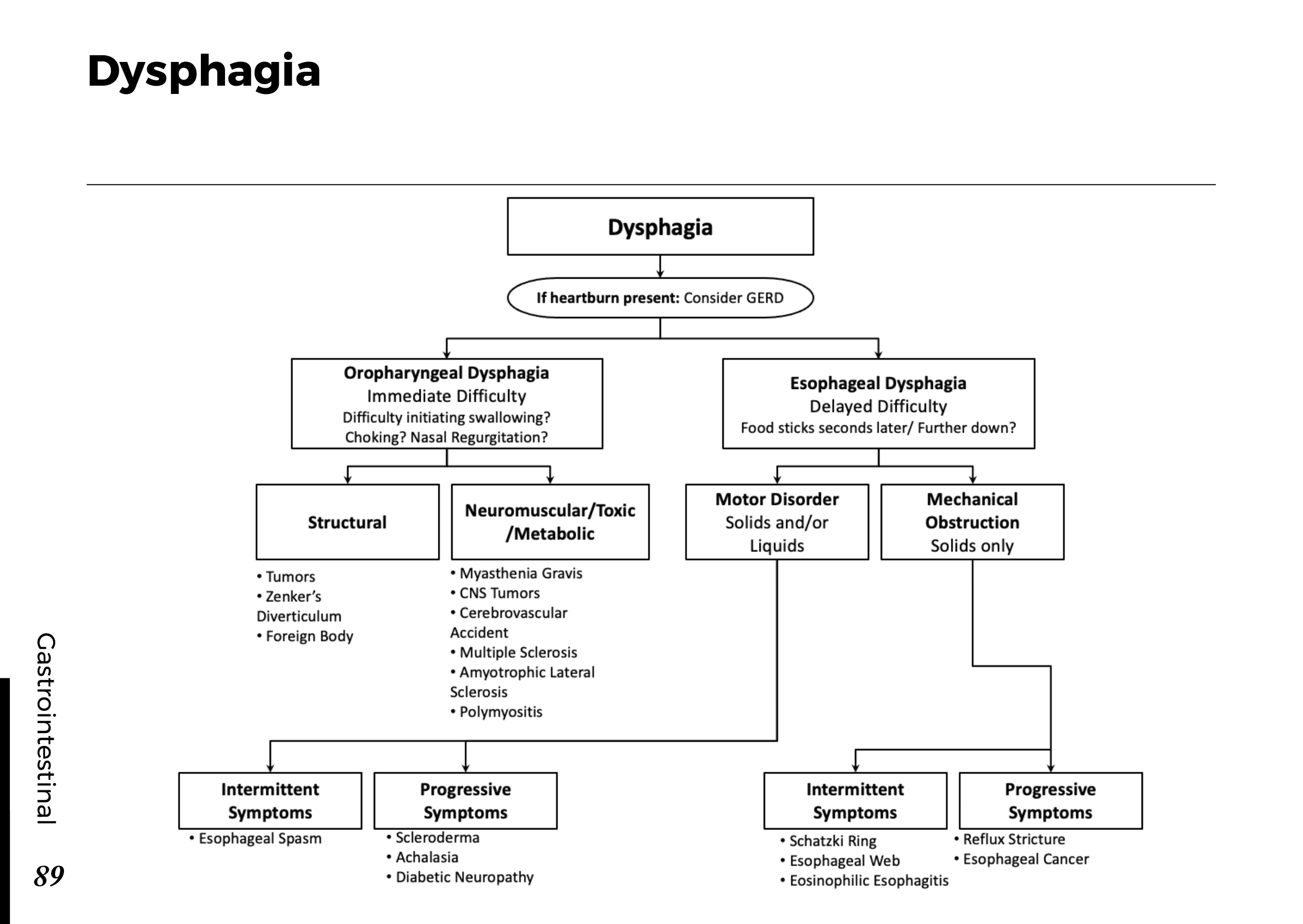
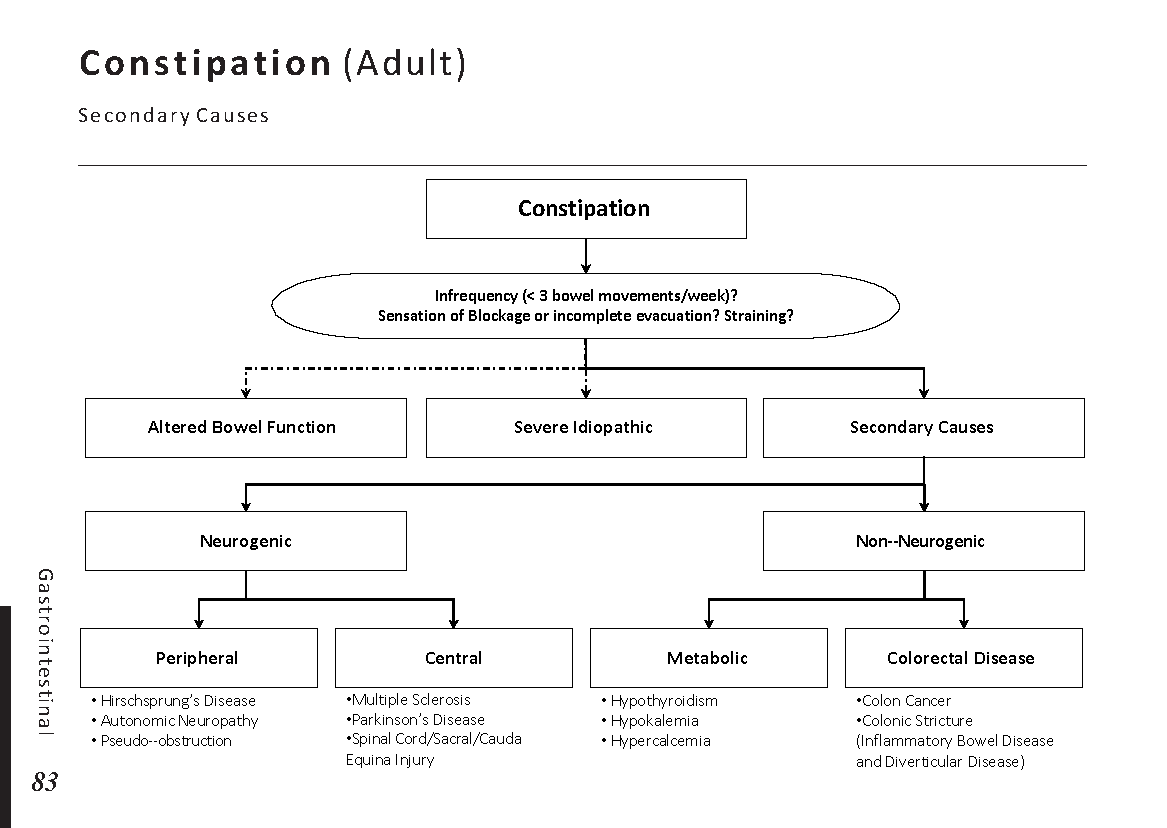
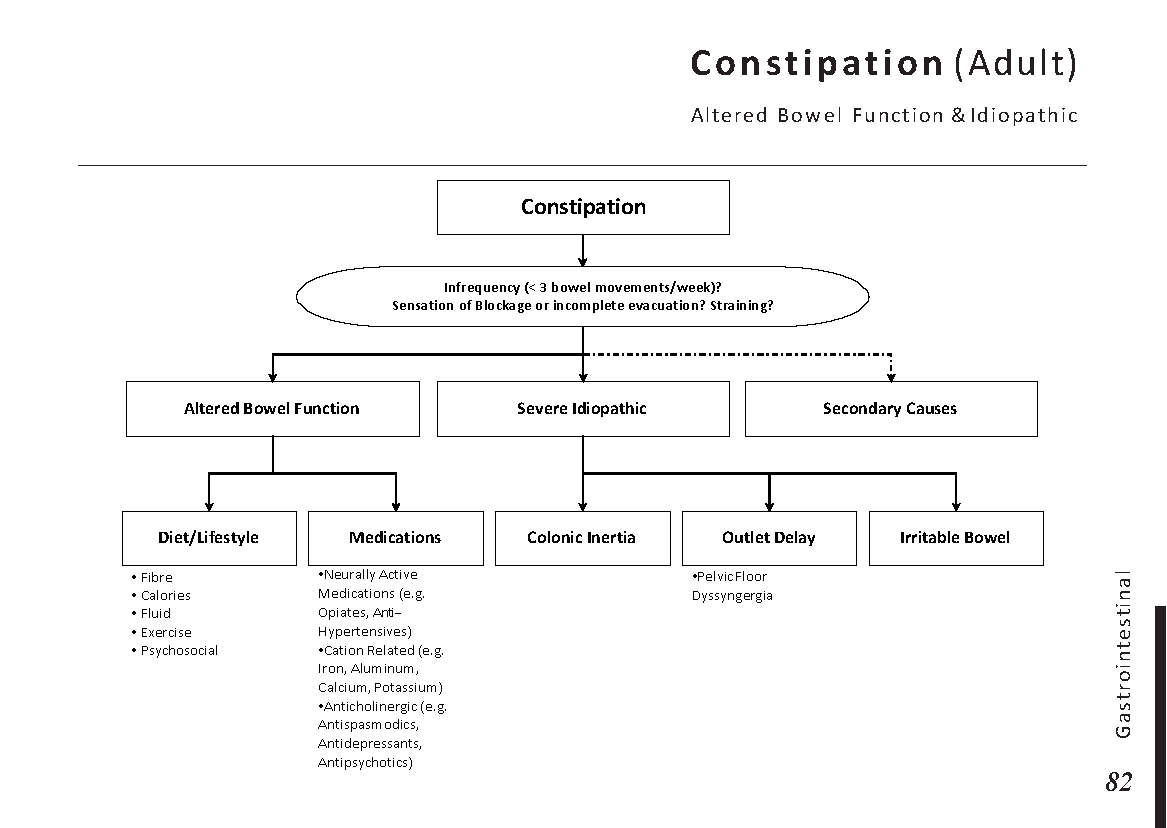
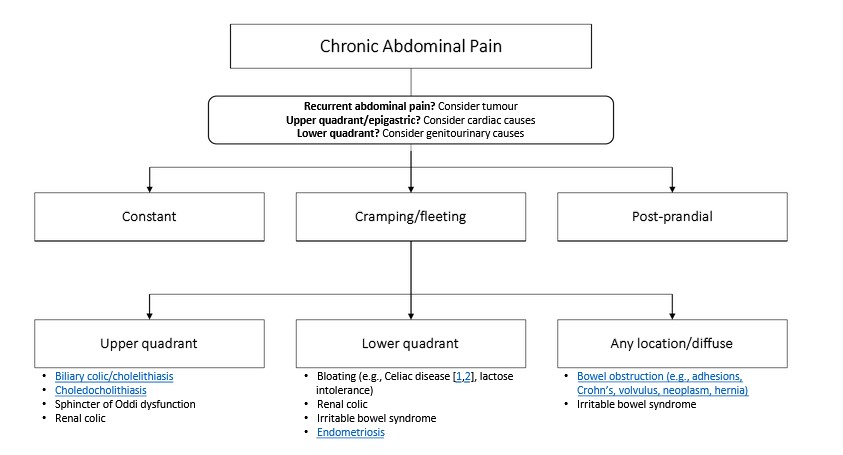
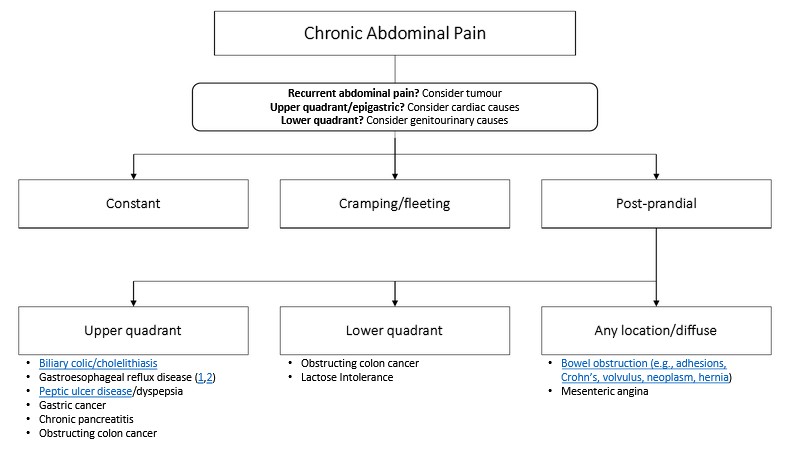
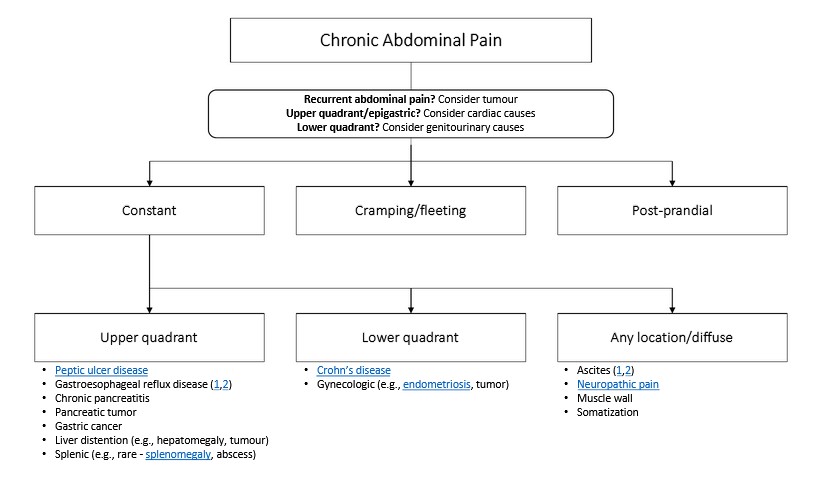
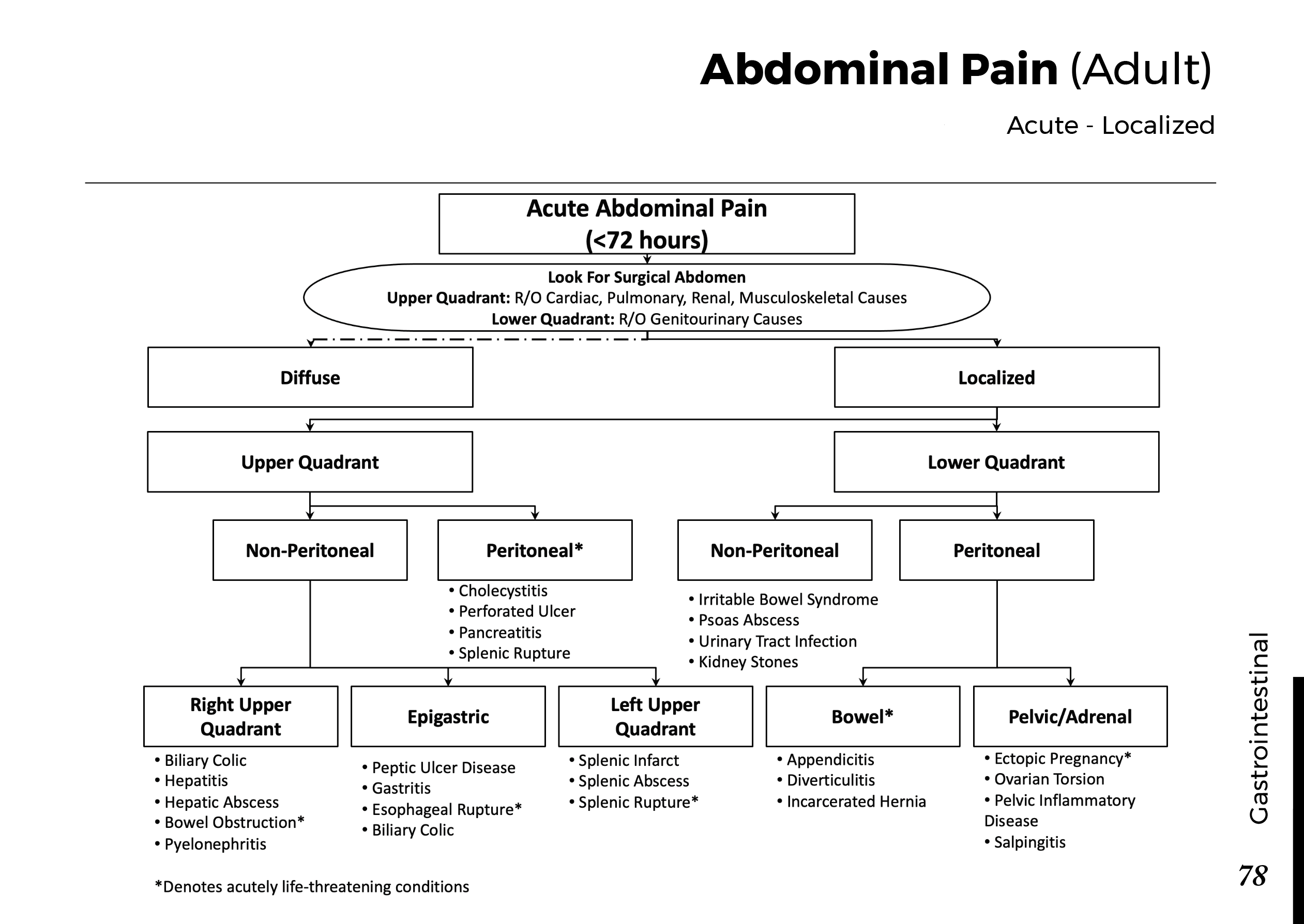
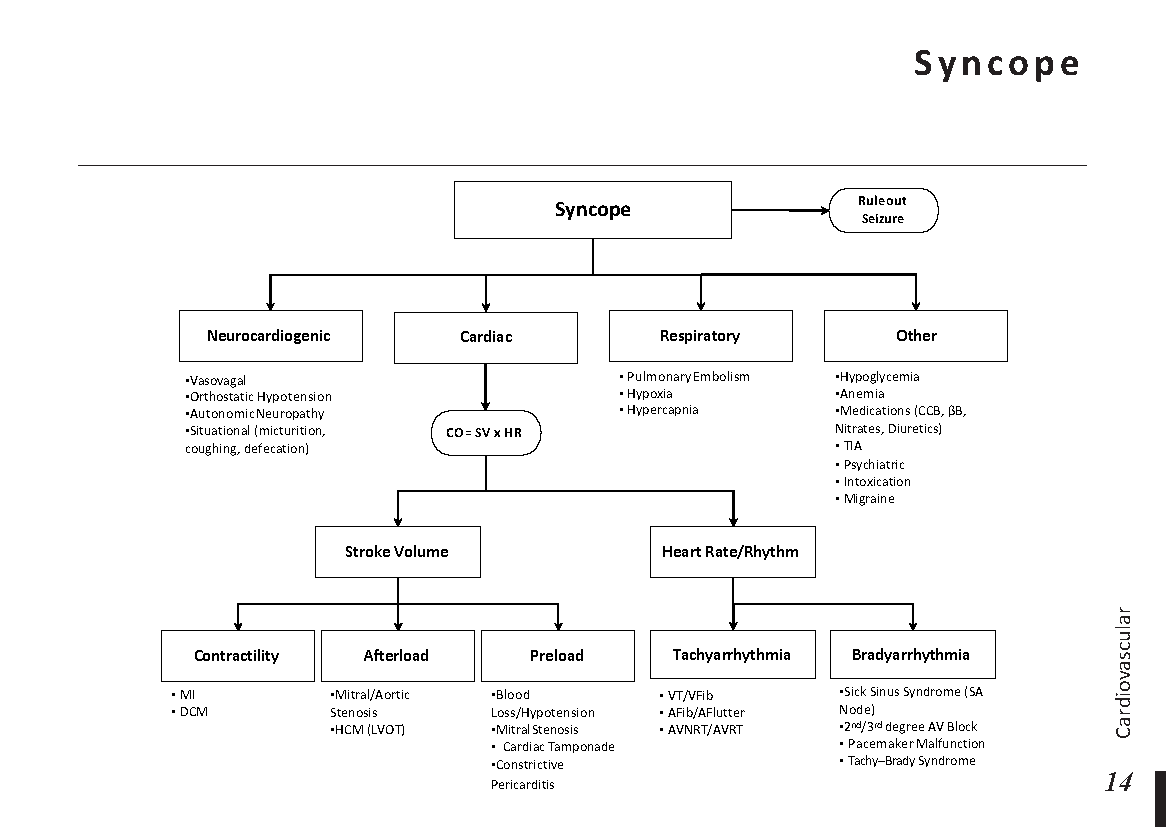
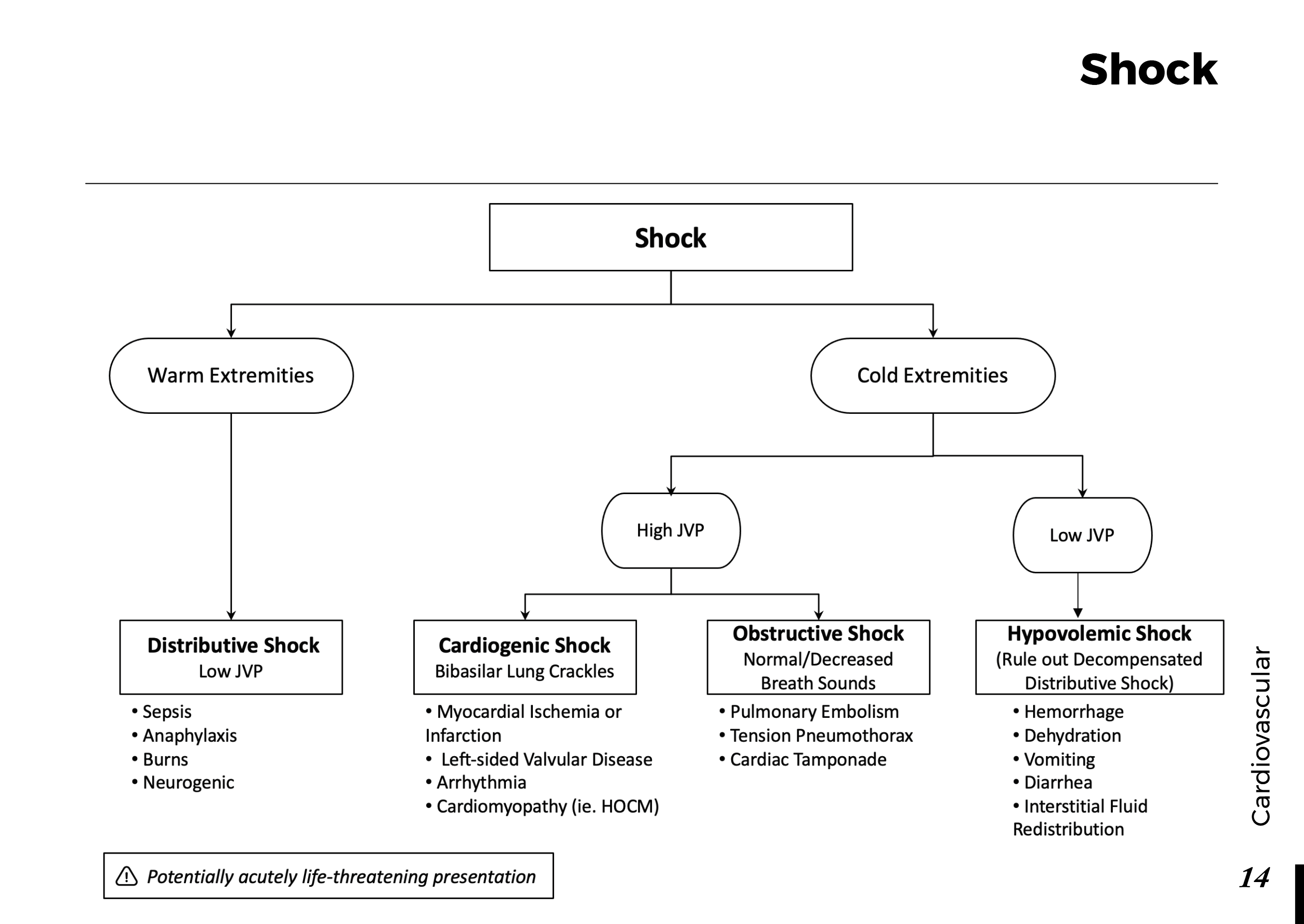
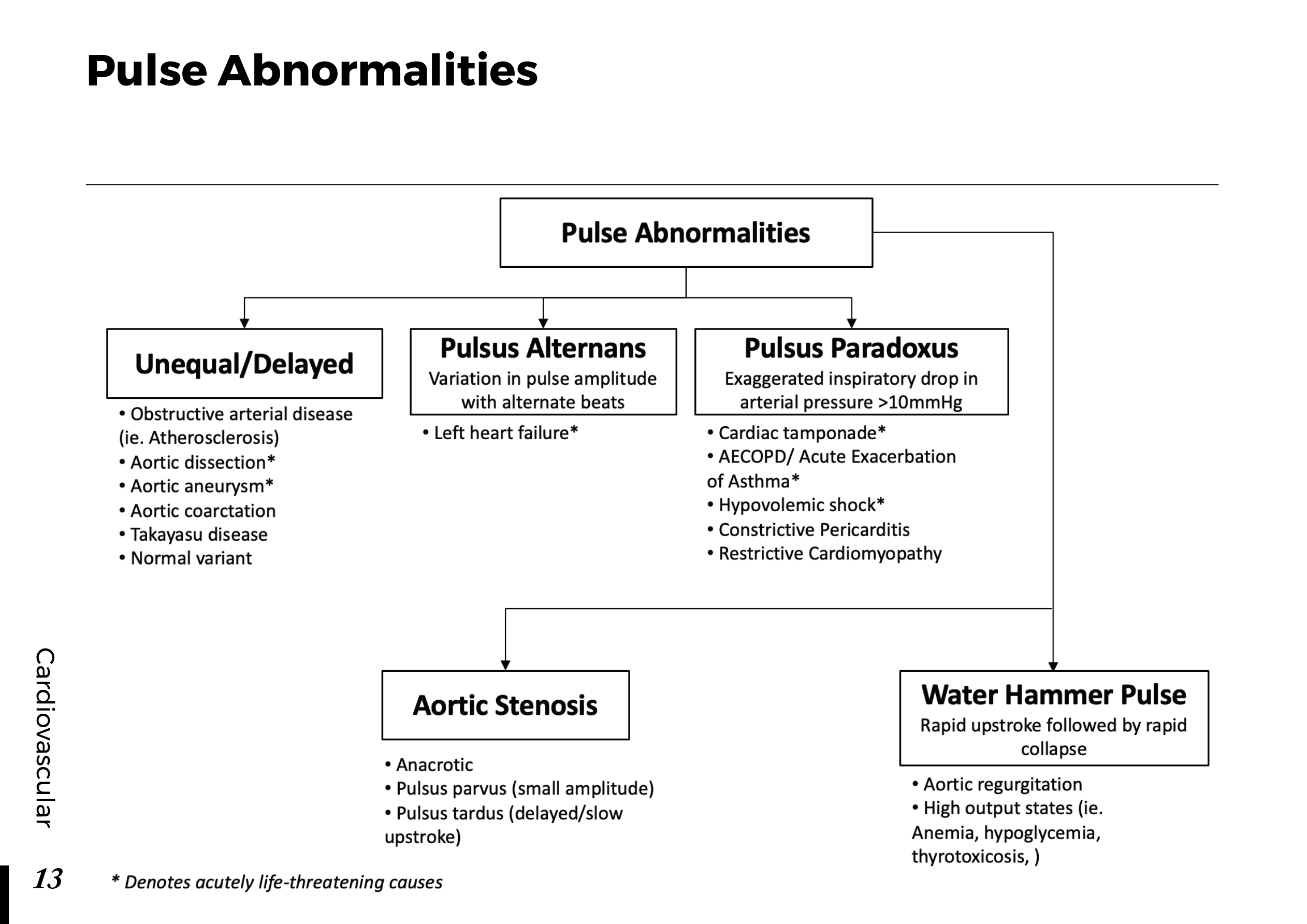
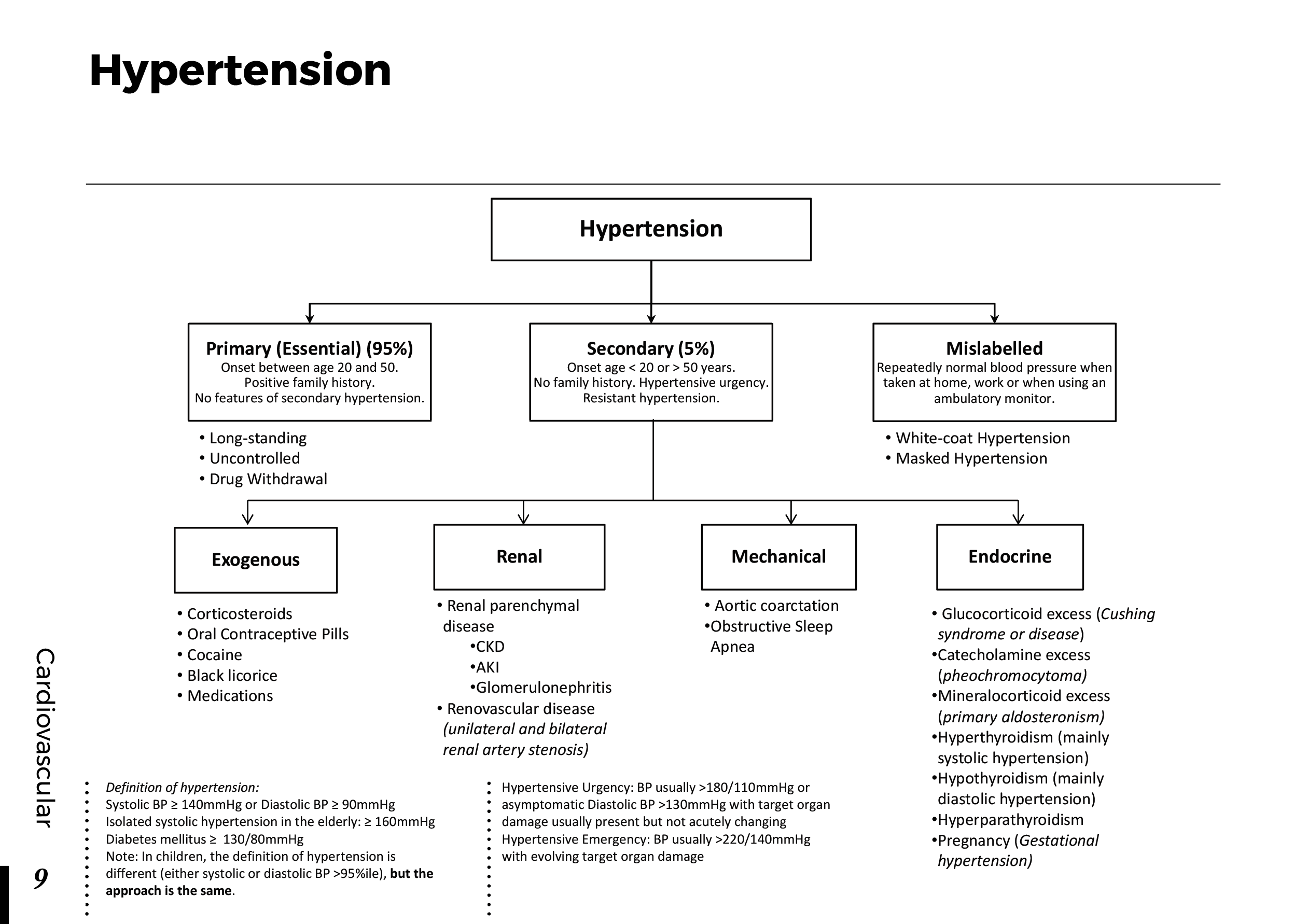
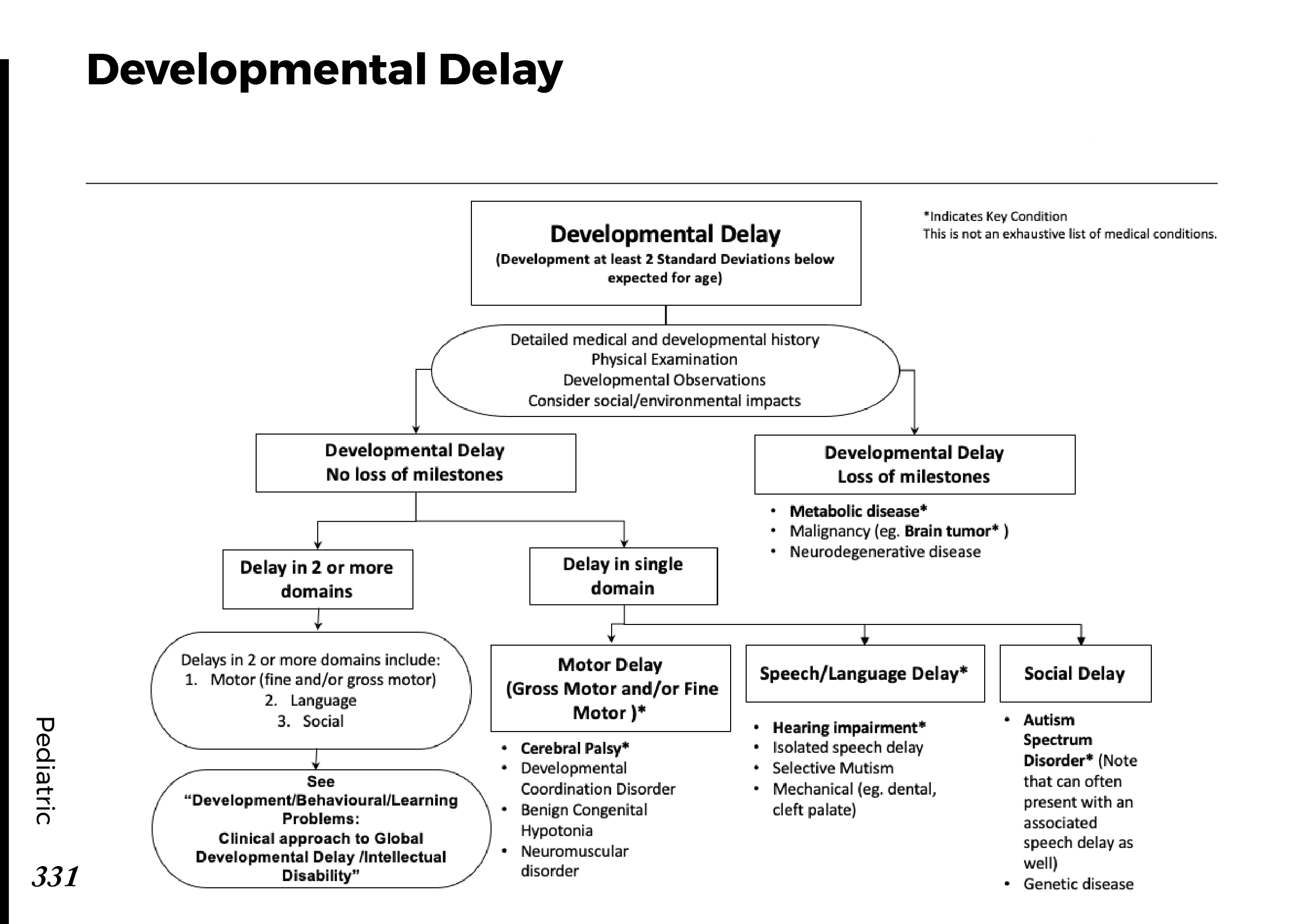
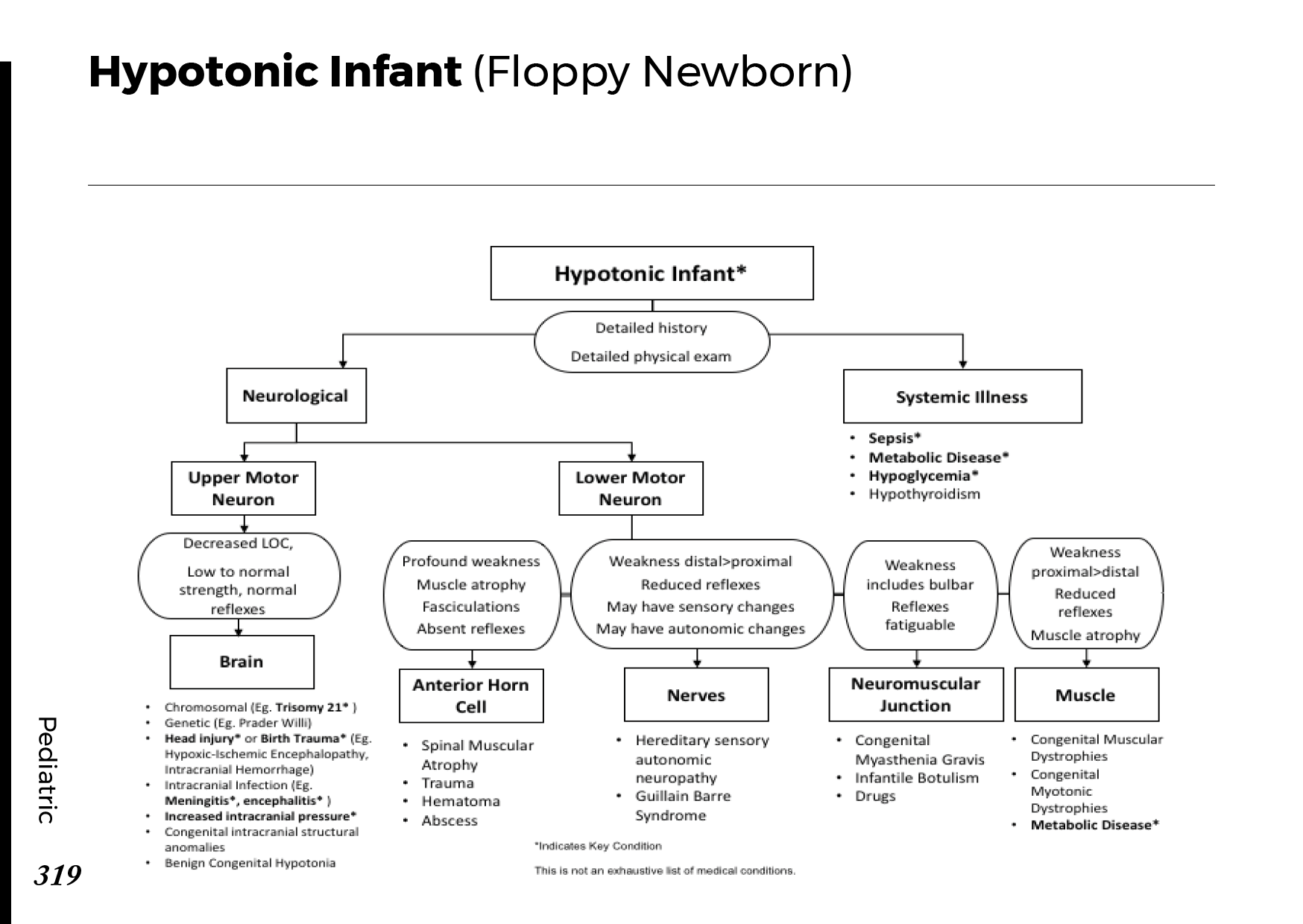
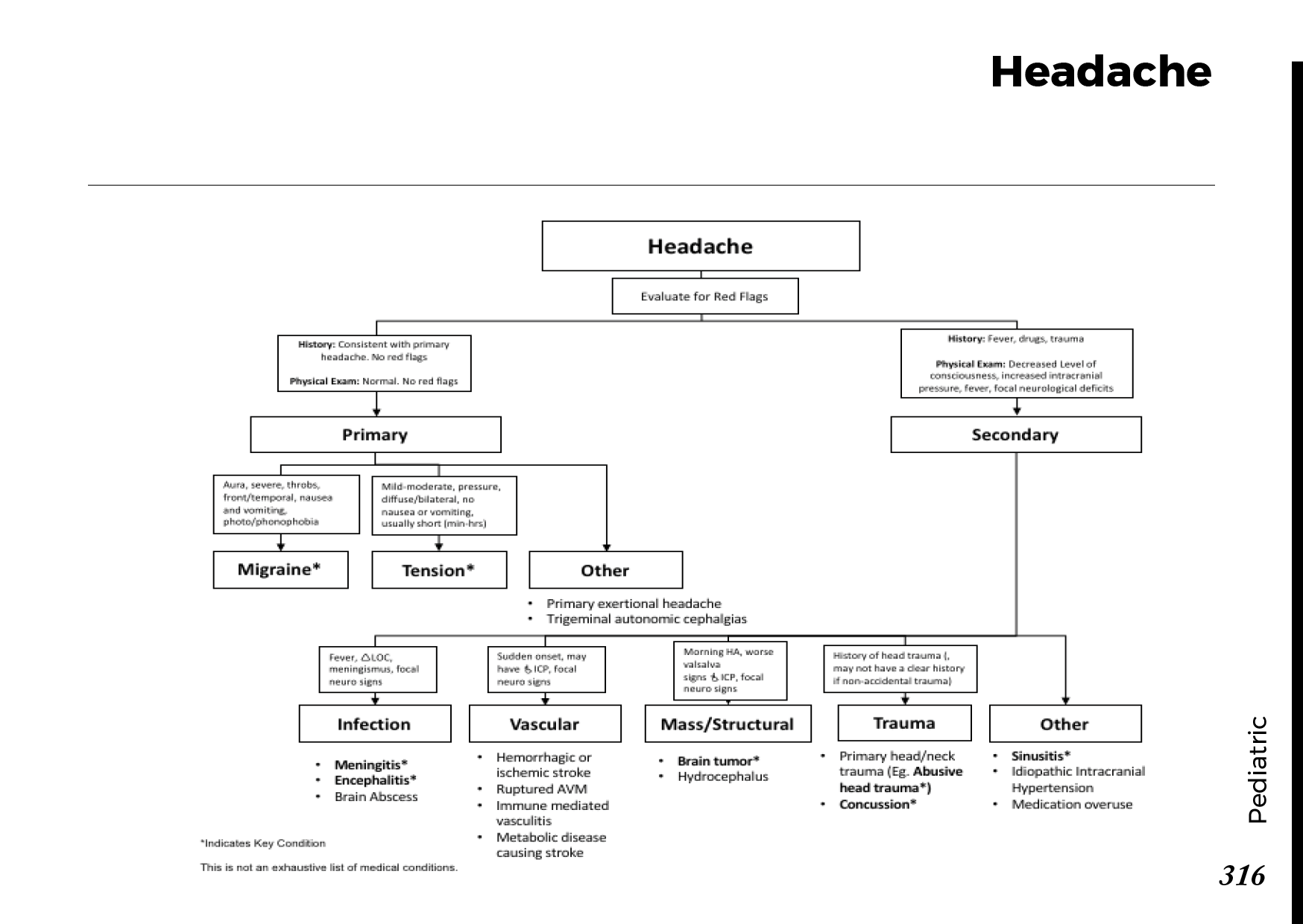
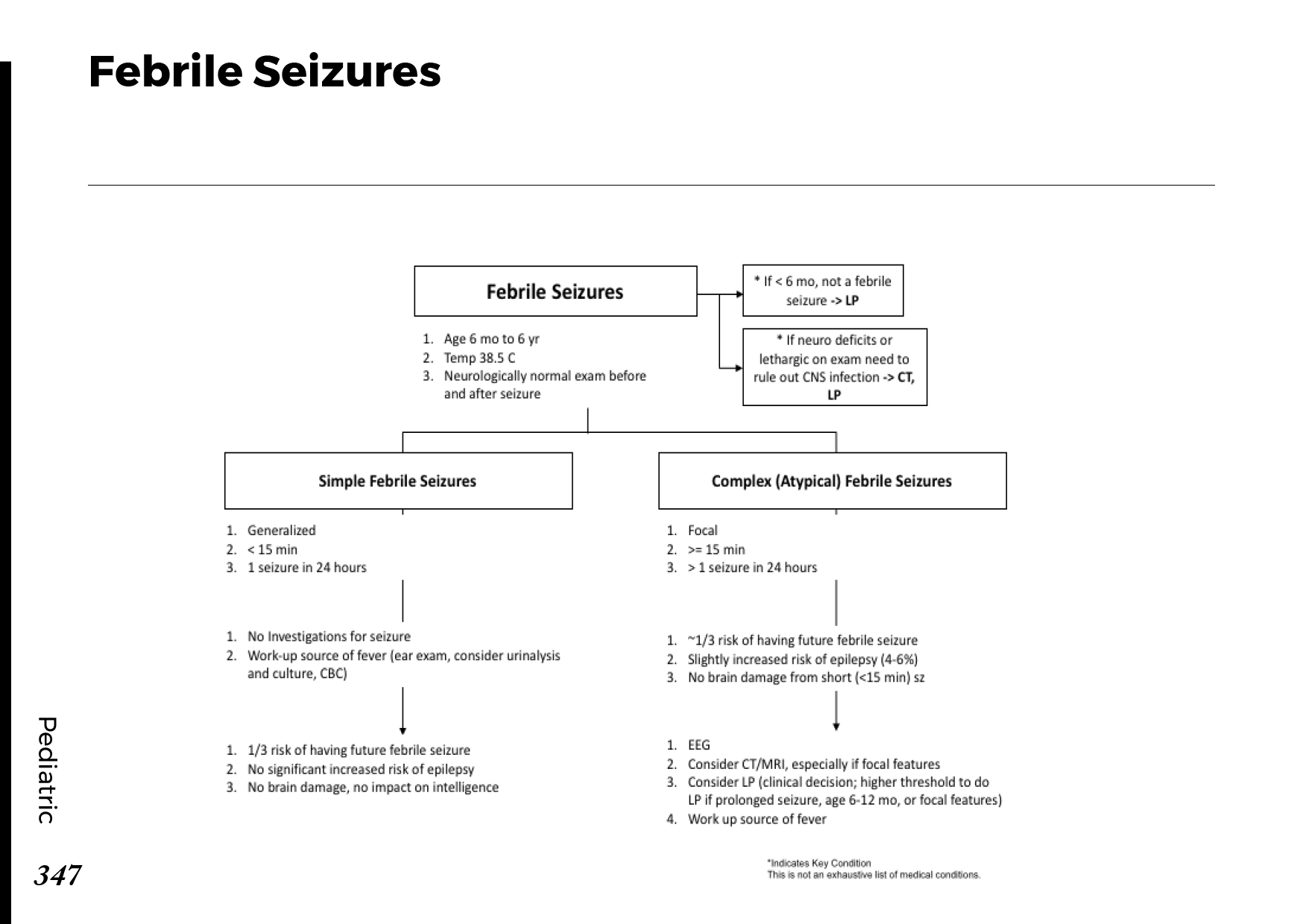
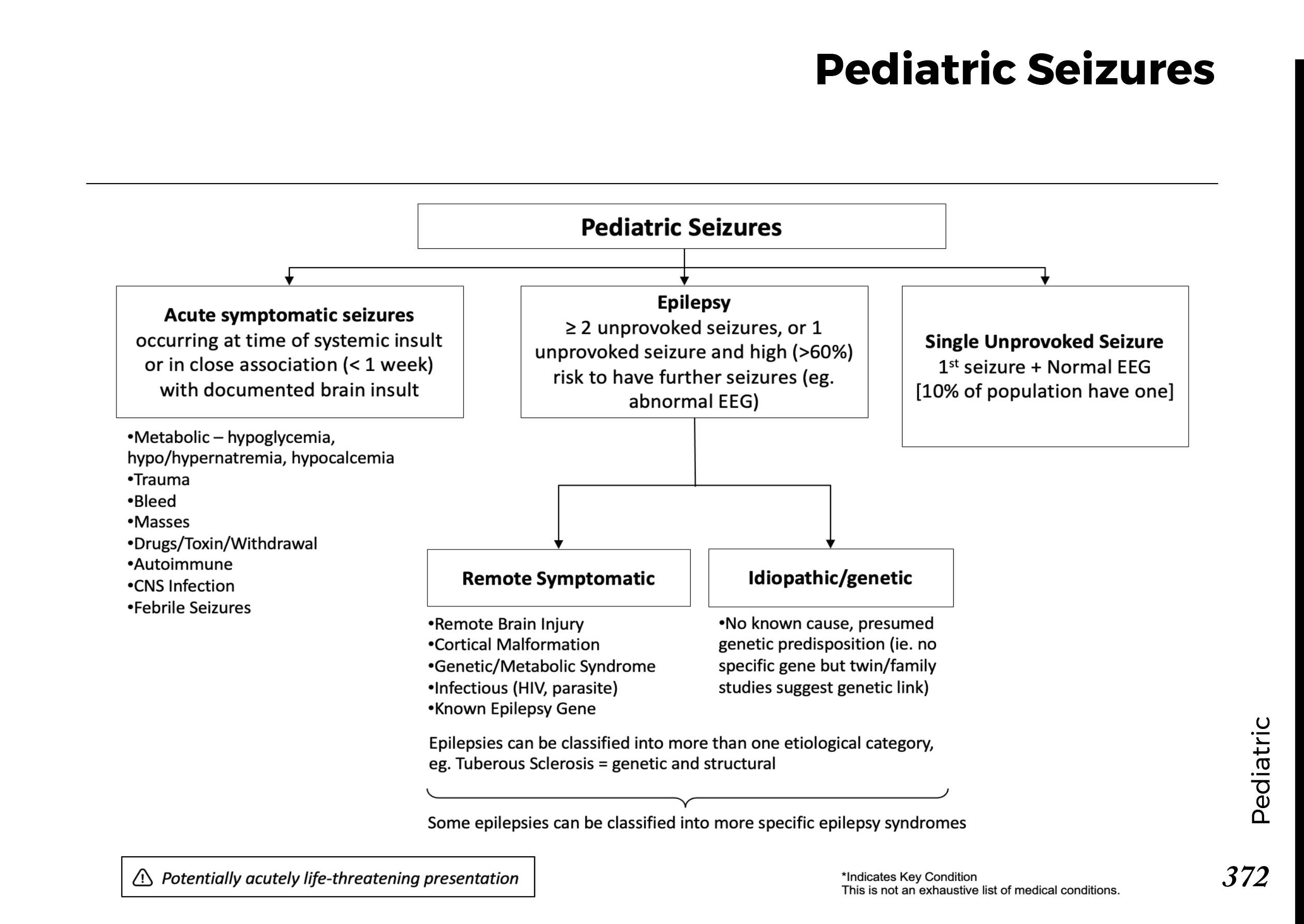
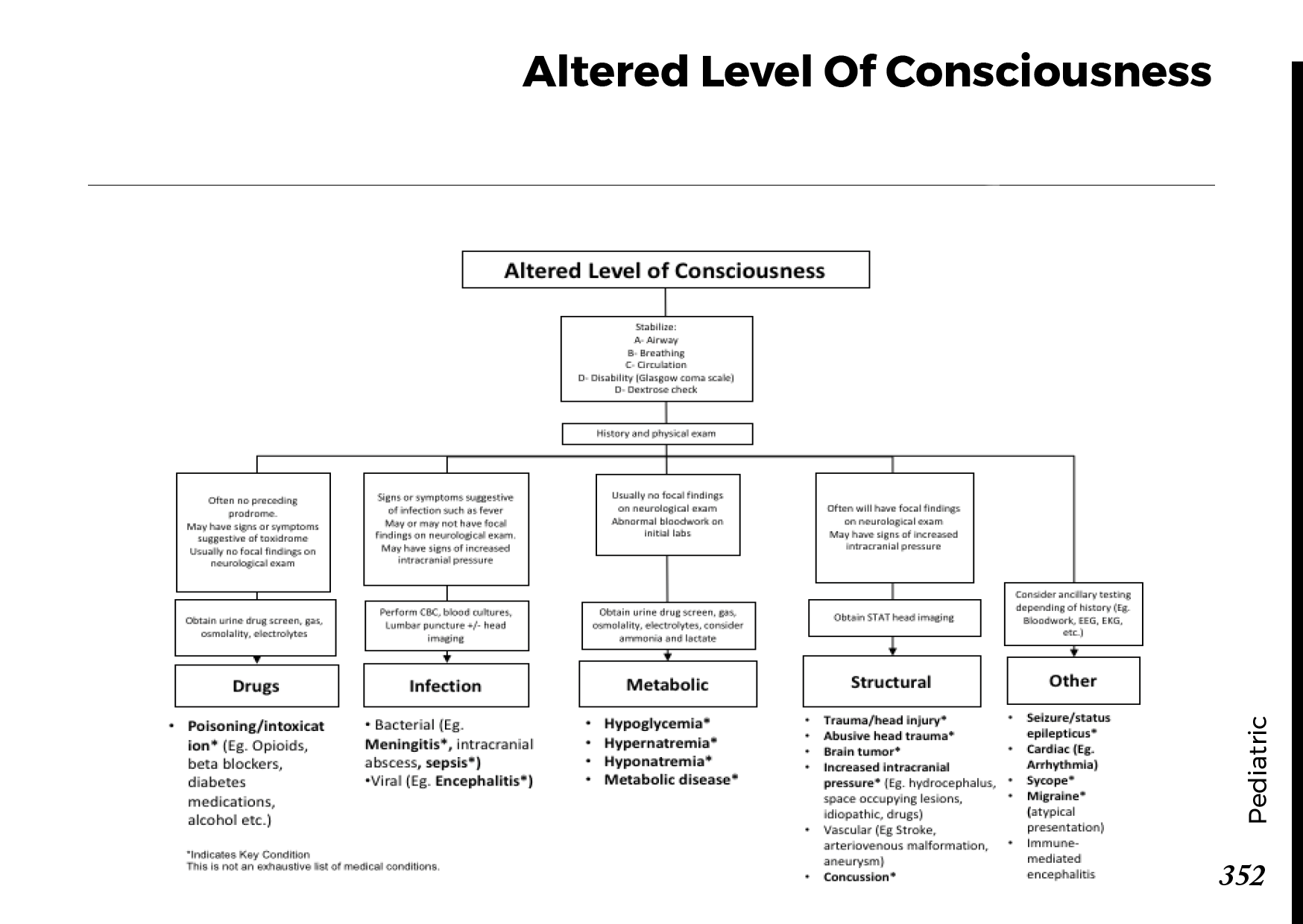
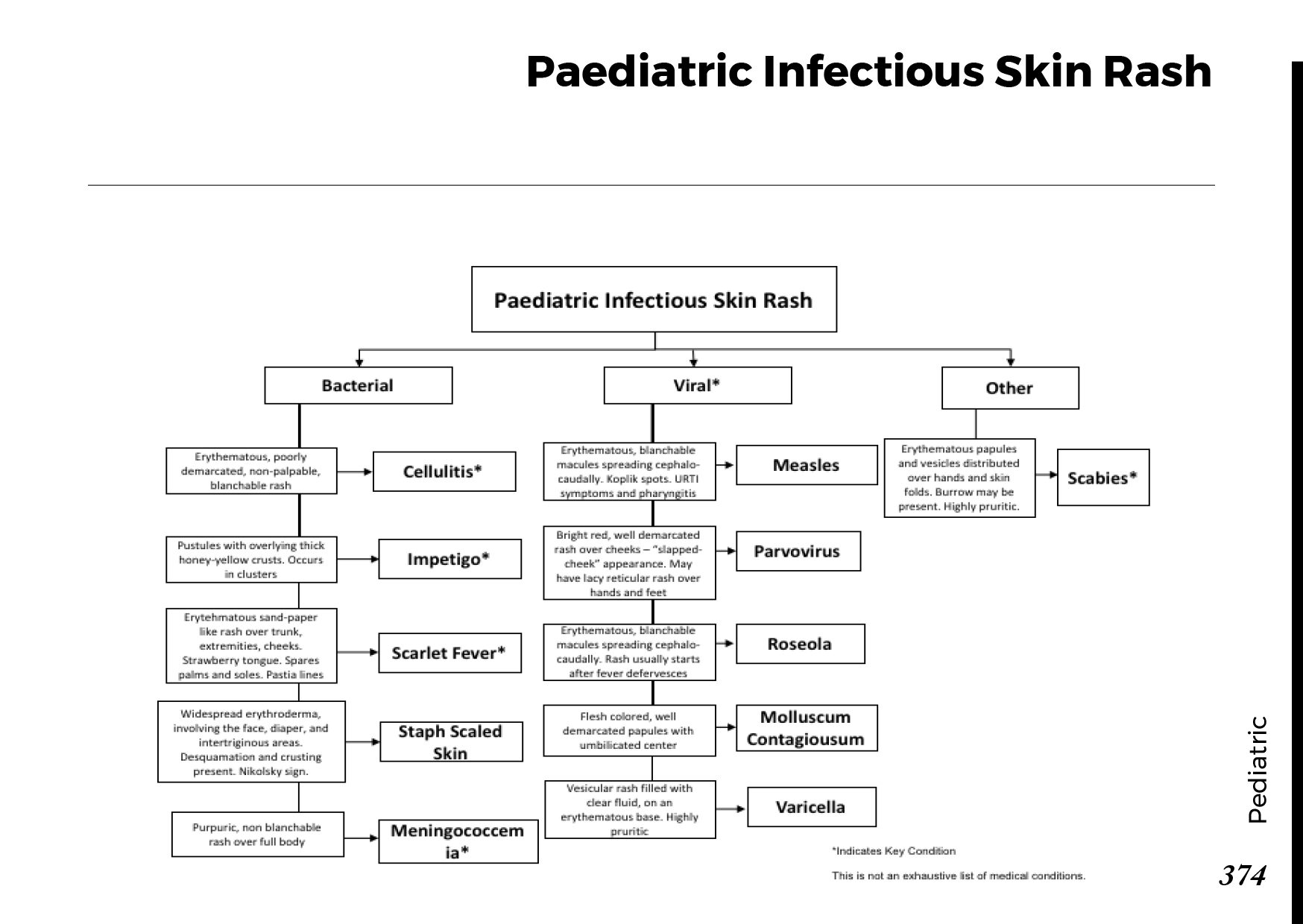
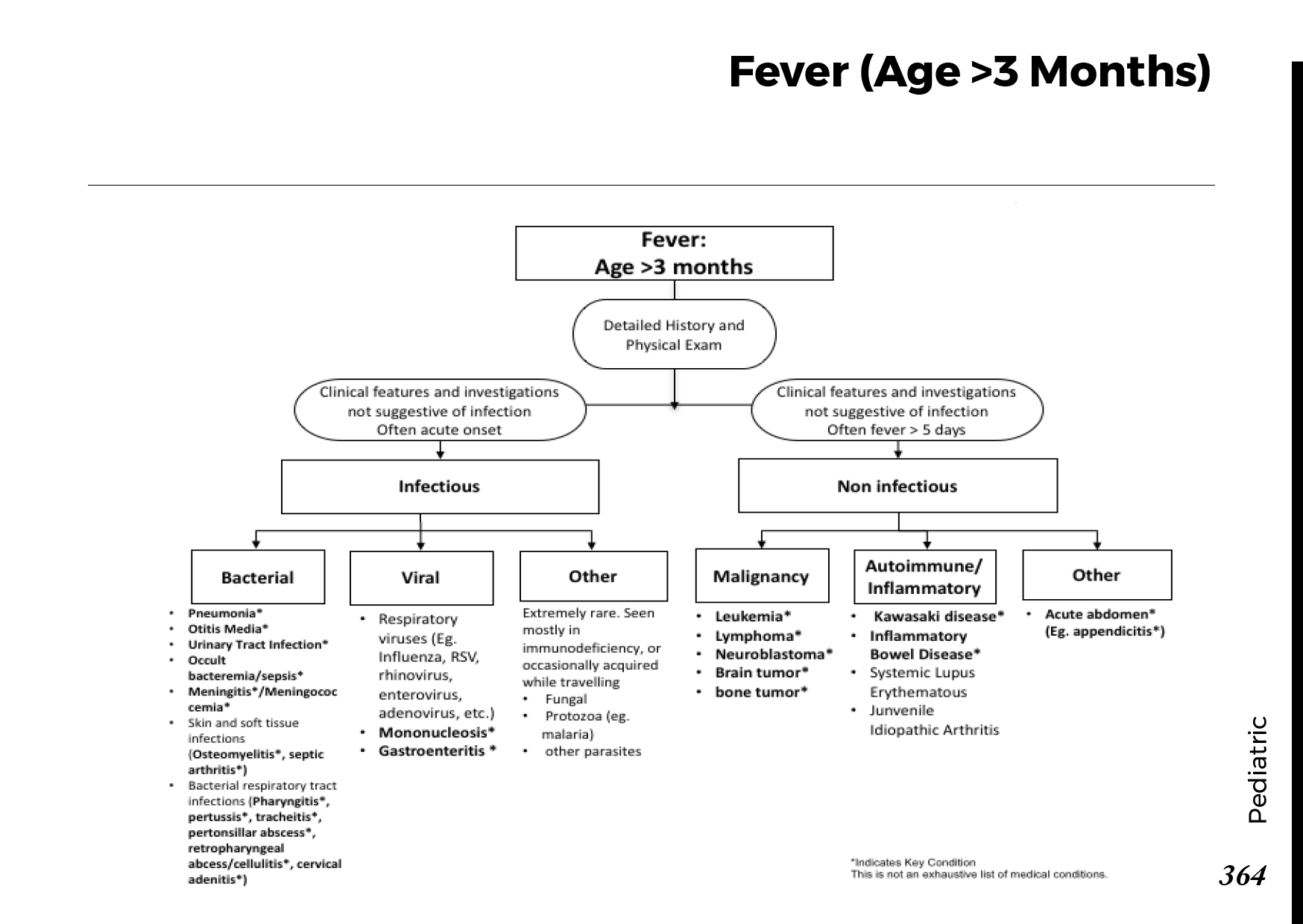
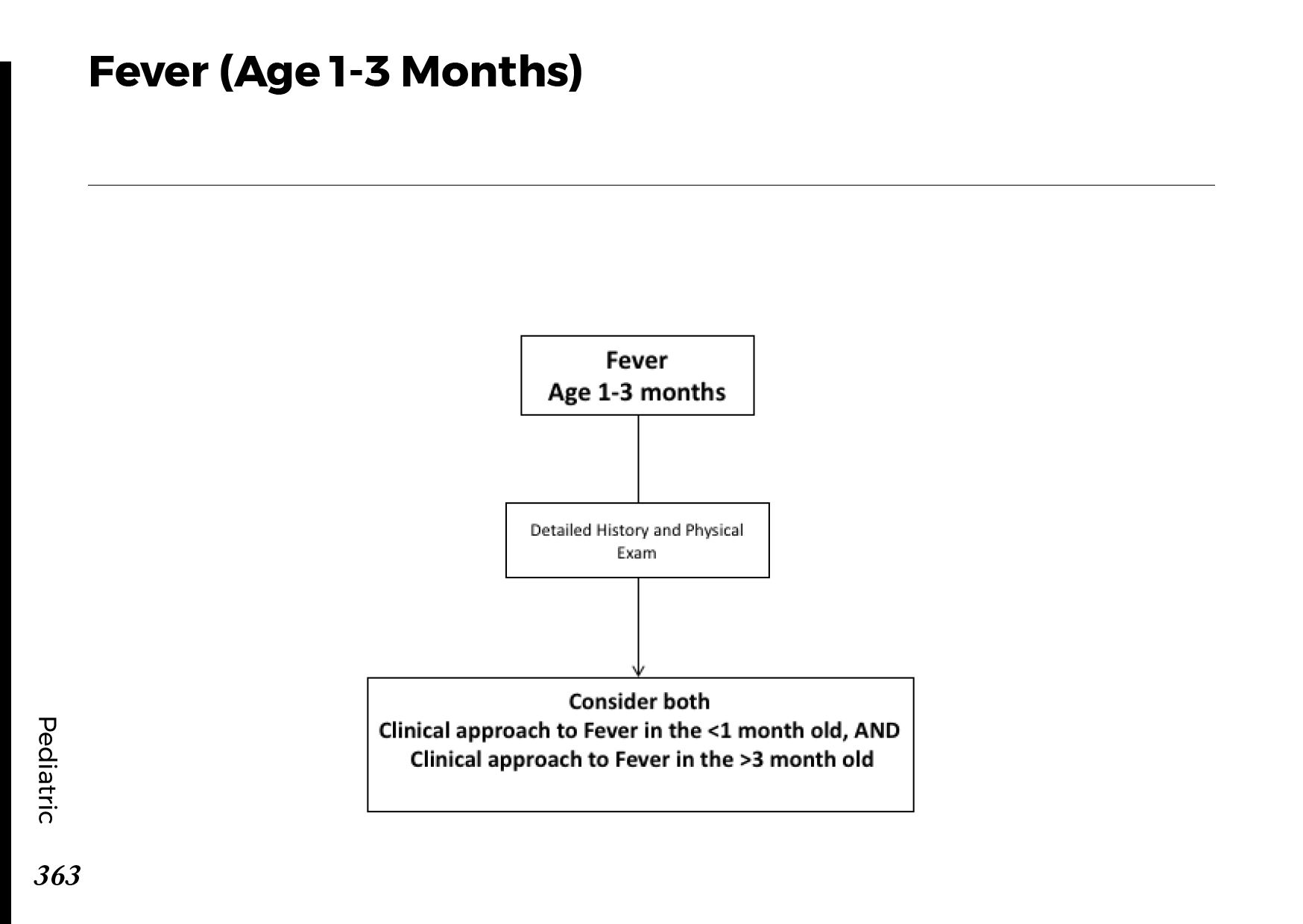
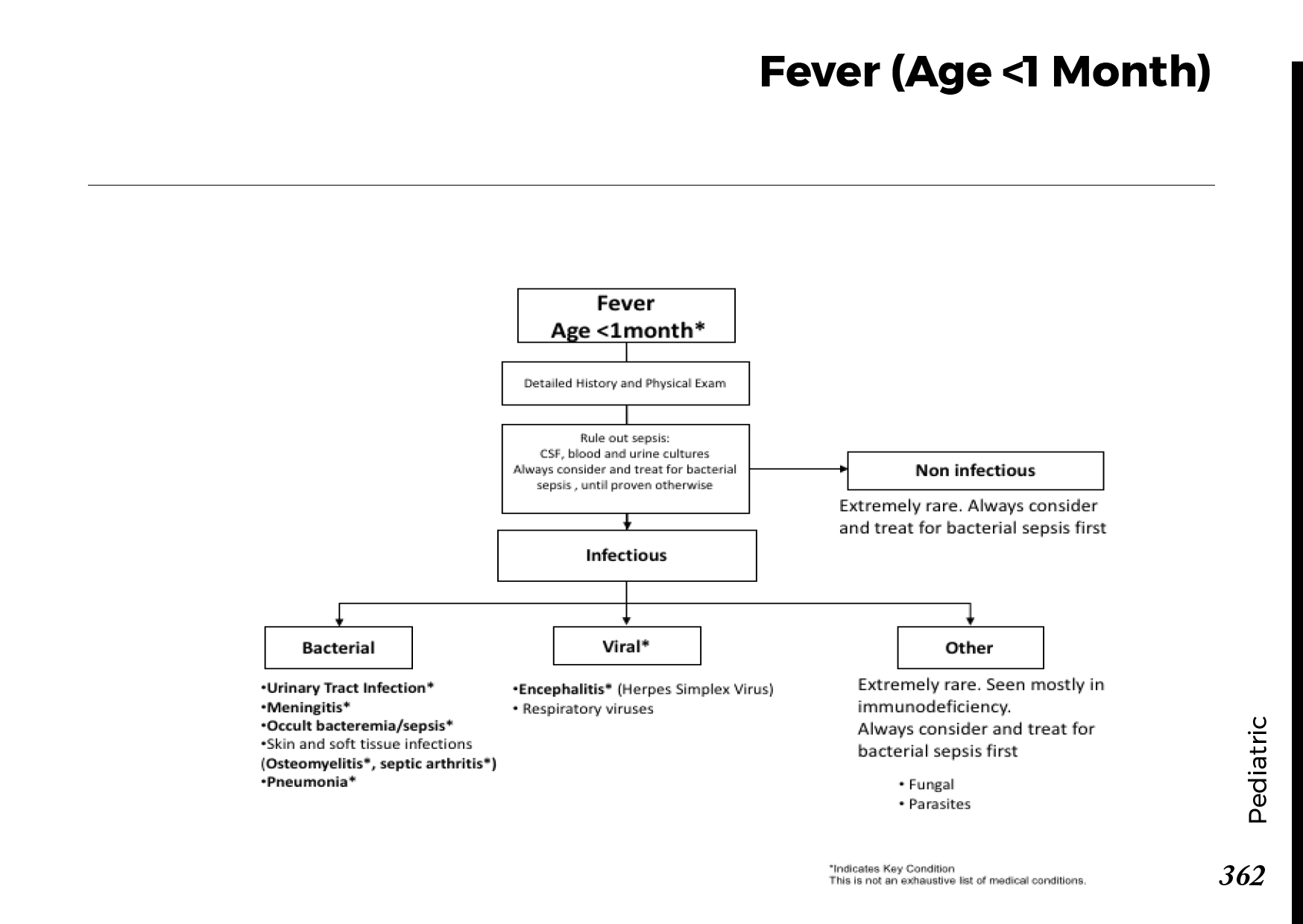
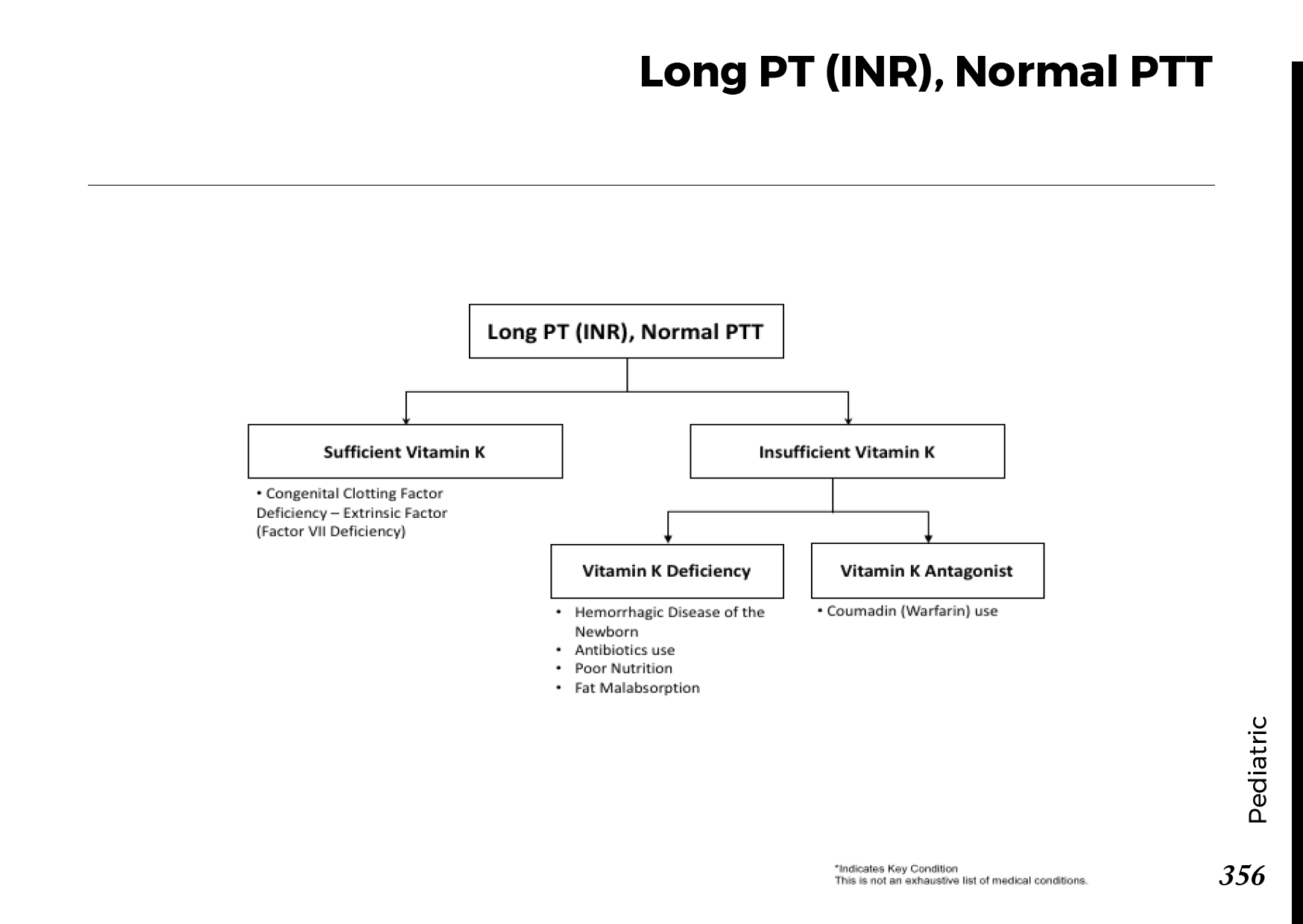
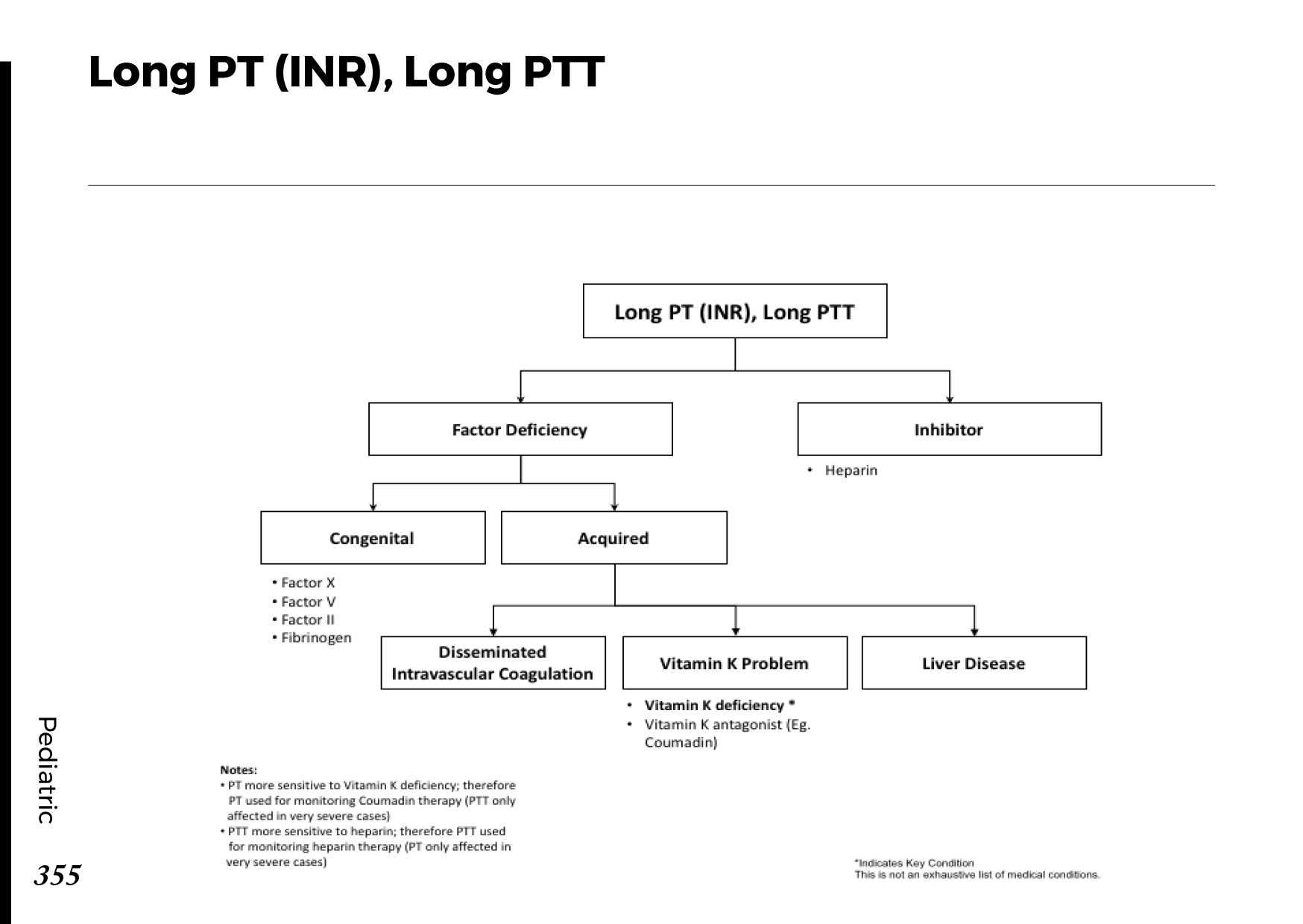
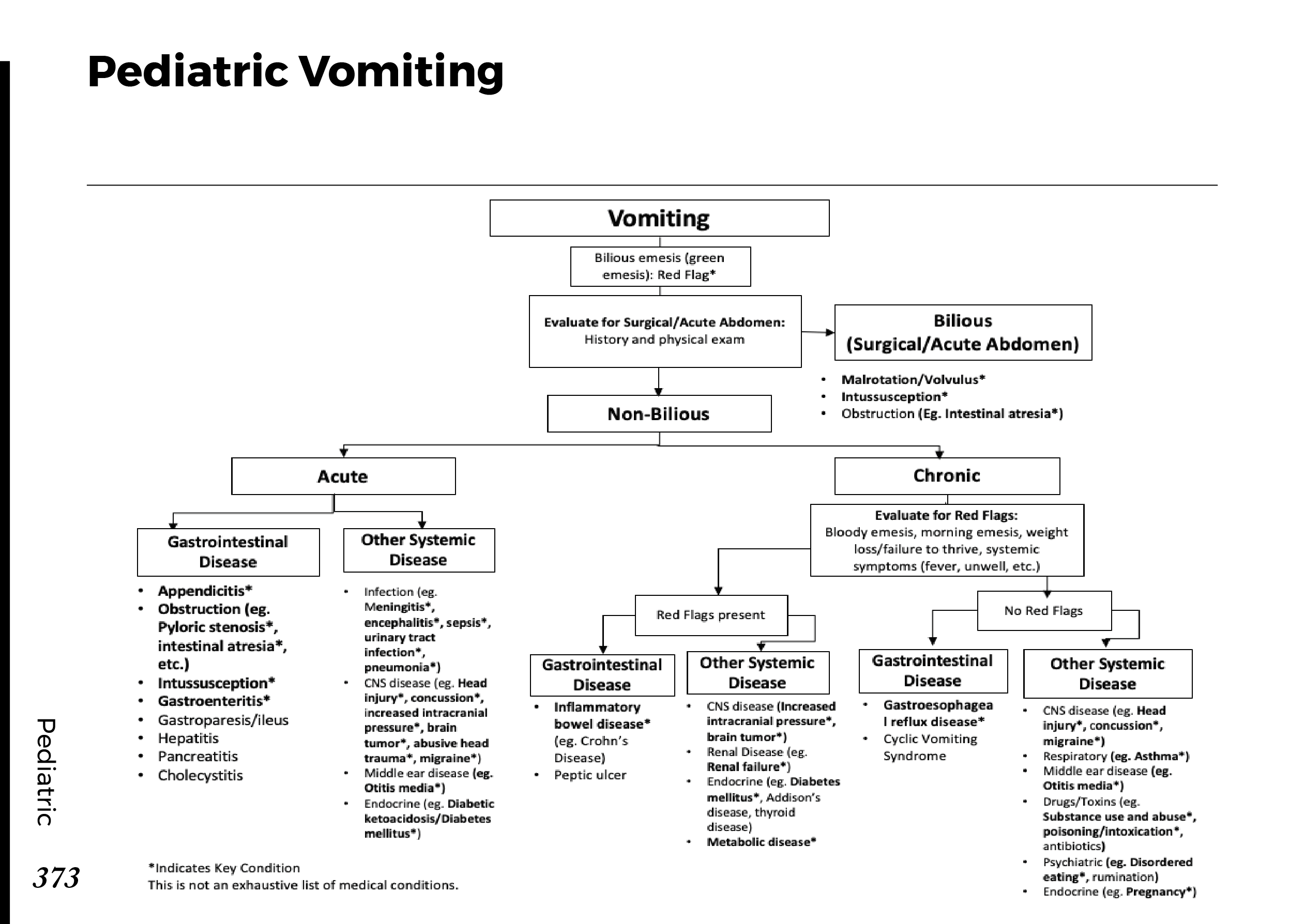
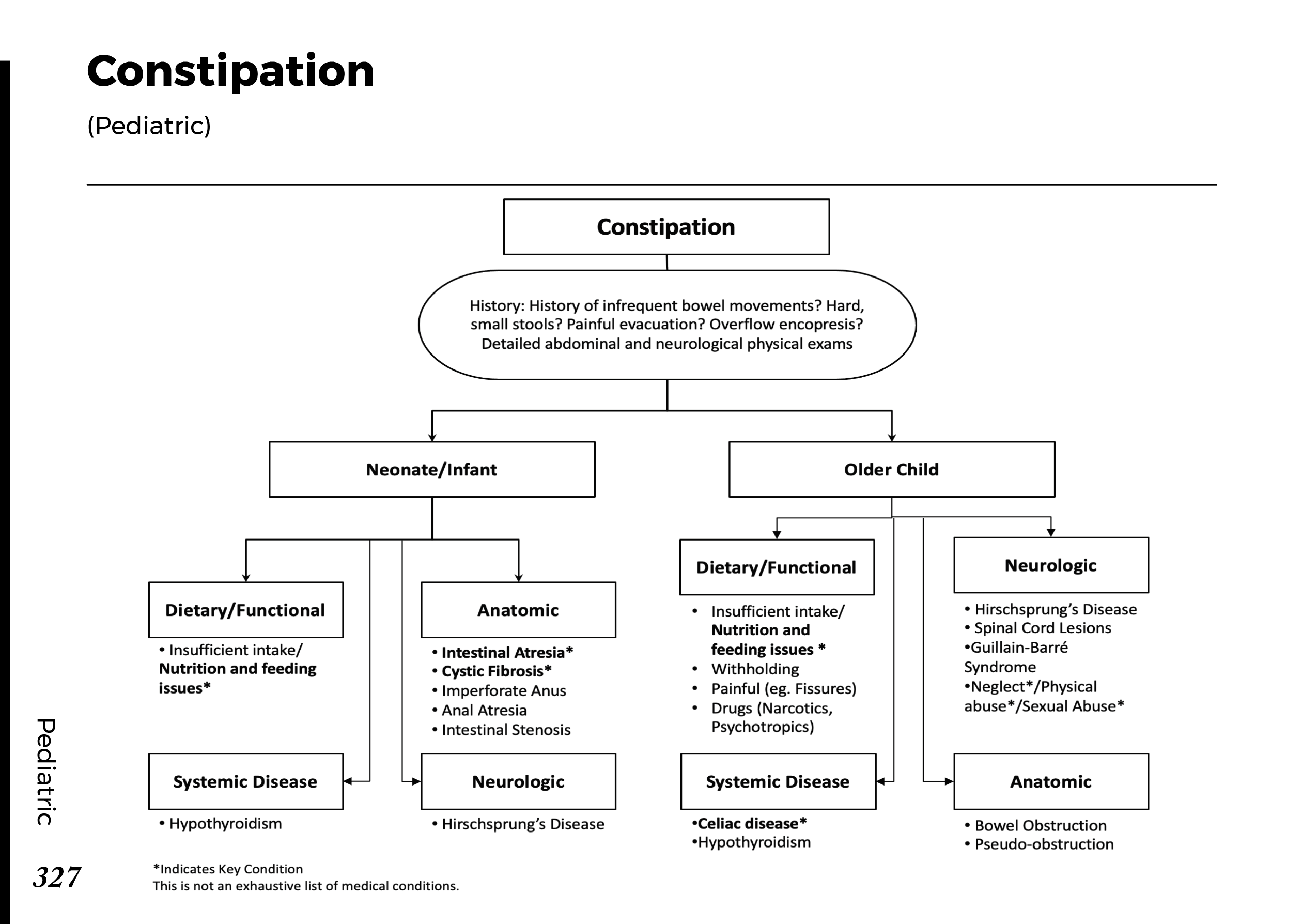
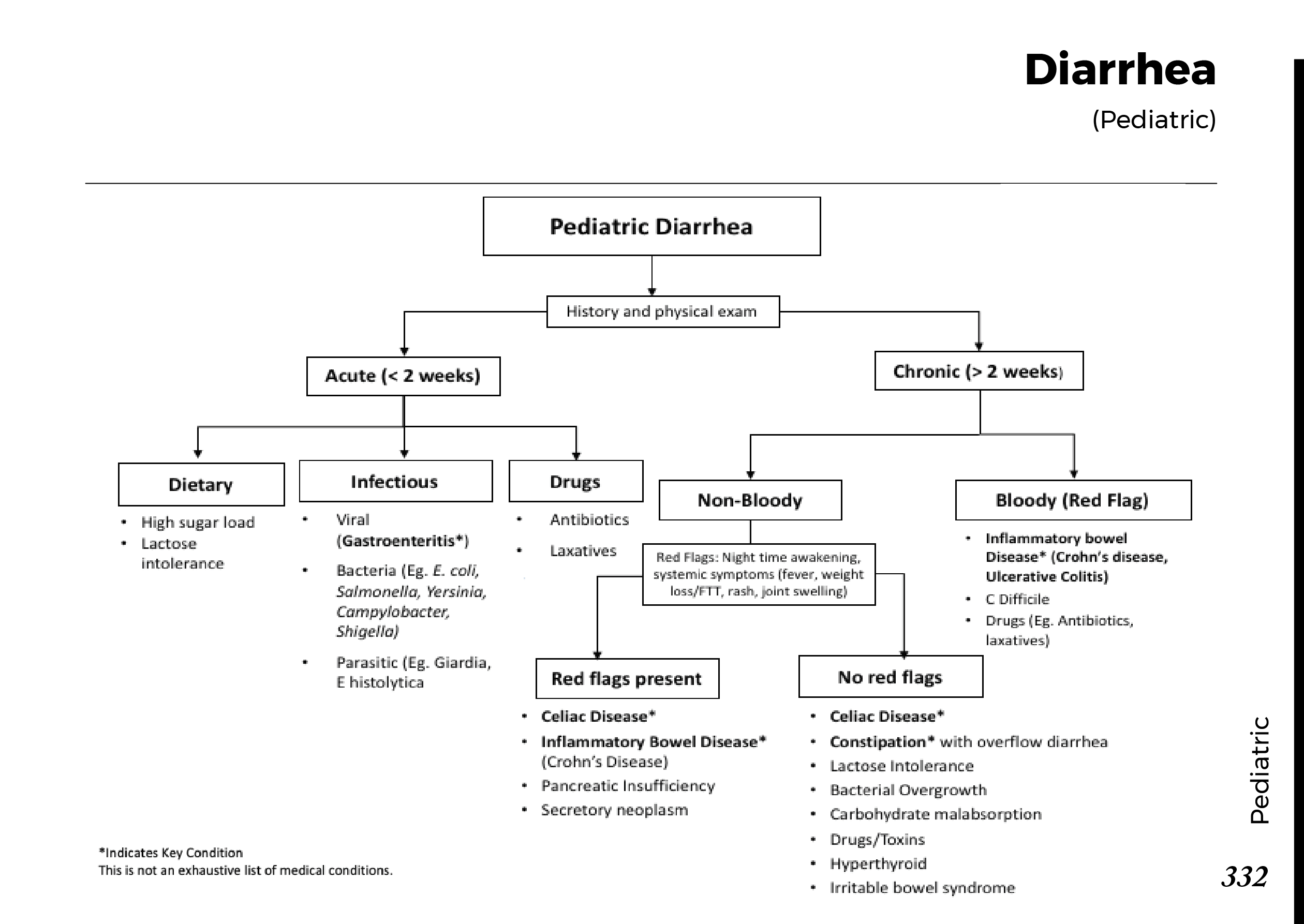
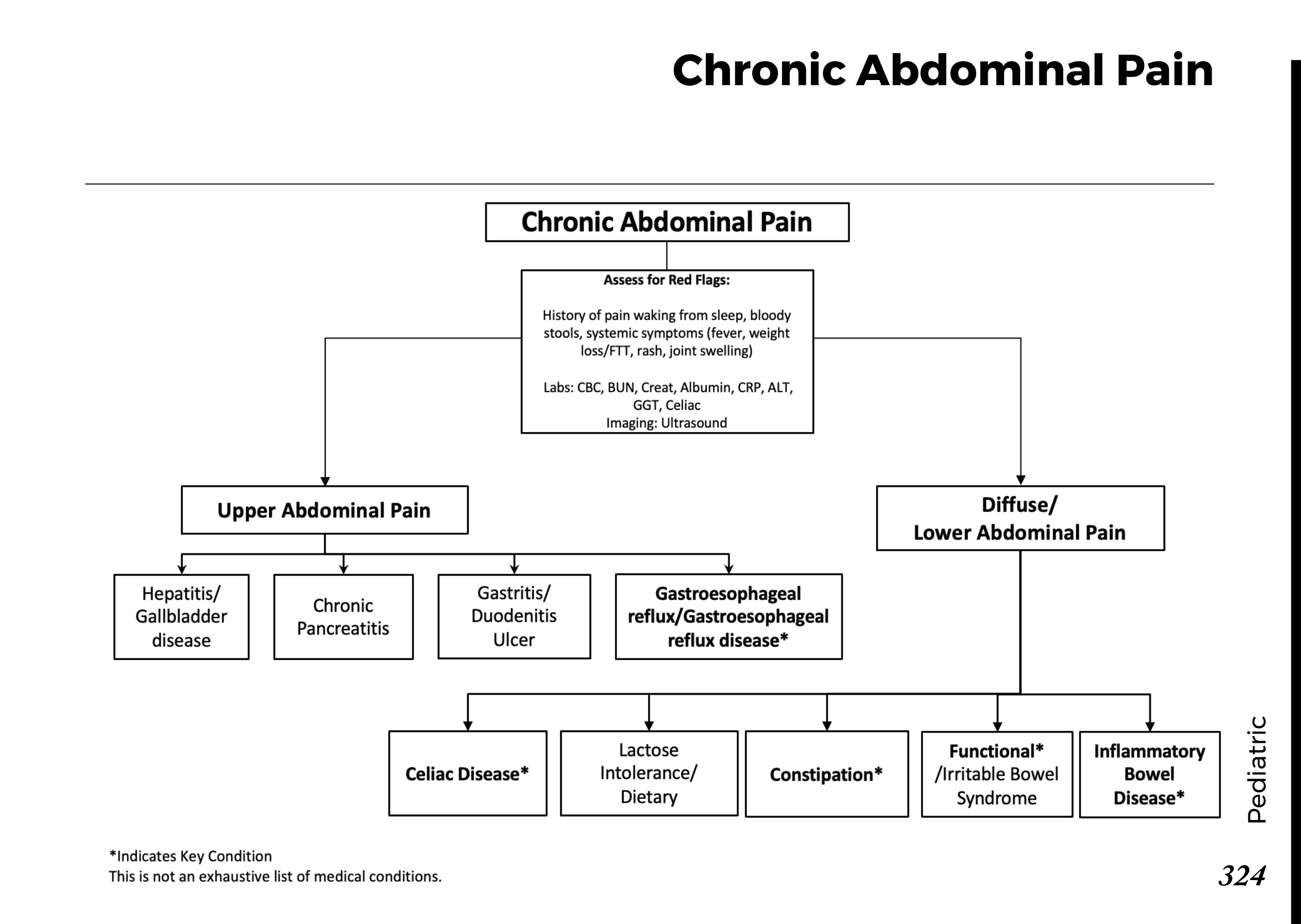
Motiyabind, commonly known as cataracts, is a prevalent eye condition that affects millions of people worldwide. This post aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of motiyabind (cataracts) by exploring its causes, symptoms, and available treatments.
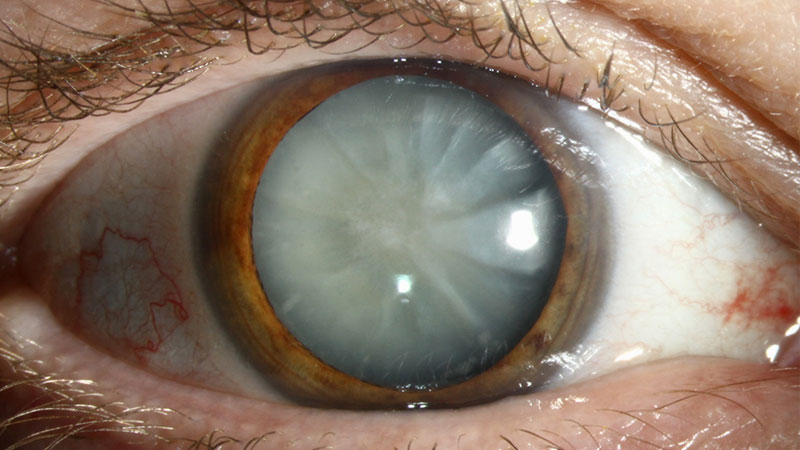
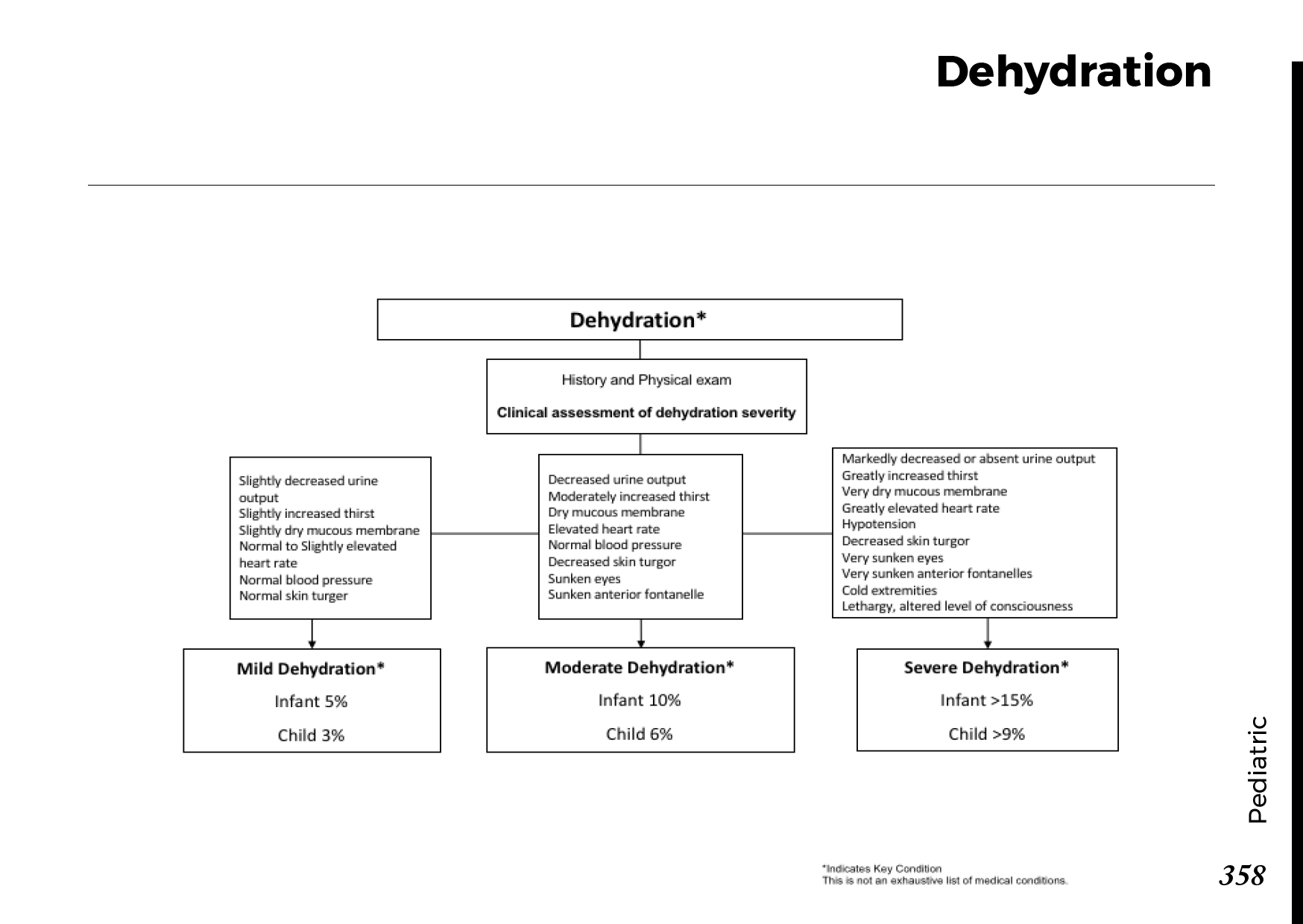
Cataracts occur when the natural lens of the eye becomes clouded, leading to blurry vision and visual impairment. This clouding prevents light from passing through the lens properly, affecting the way images are transmitted to the retina.
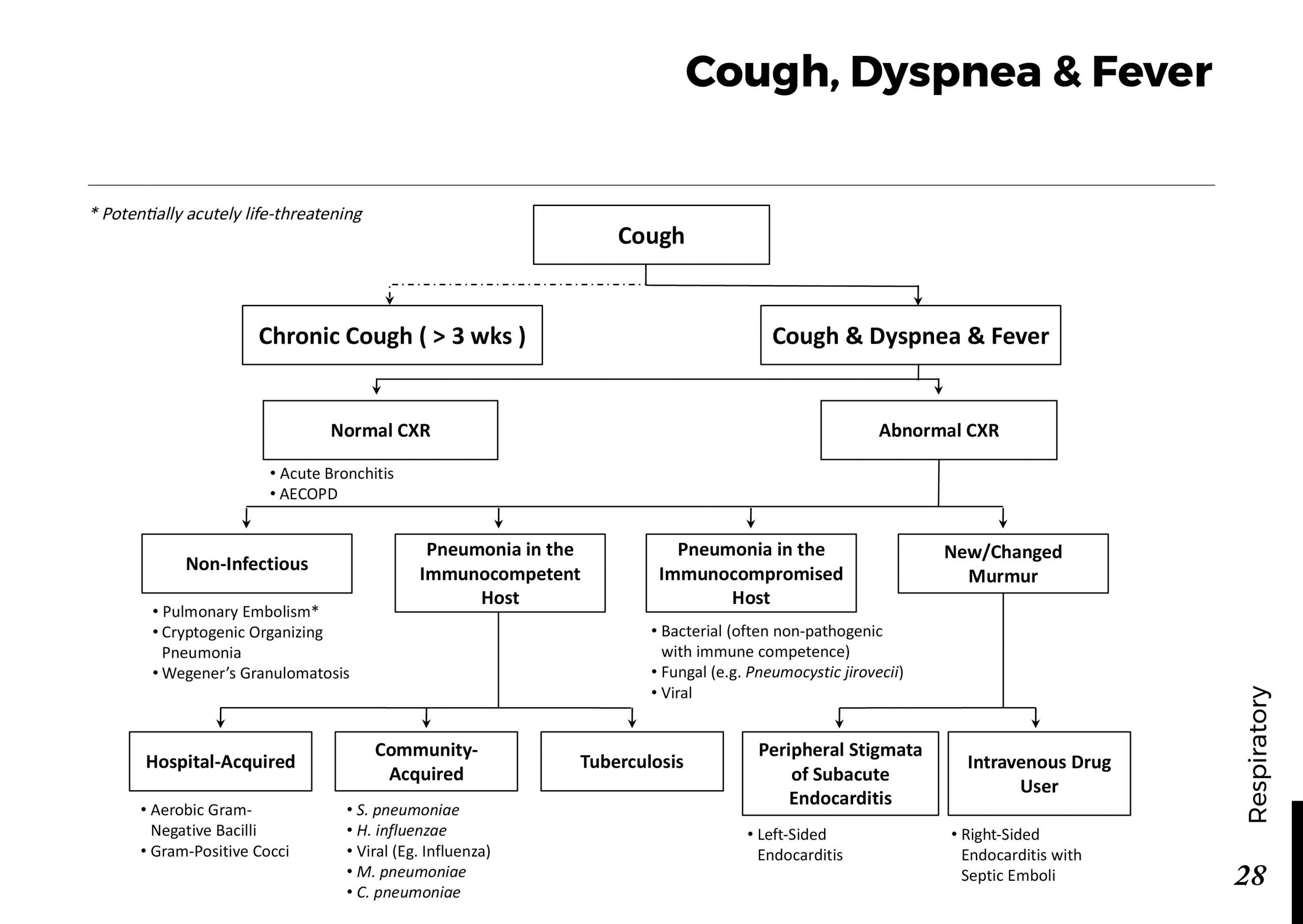
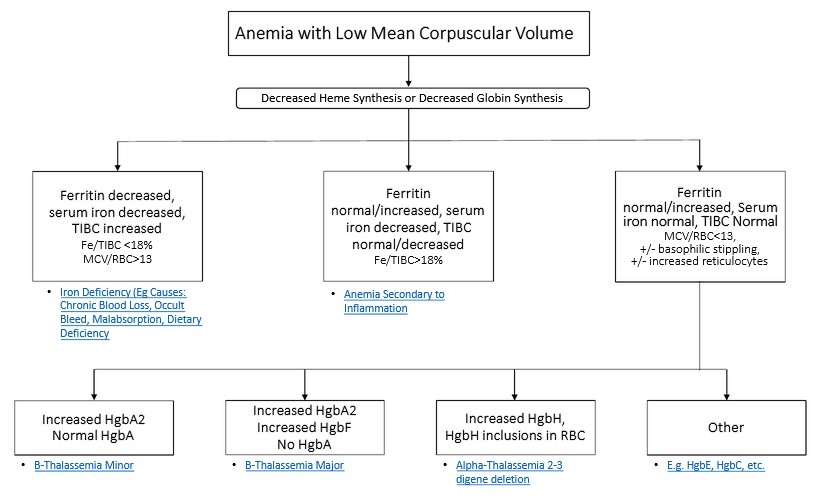
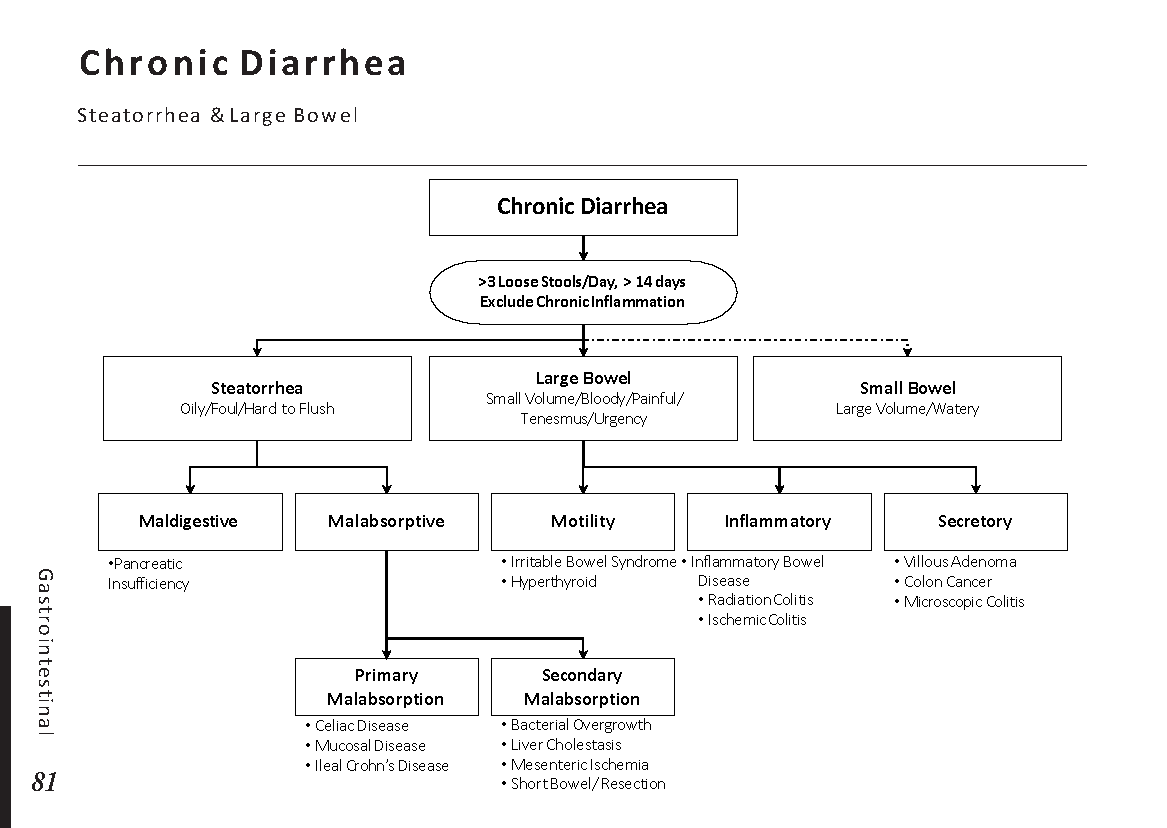
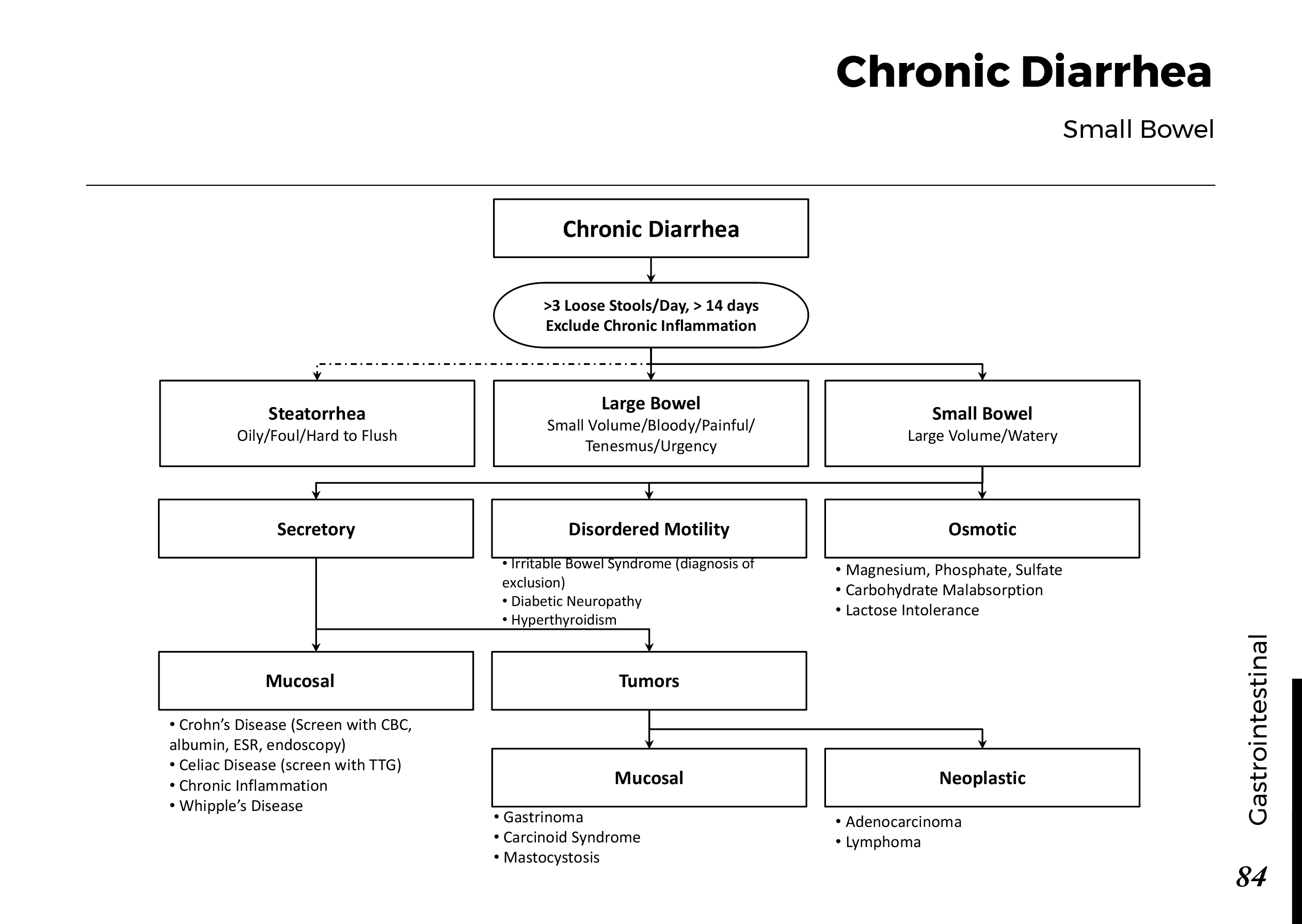
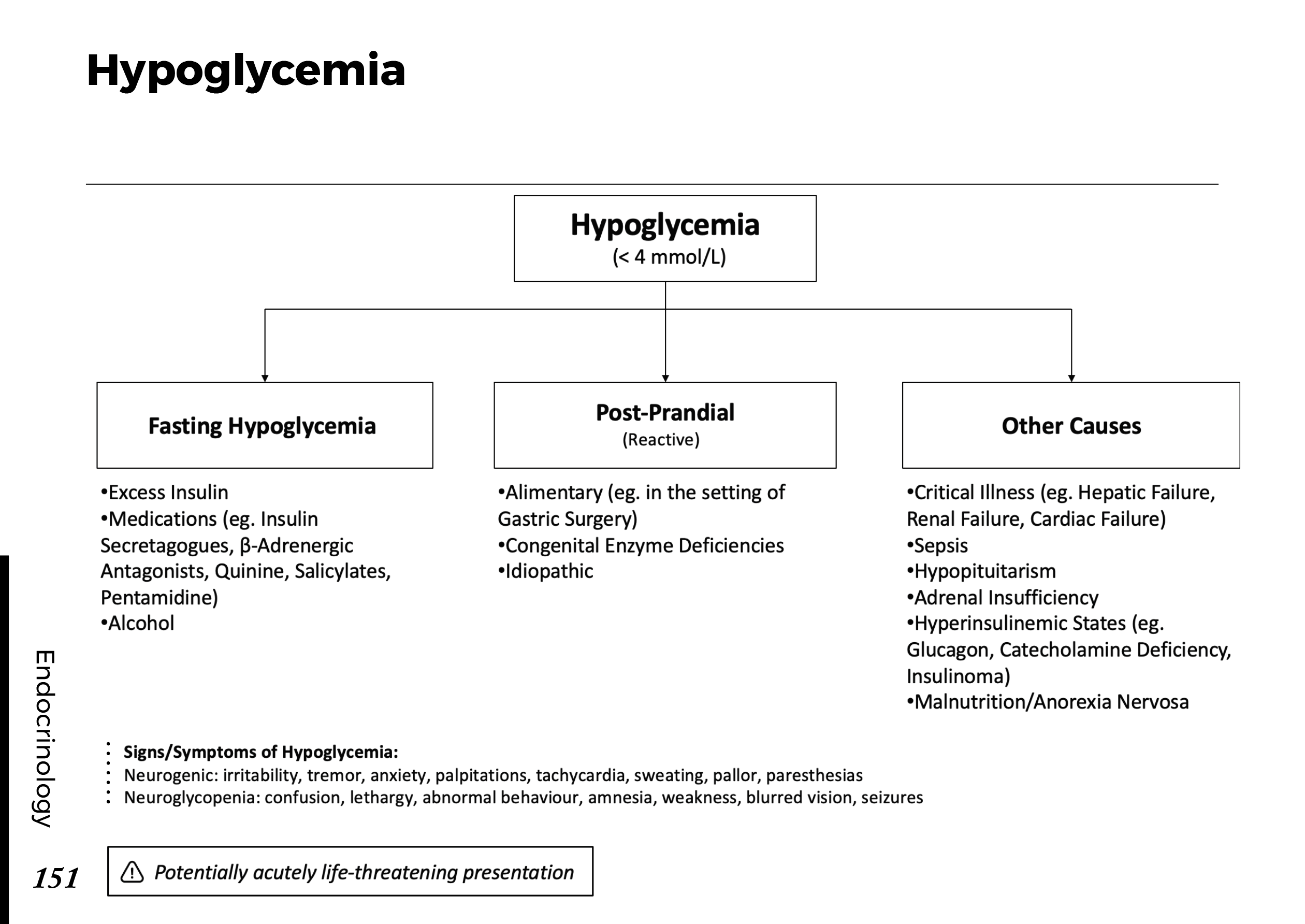
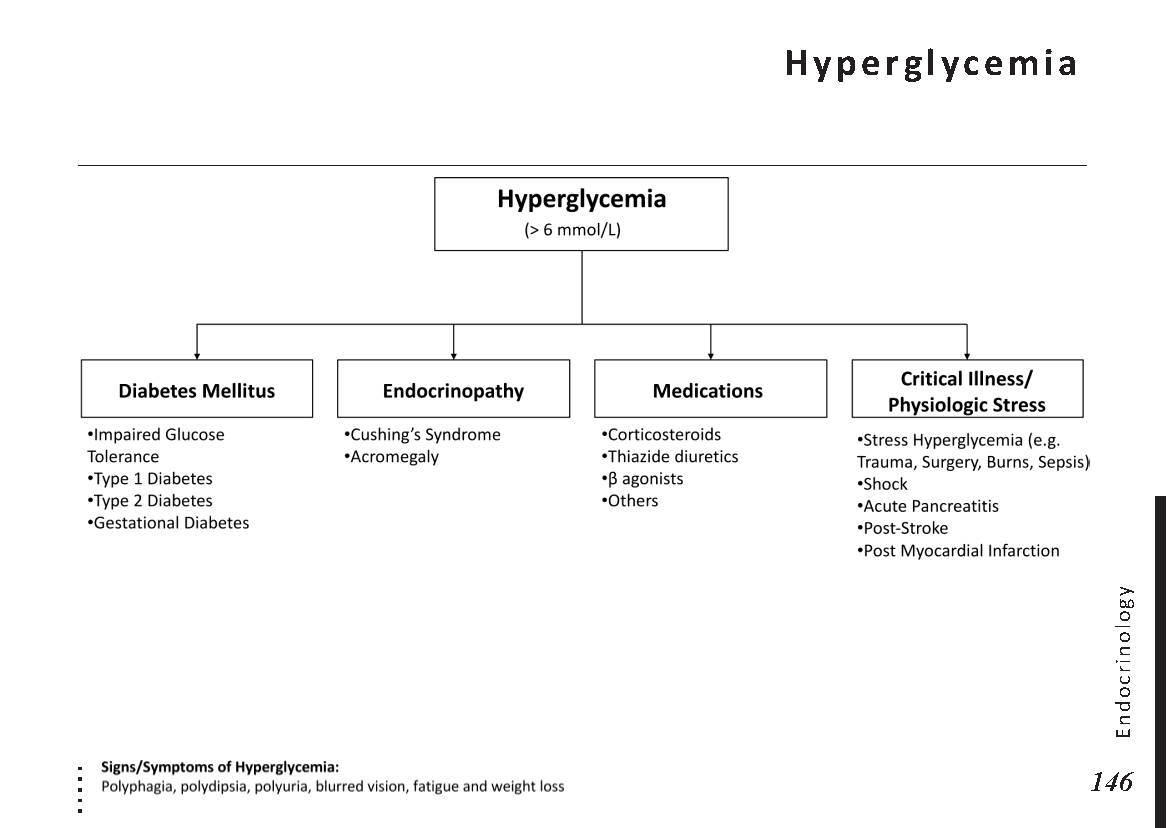
Several factors contribute to the development of cataracts, including:
a) Age: Aging is one of the most common causes of cataracts, with people over 60 being more susceptible.
b) Genetics: Family history can increase the risk of developing cataracts.
c) Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes are more likely to develop cataracts earlier in life.
d) Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation: Prolonged exposure to UV rays can accelerate cataract formation.
e) Smoking and Alcohol: Both smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to an increased risk of cataracts.
f) Eye Injuries: Trauma to the eye can lead to the development of cataracts.
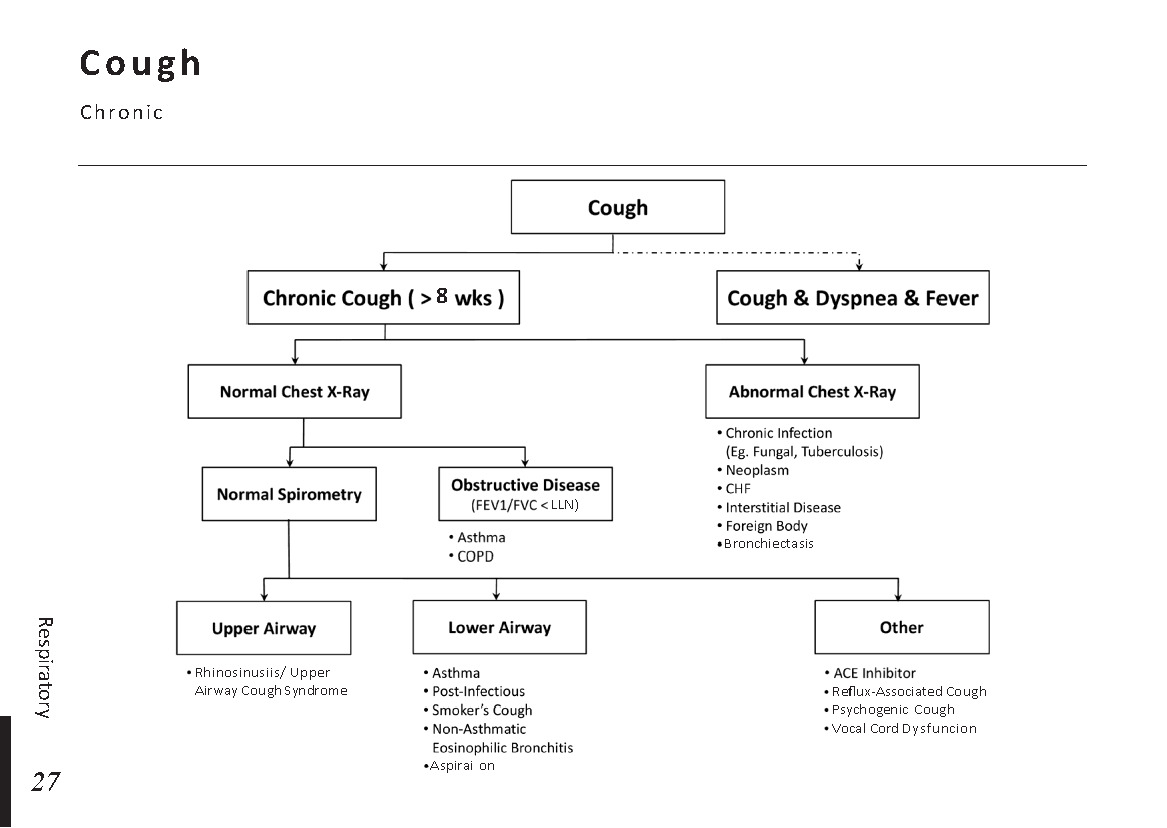
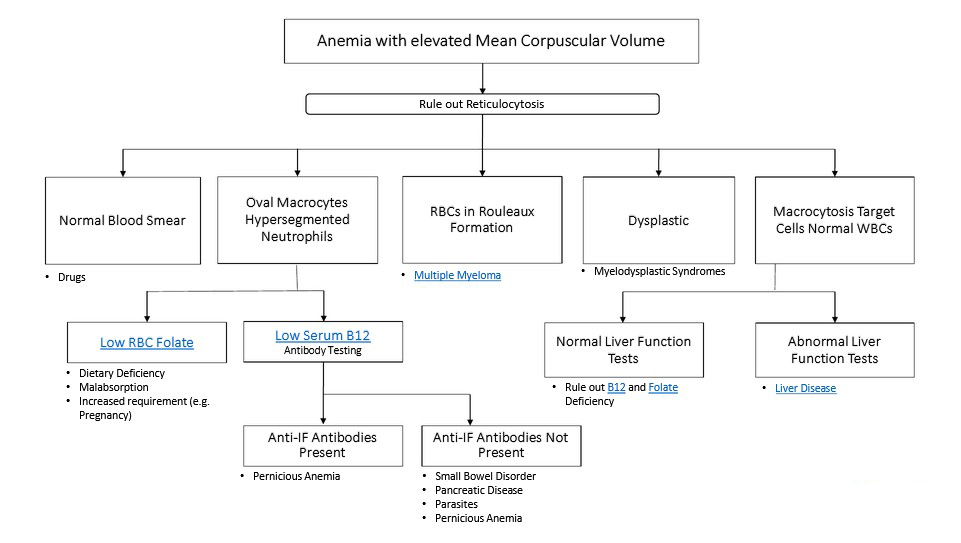
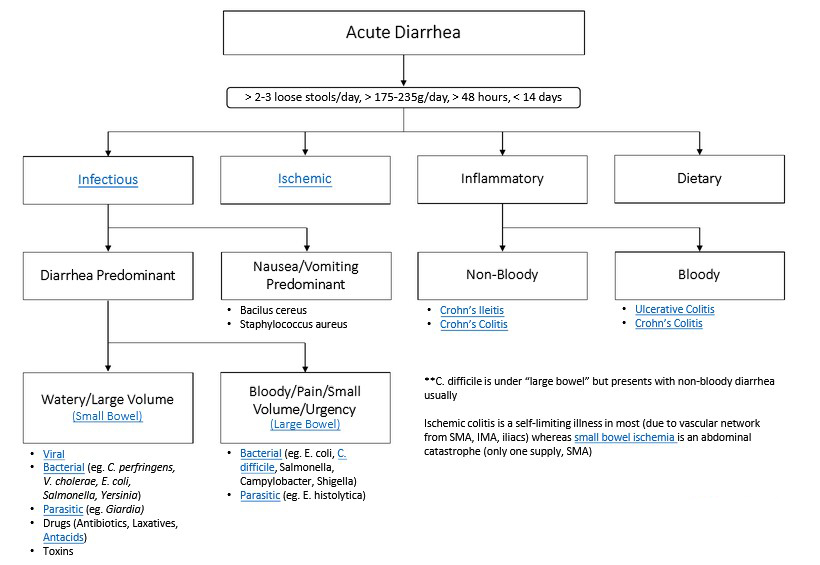
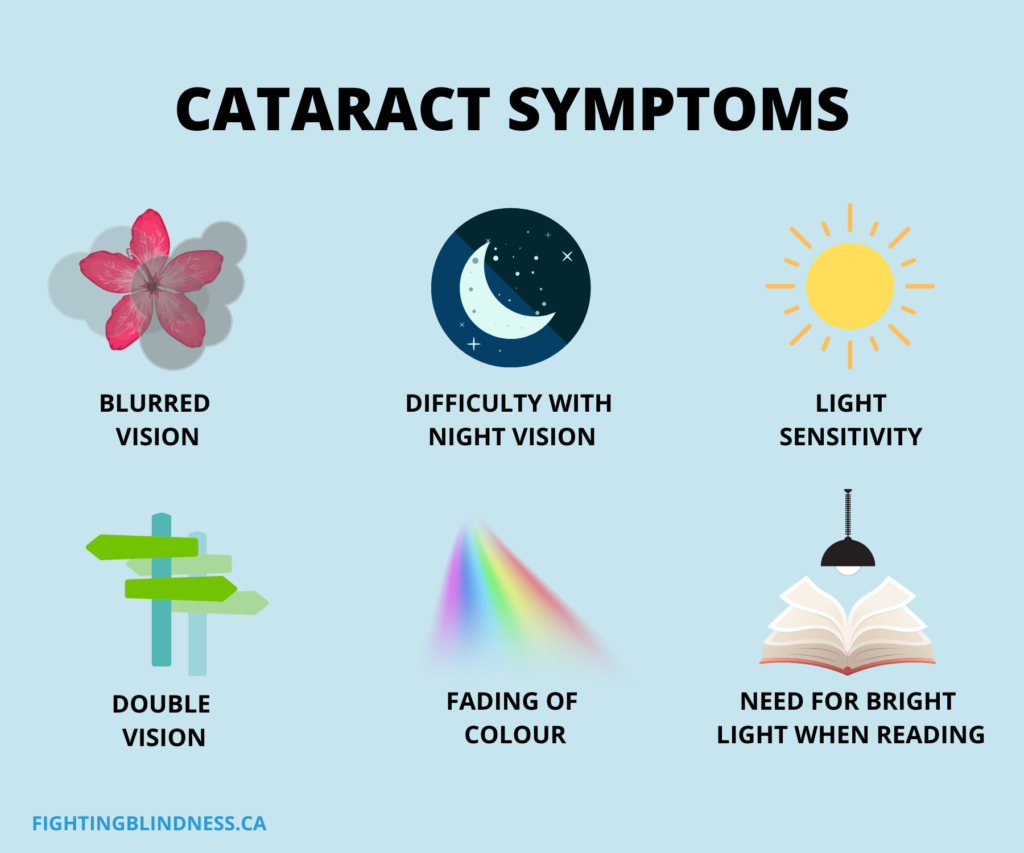
Recognizing the early signs of cataracts can help in seeking timely treatment. Common symptoms include:
a) Blurred Vision: Objects may appear hazy or out of focus.
b) Sensitivity to Light: Bright lights may cause discomfort or glare.
c) Color Distortion: Colors may appear faded or yellowed.
d) Reduced Night Vision: Difficulty seeing in low-light conditions.
e) Double Vision: Seeing multiple images of a single object.
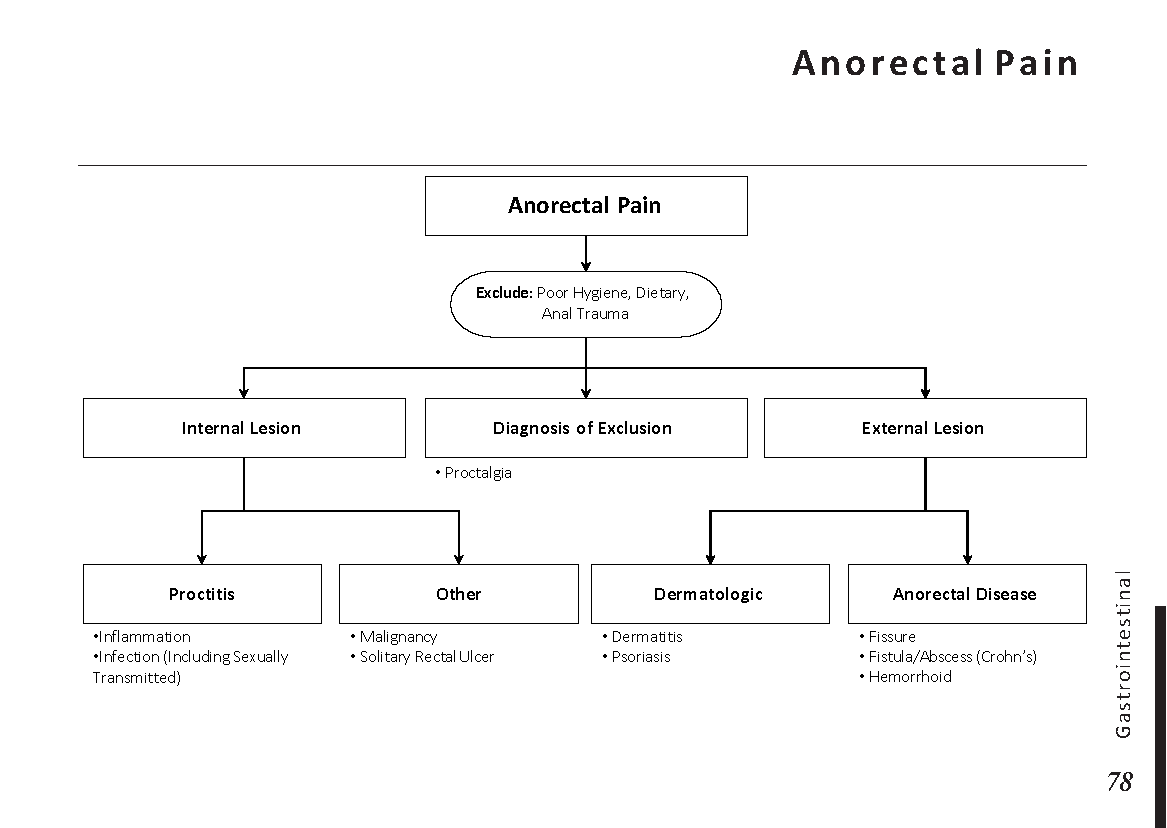
If you experience any of the above symptoms, it’s essential to visit an ophthalmologist for a comprehensive eye examination. During this examination, the eye doctor will evaluate the clarity of your lens and assess the severity of the cataracts.
Fortunately, cataracts can be treated effectively, allowing individuals to regain clear vision. The most common treatment for cataracts is surgery. During the procedure, the cloudy lens is replaced with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL) to restore vision.
While some risk factors are beyond our control, there are steps you can take to reduce the risk of cataracts:
a) Protect Your Eyes from UV Rays: Wear sunglasses that block UV rays when outdoors.
b) Quit Smoking: If you smoke, quitting can significantly reduce your cataract risk.
c) Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in antioxidants may support eye health.
d) Regular Eye Checkups: Schedule routine eye exams to monitor your eye health.
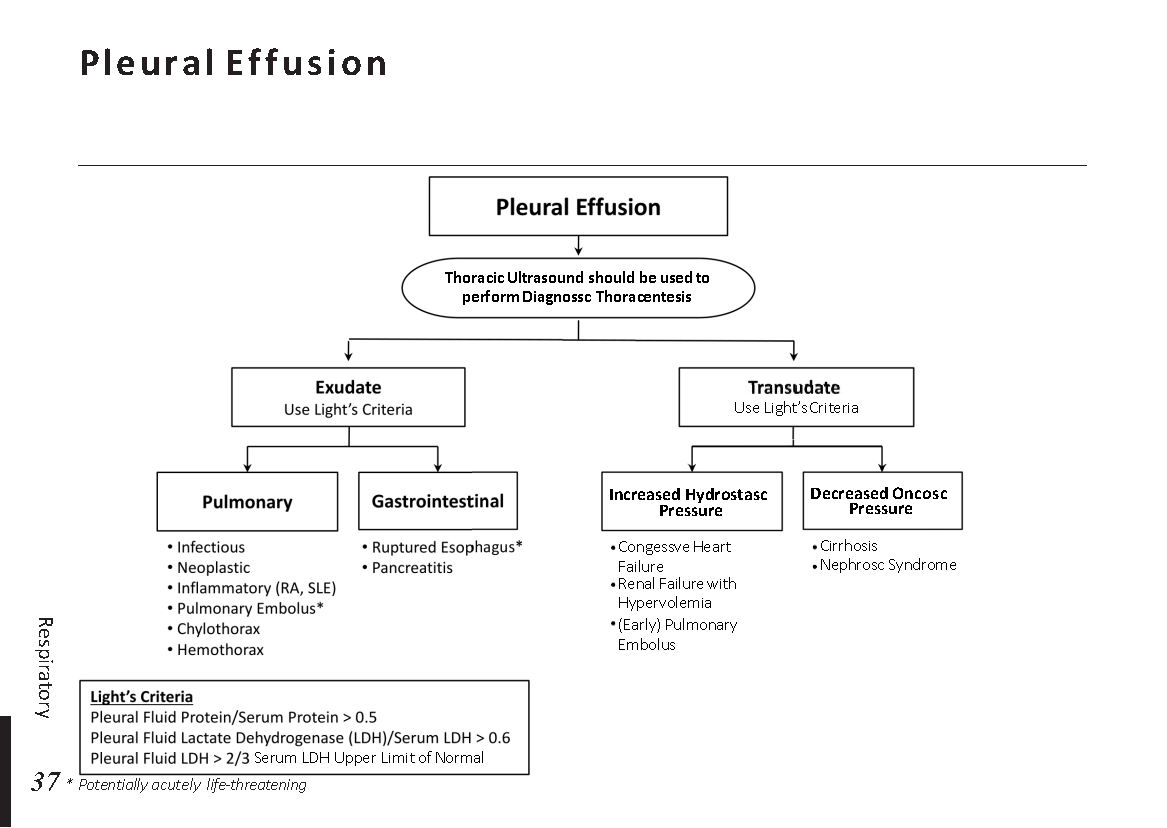
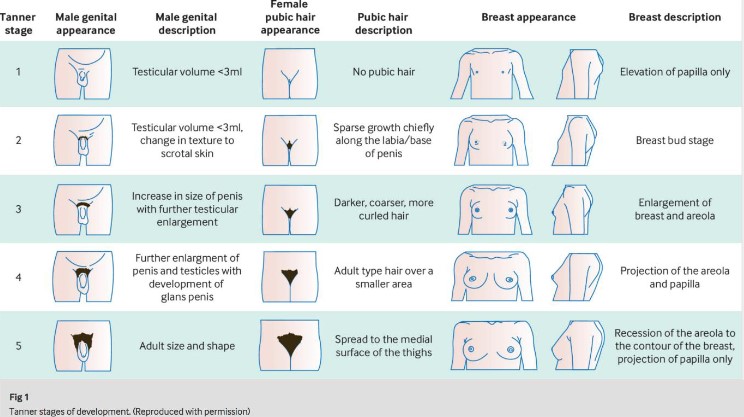
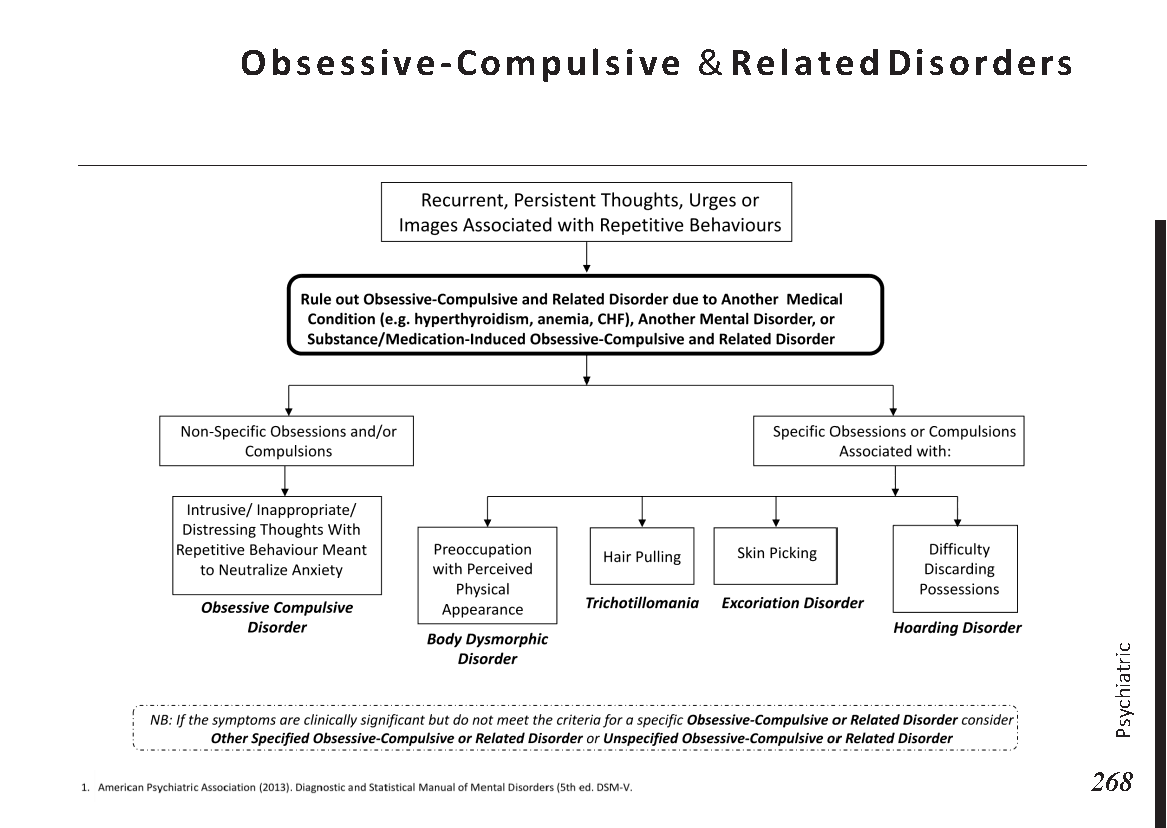
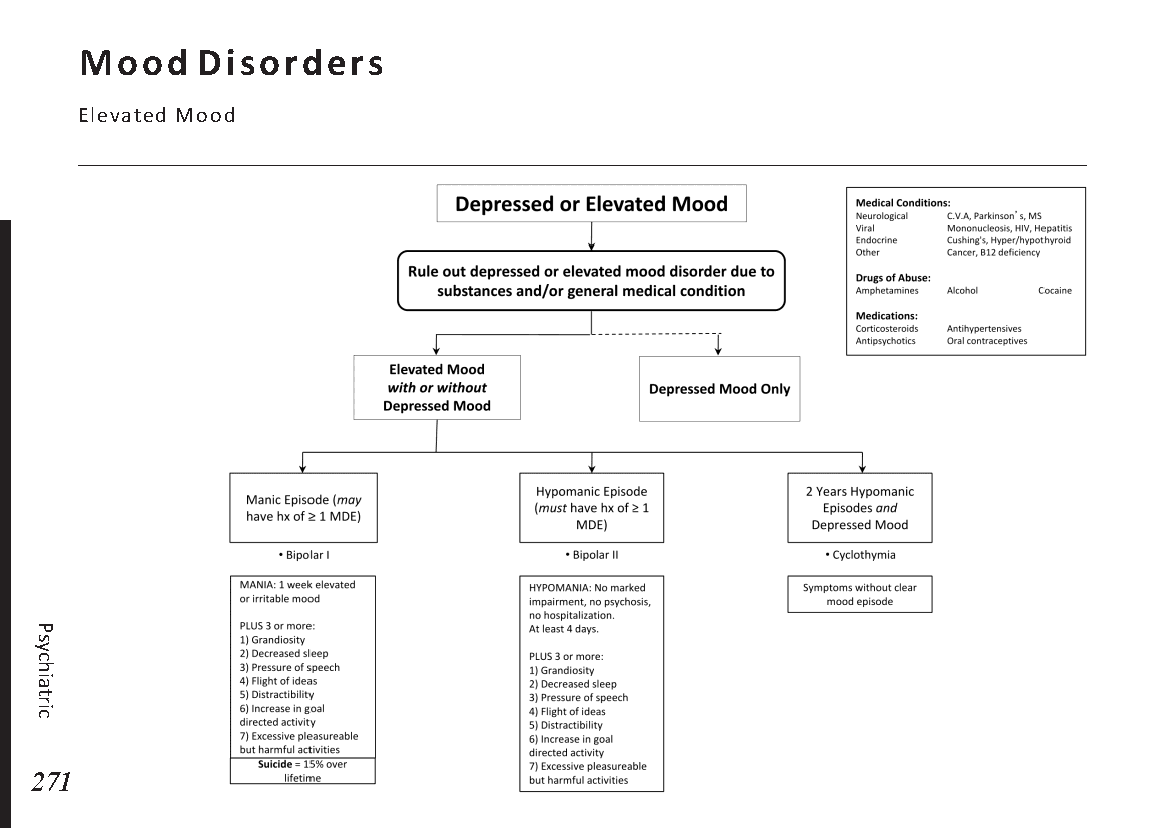
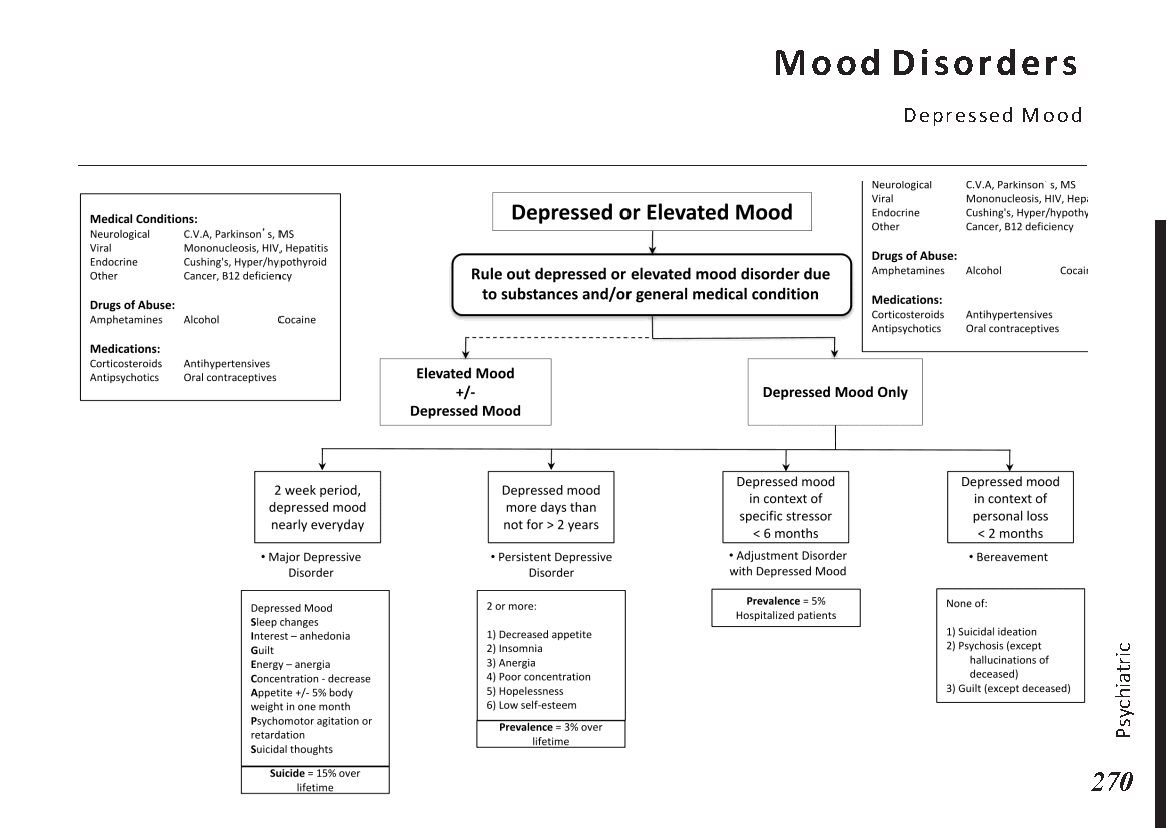
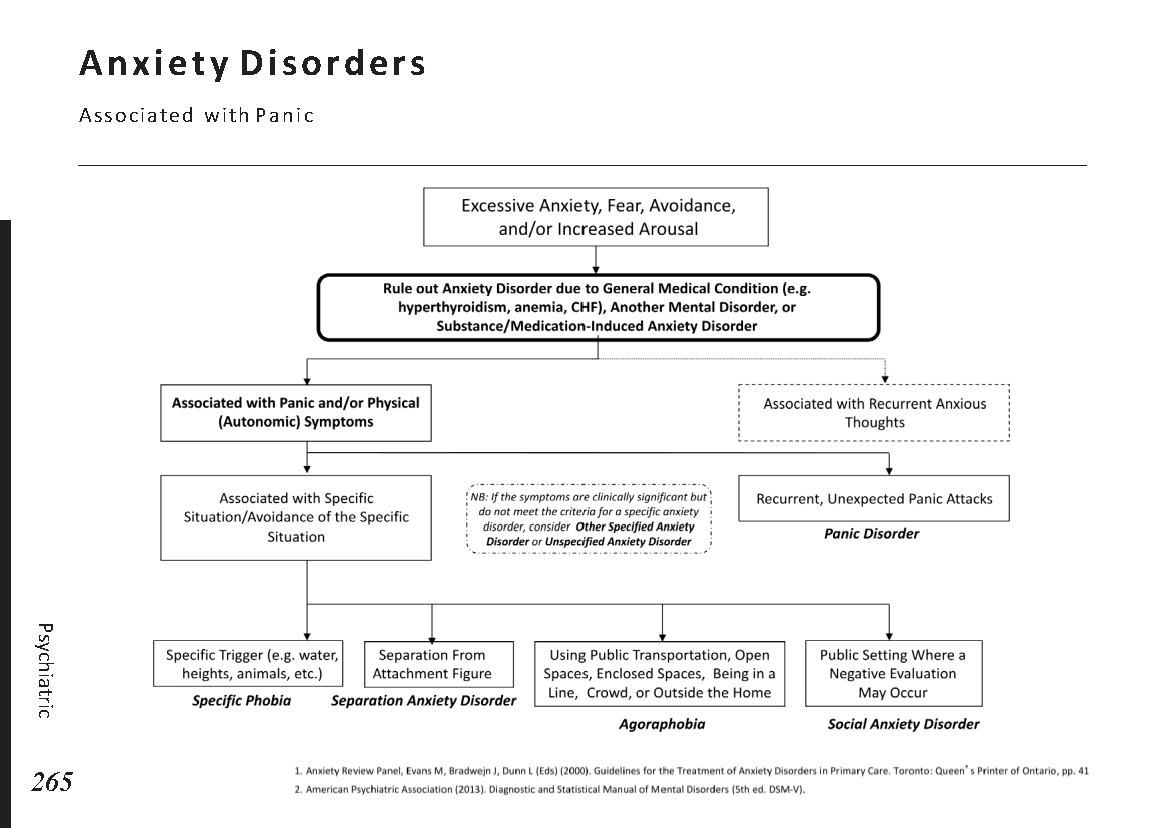
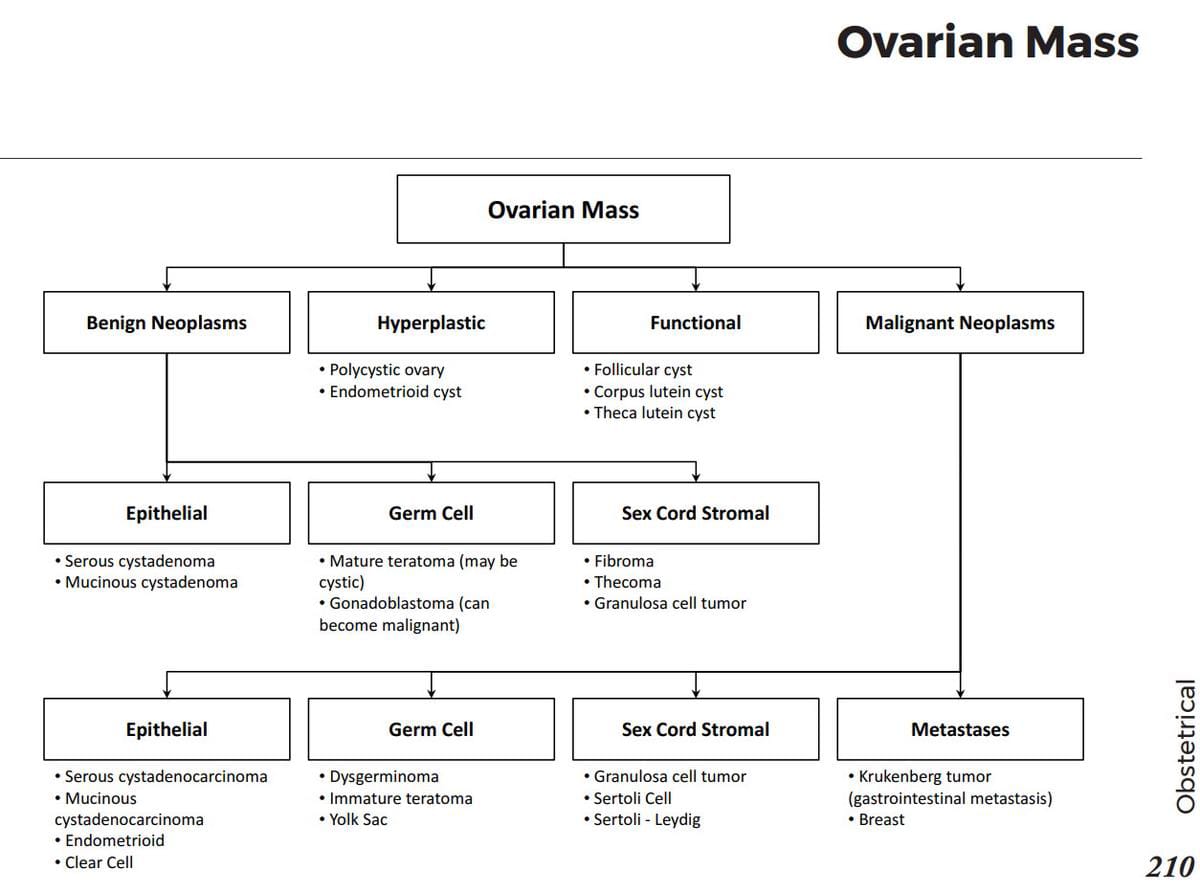
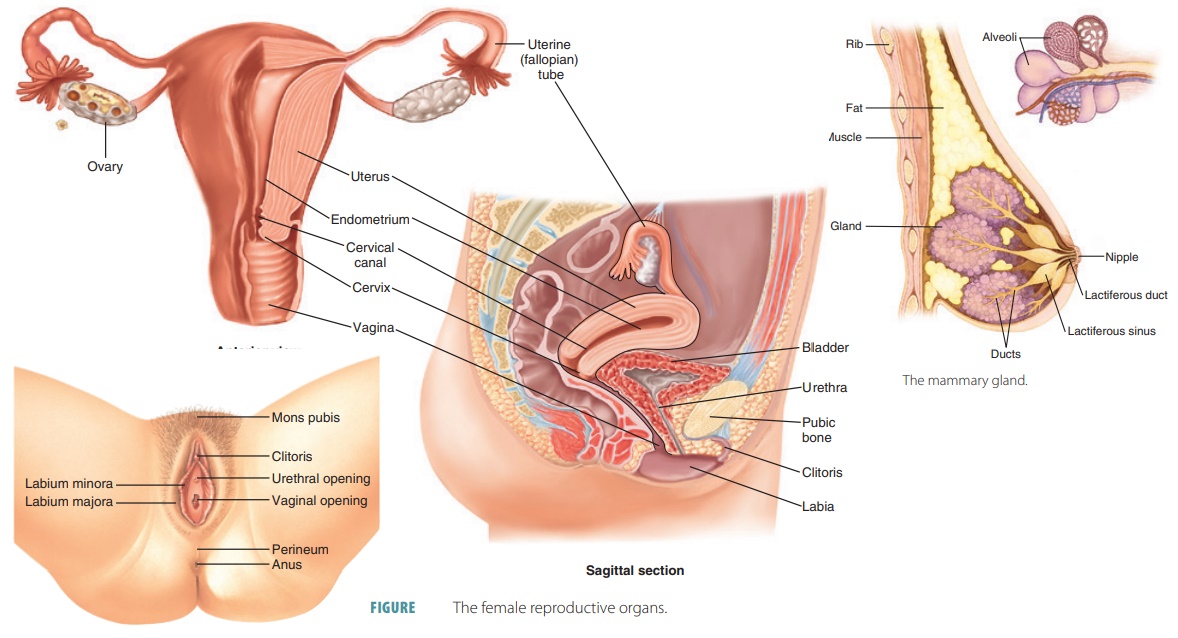
Female reproductive anatomy:
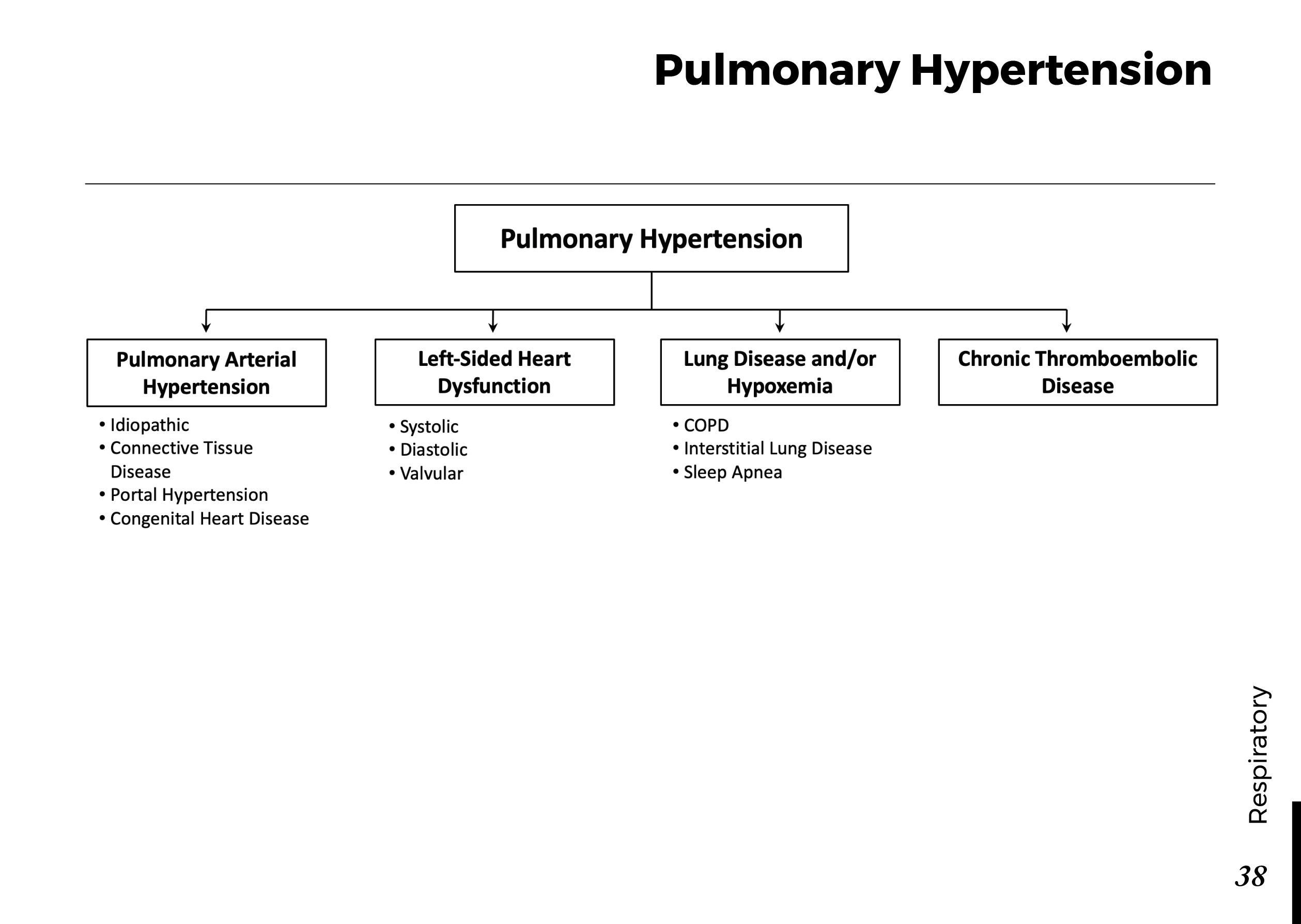
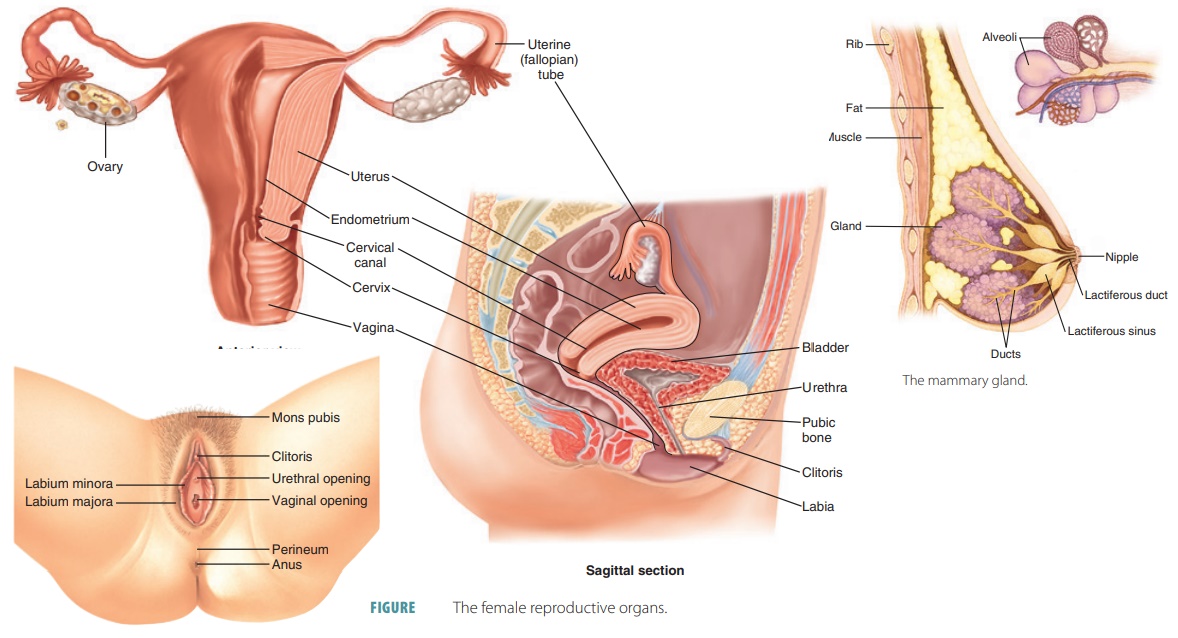 Menstrual cycle physiology:
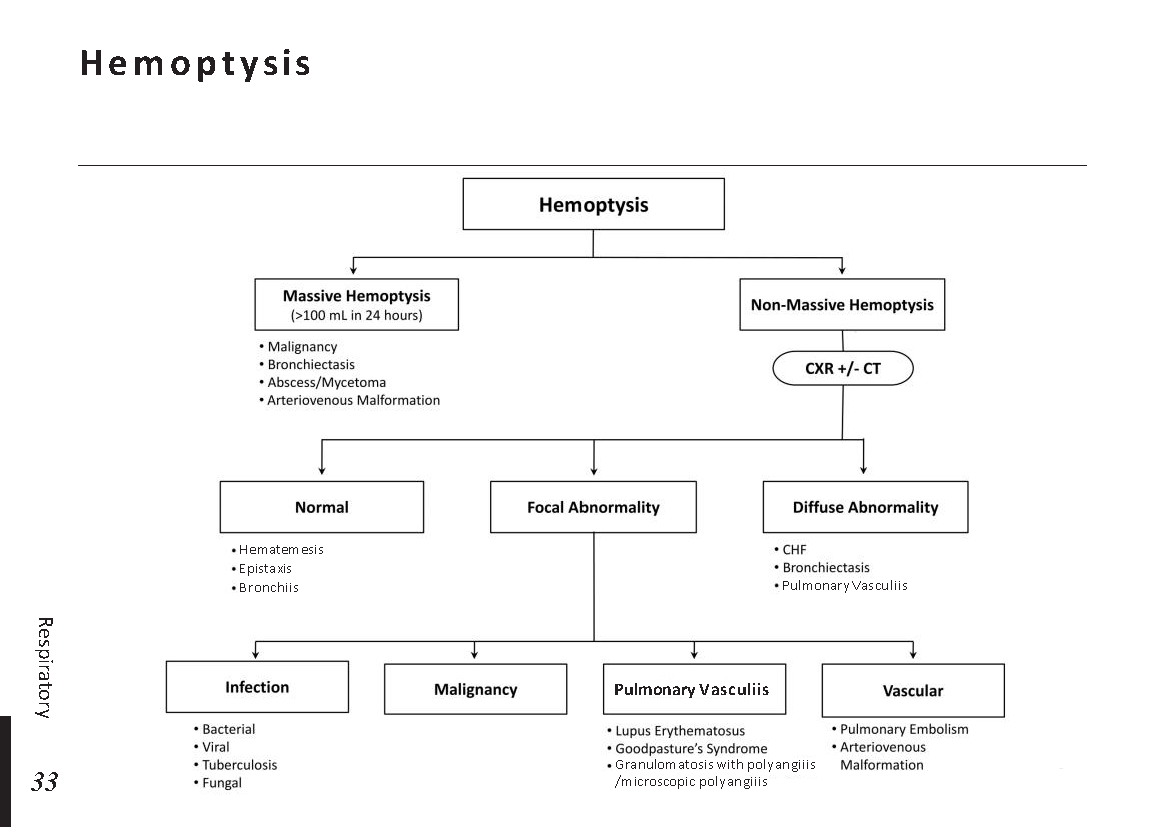
Menstrual cycle physiology:

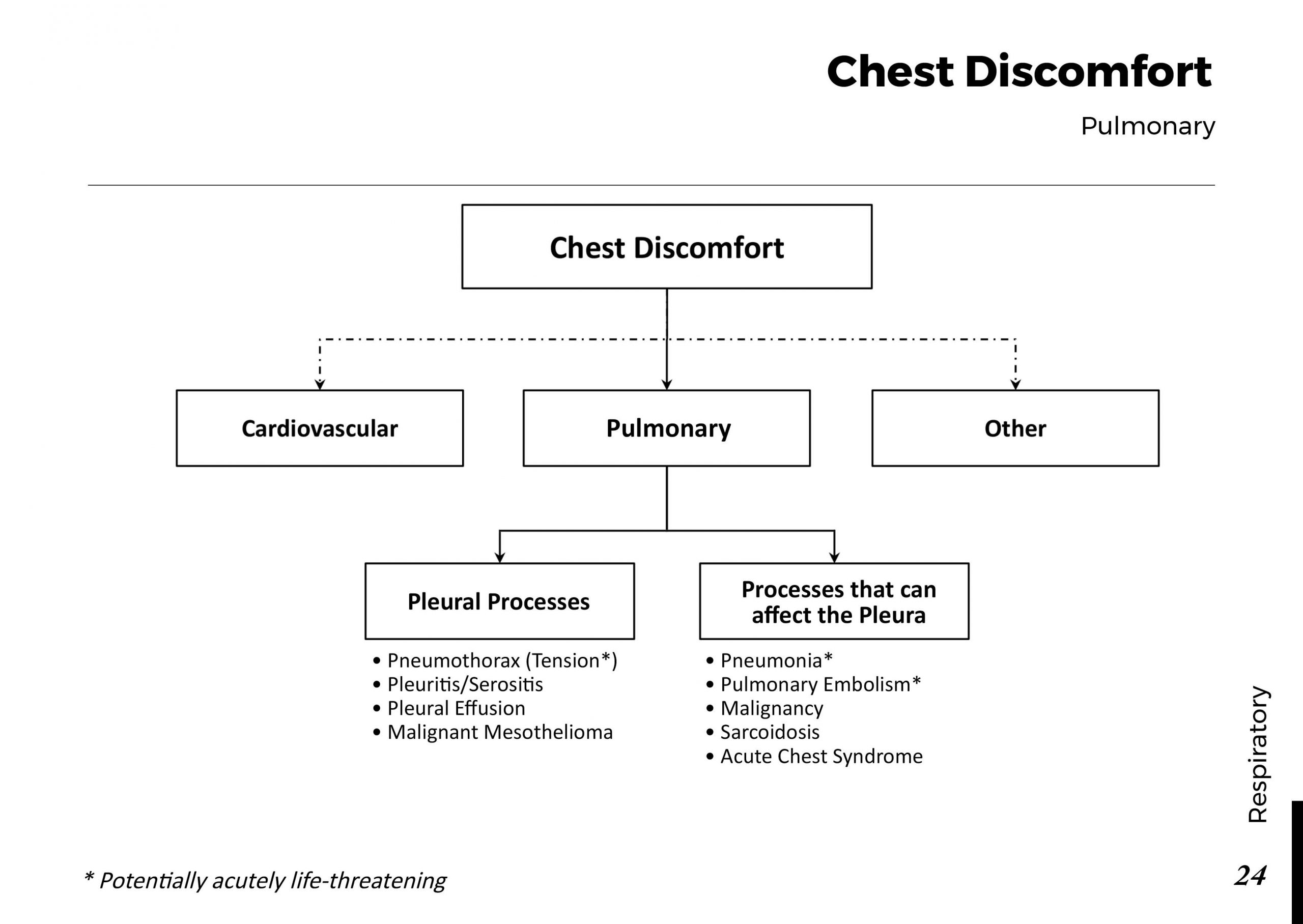
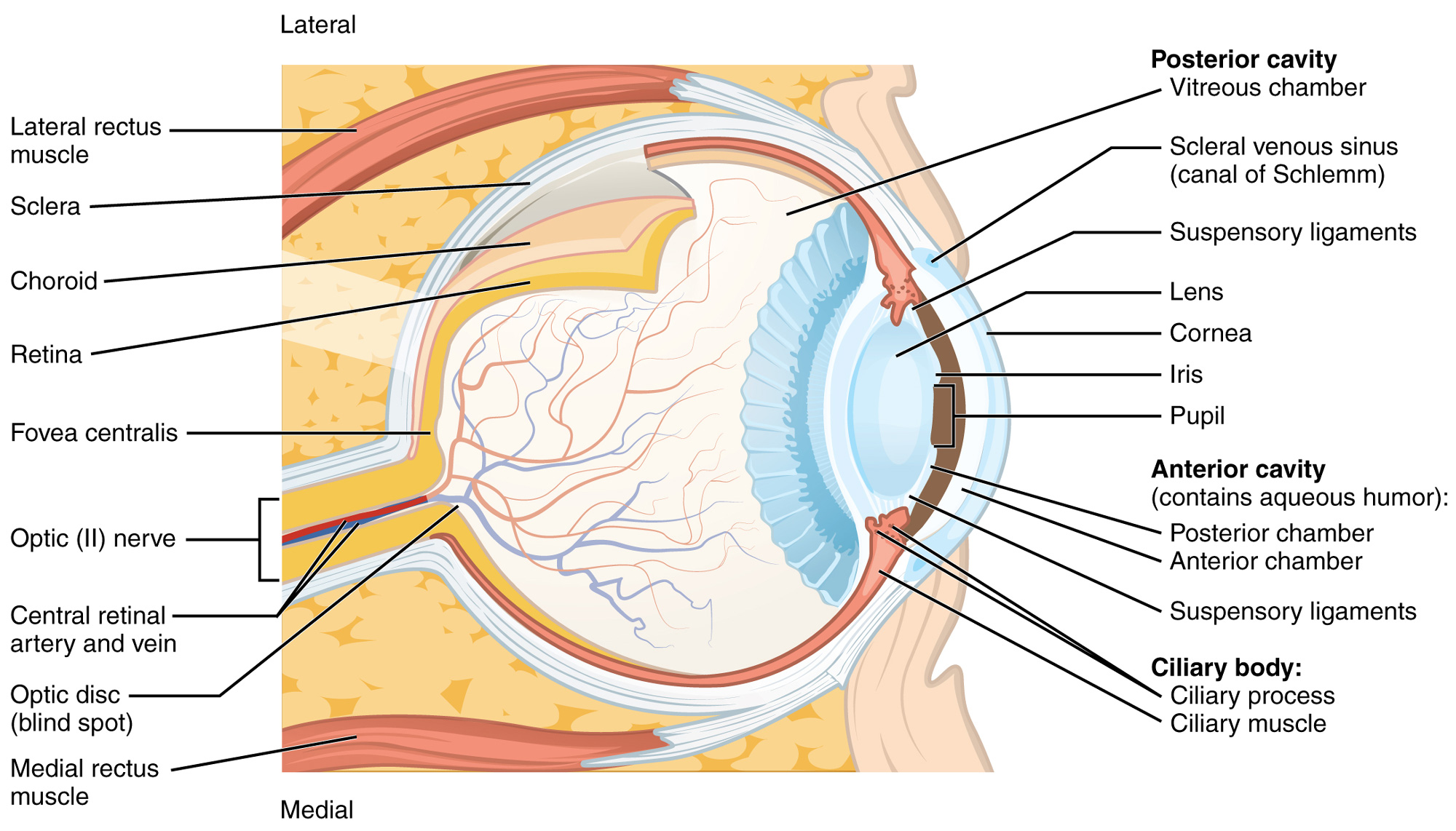
Eye anatomy:
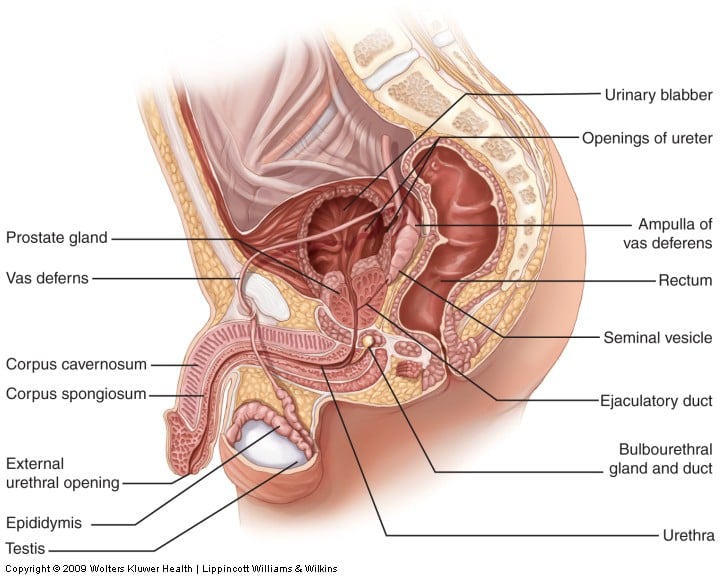
Male reproductive system anatomy:
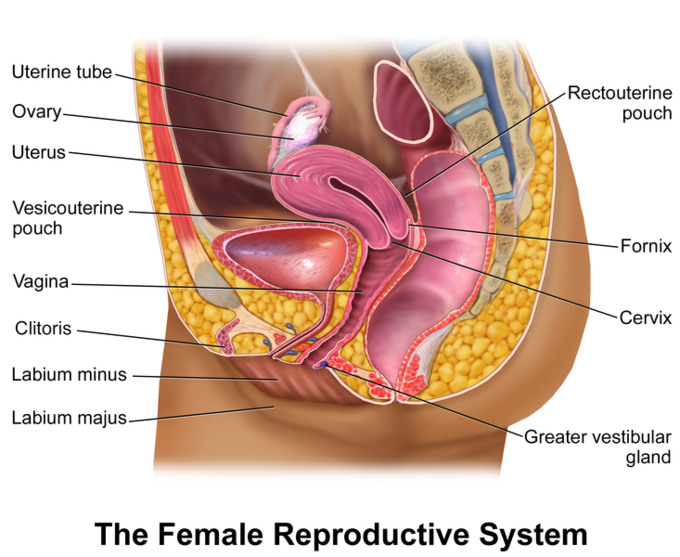
Female reproductive system anatomy:
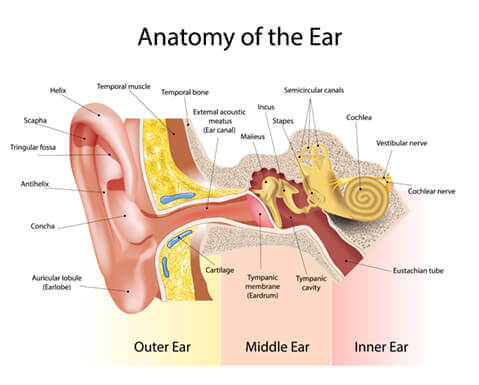
Ear anatomy:
Sinuses anatomy:

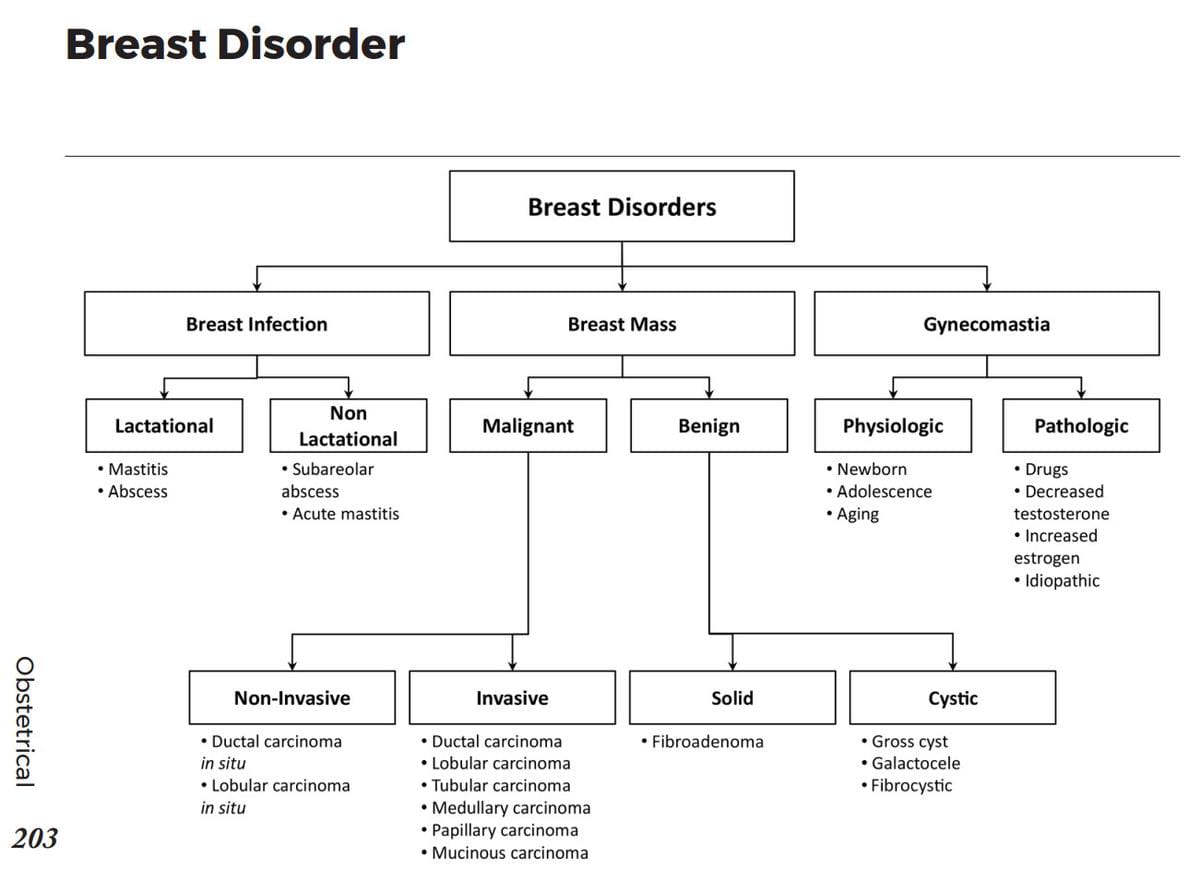
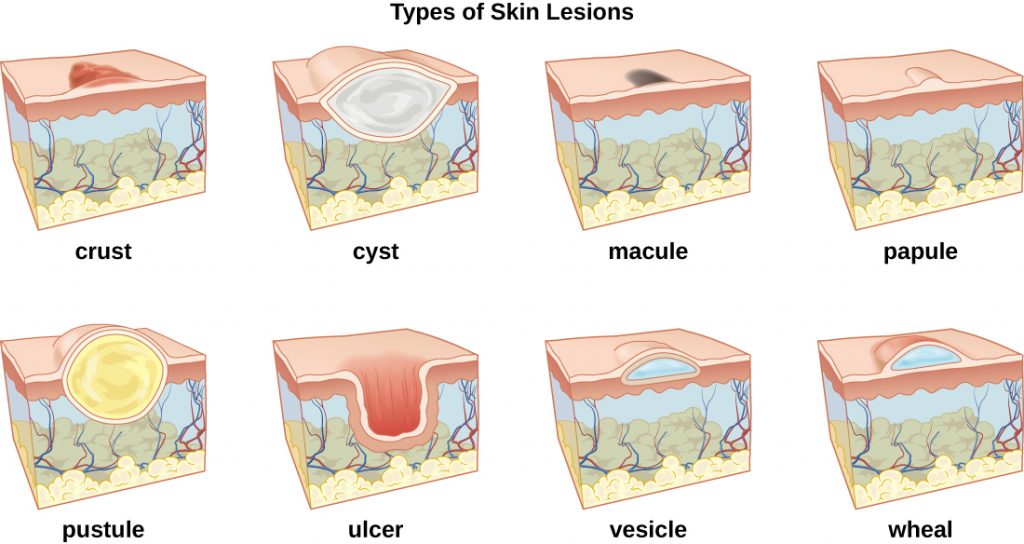
Common skin lesions:
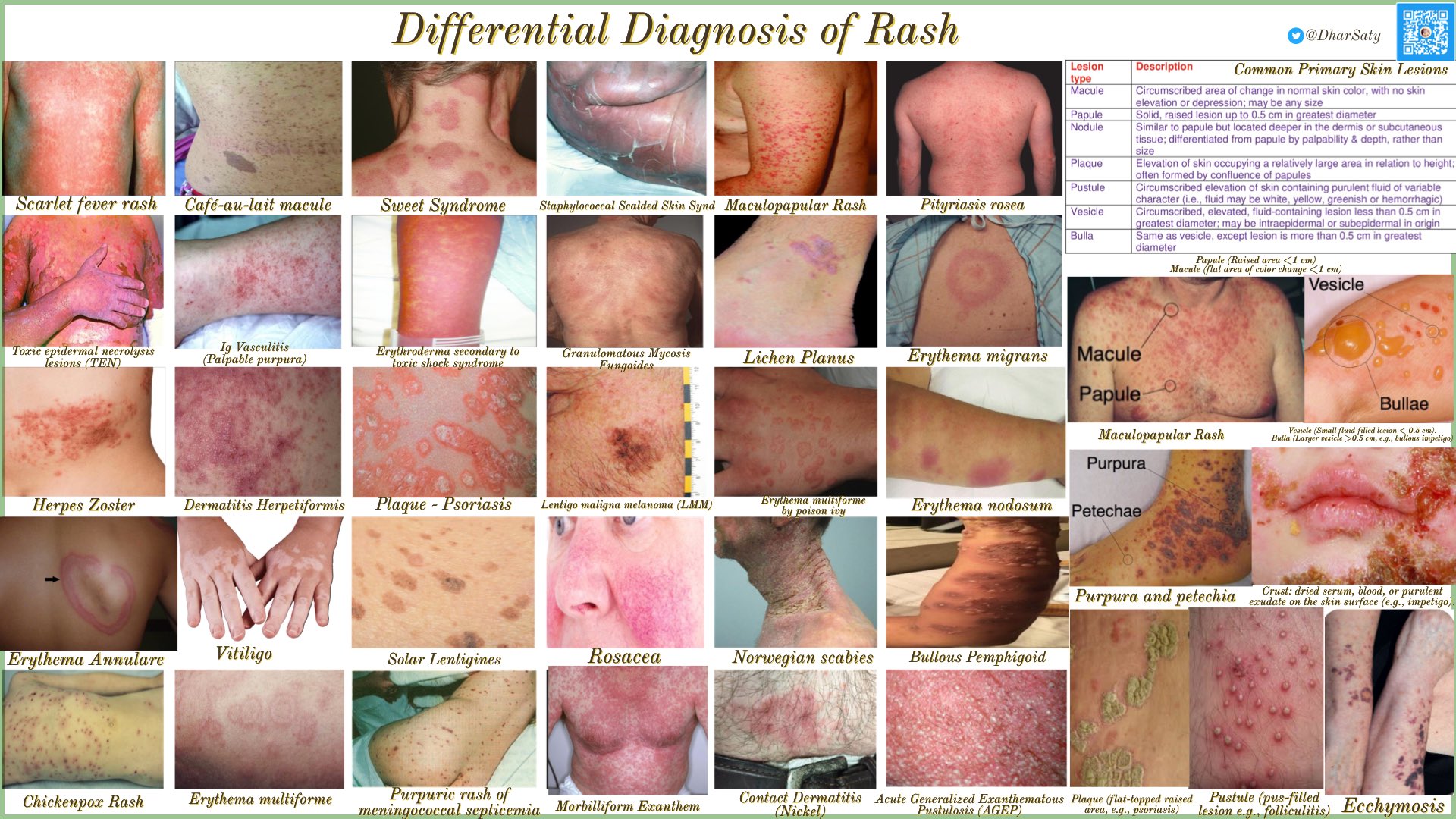
Common skin rashes:
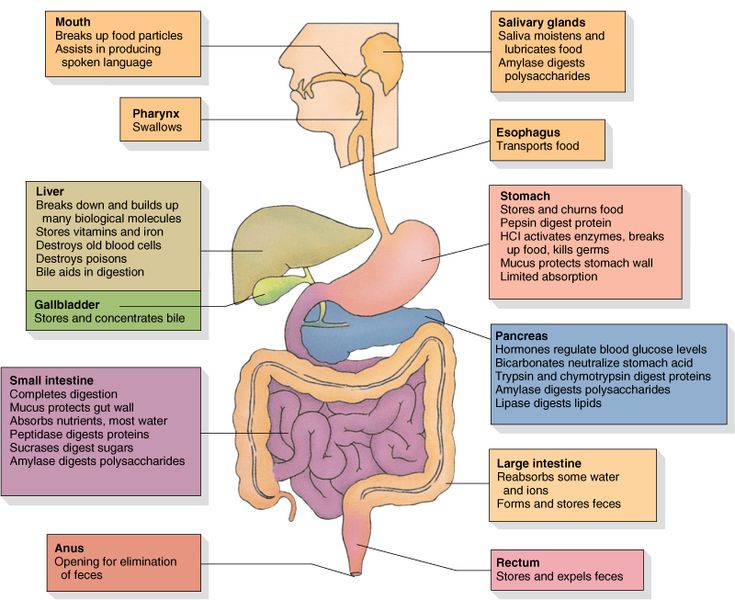
Digestive process and key enzymes:
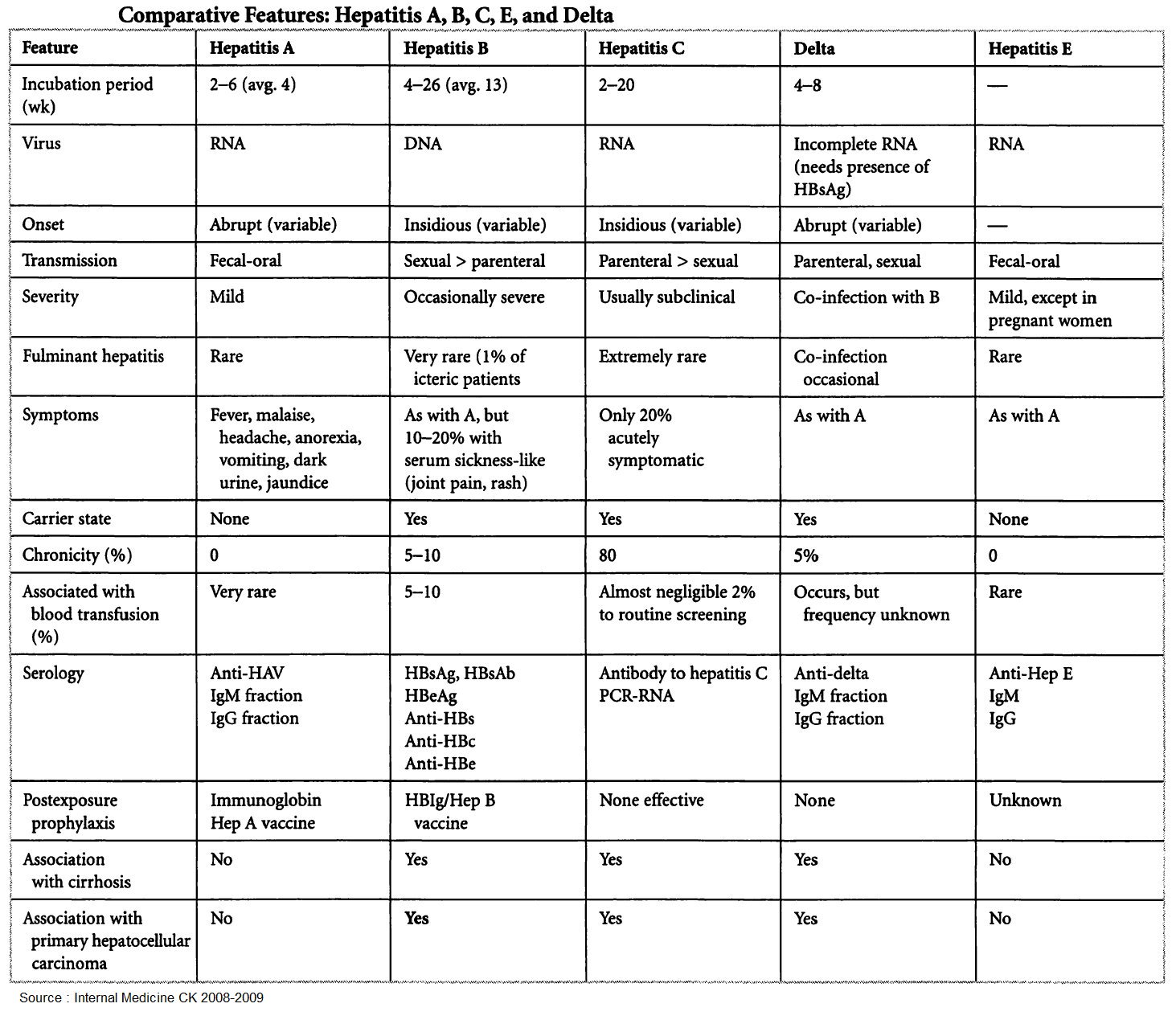
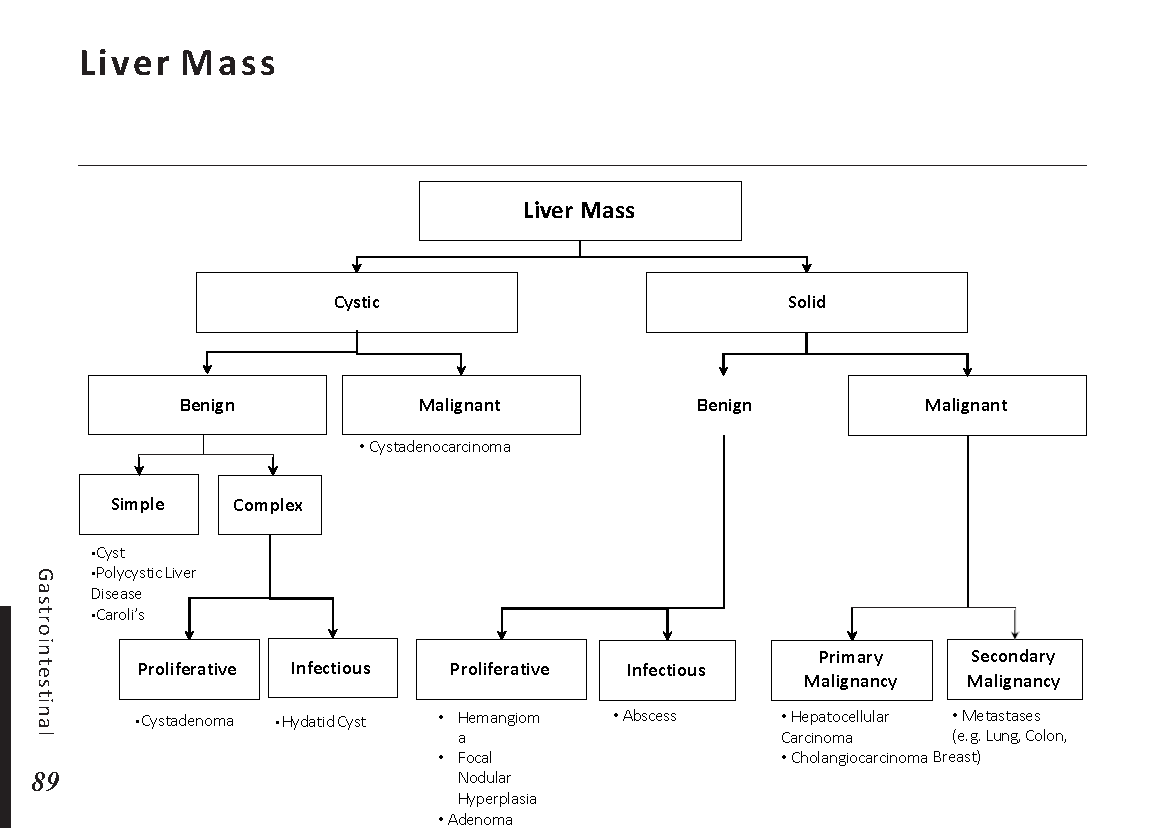
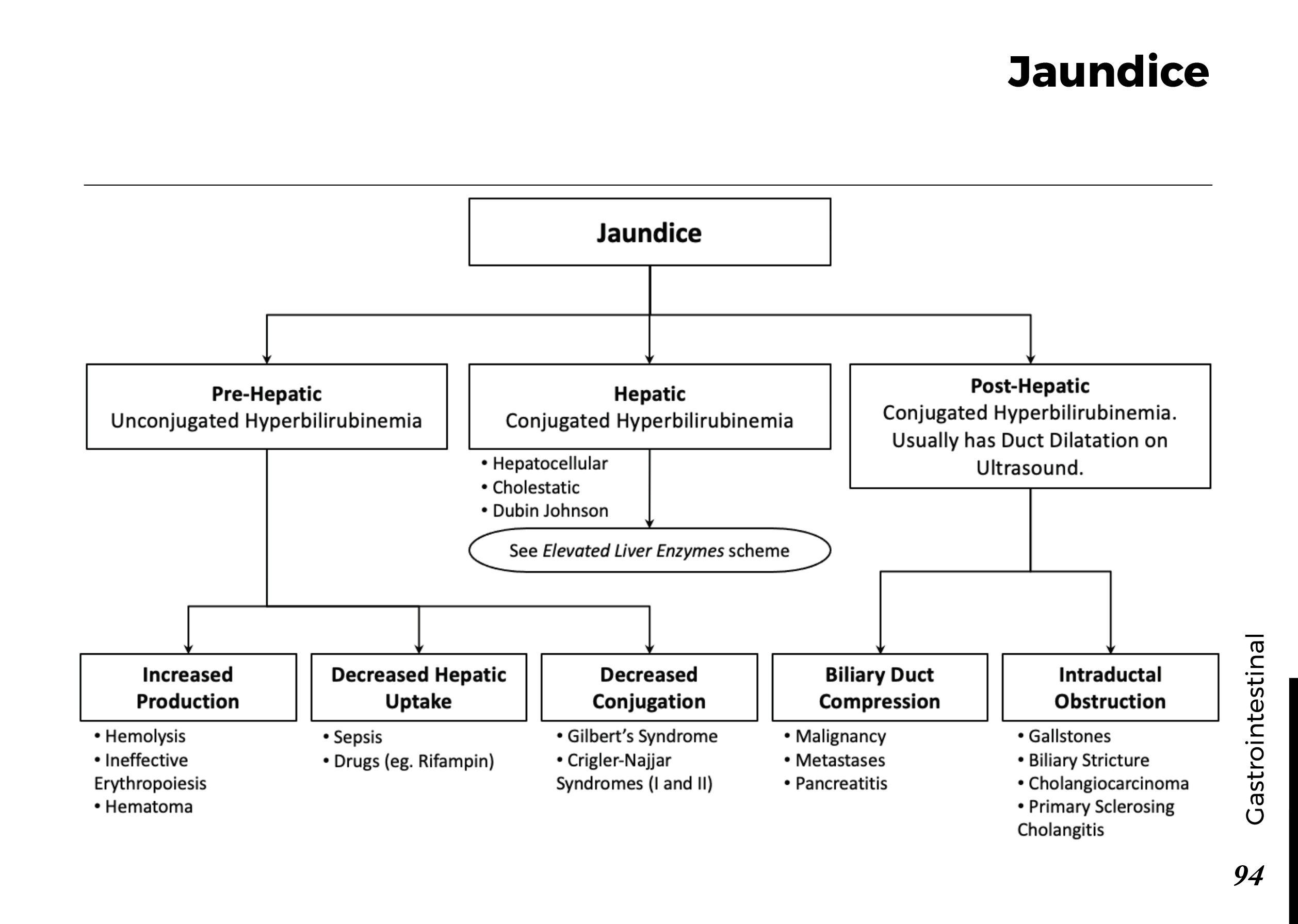
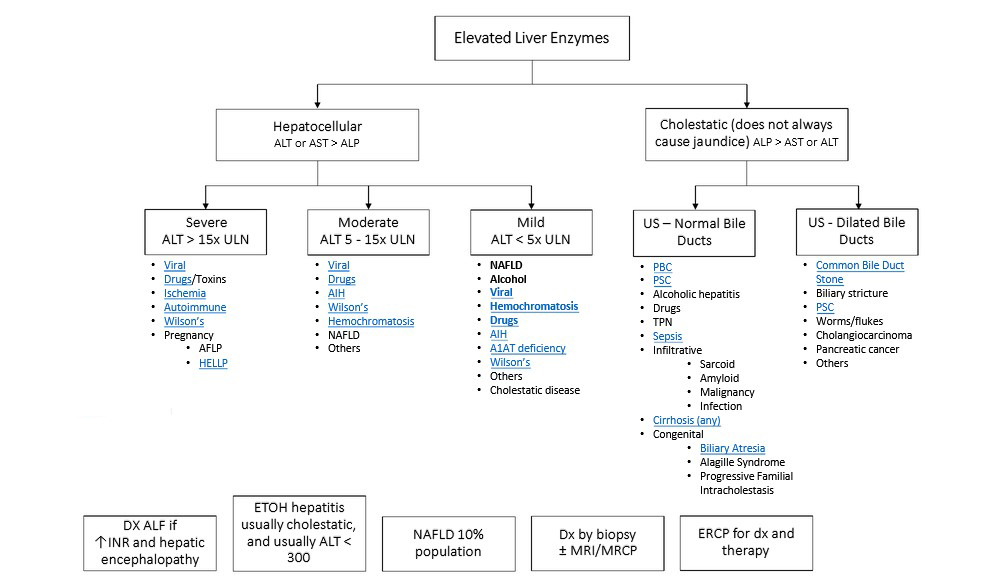
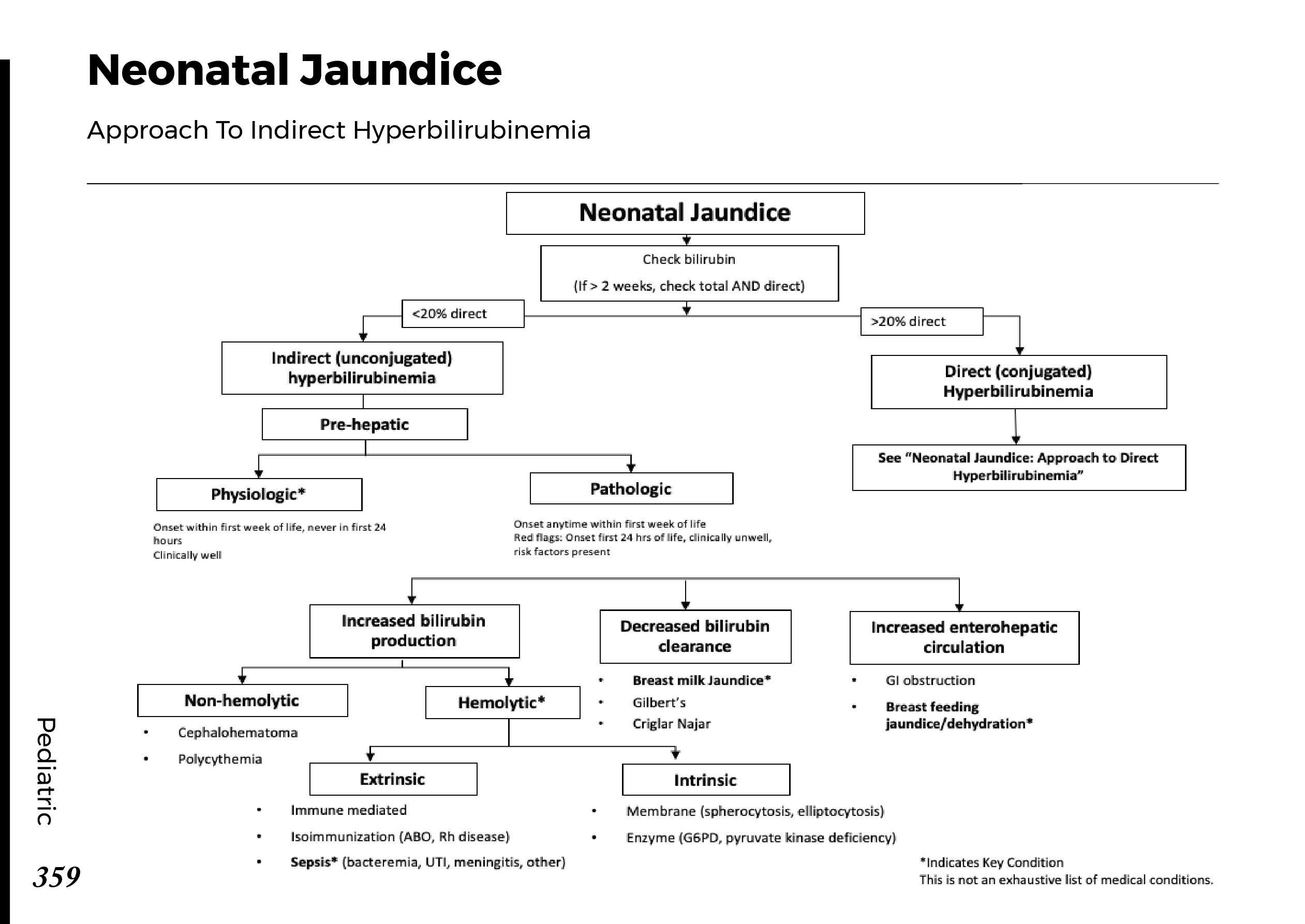
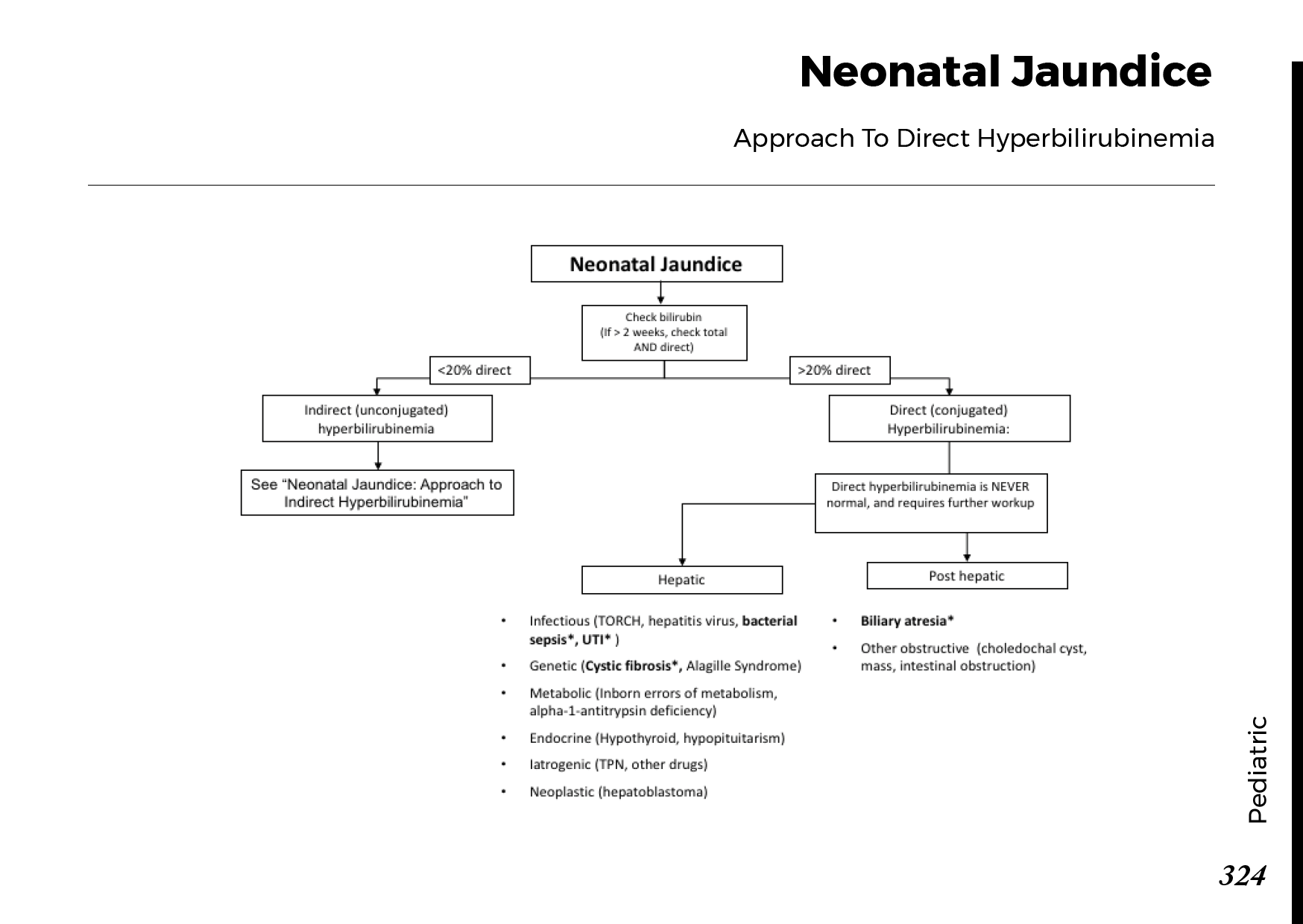
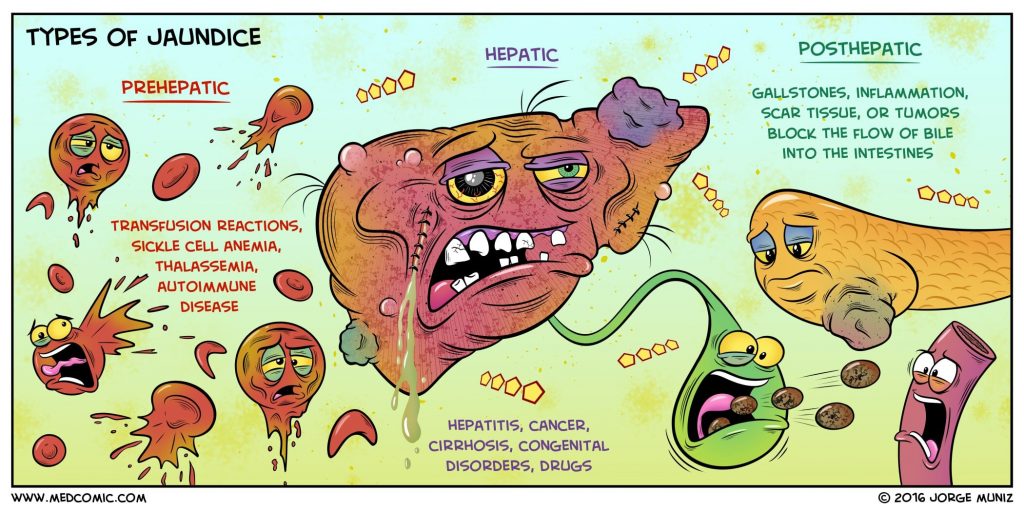
Types of jaundice:
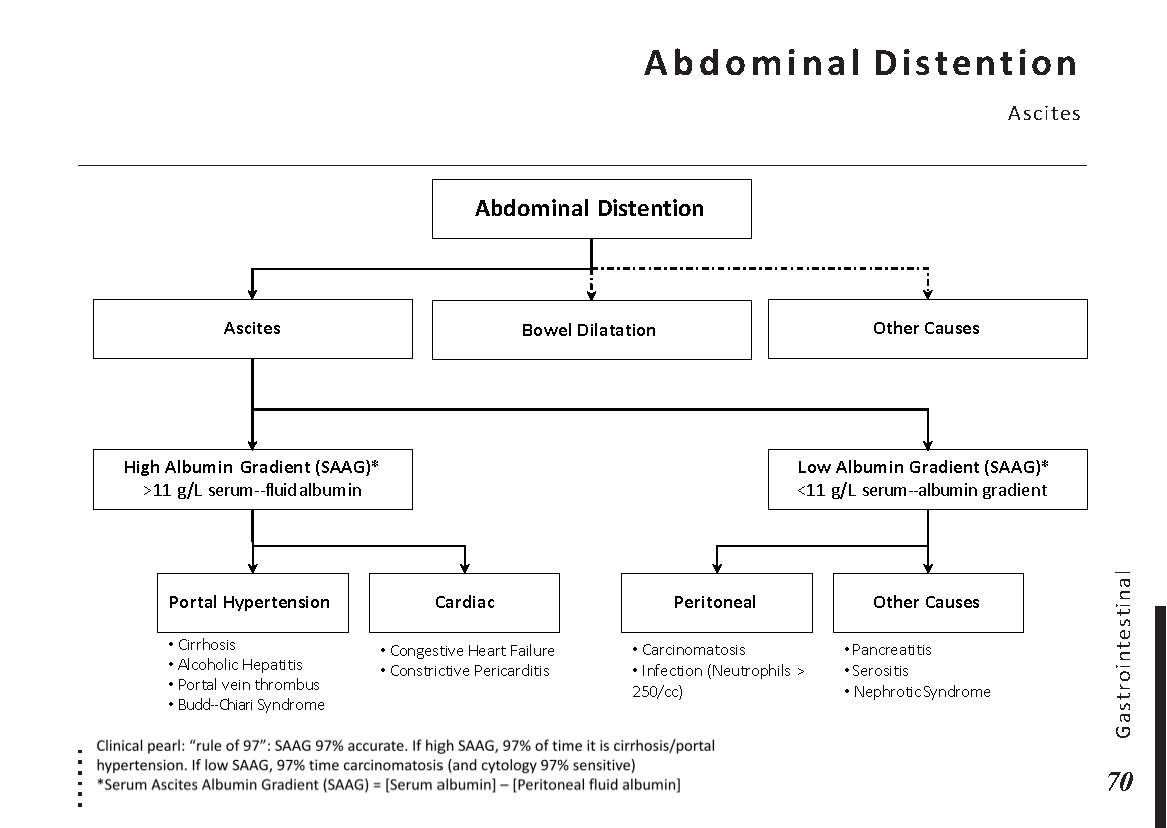
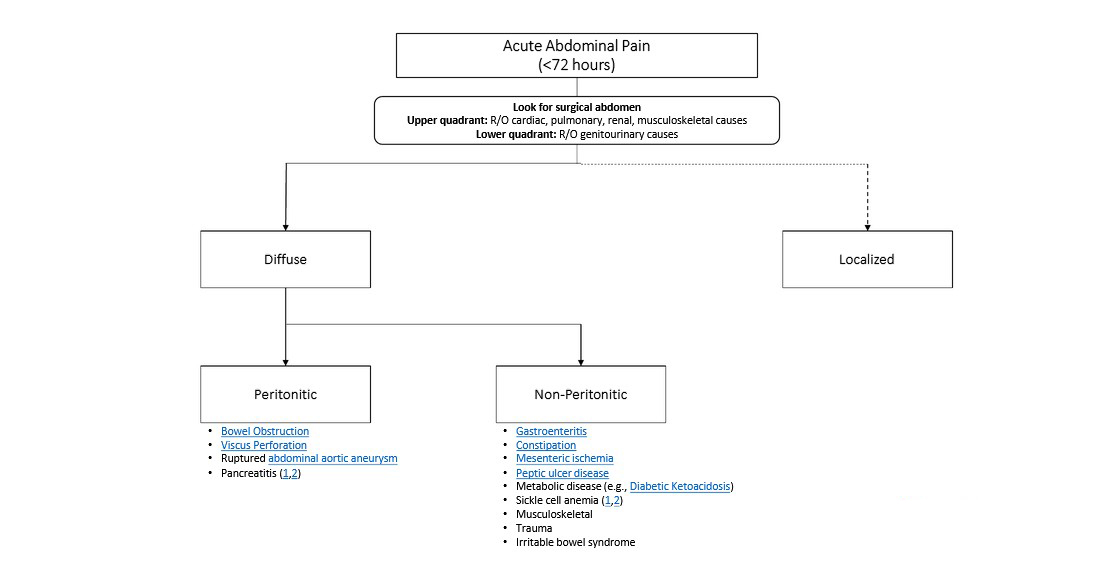
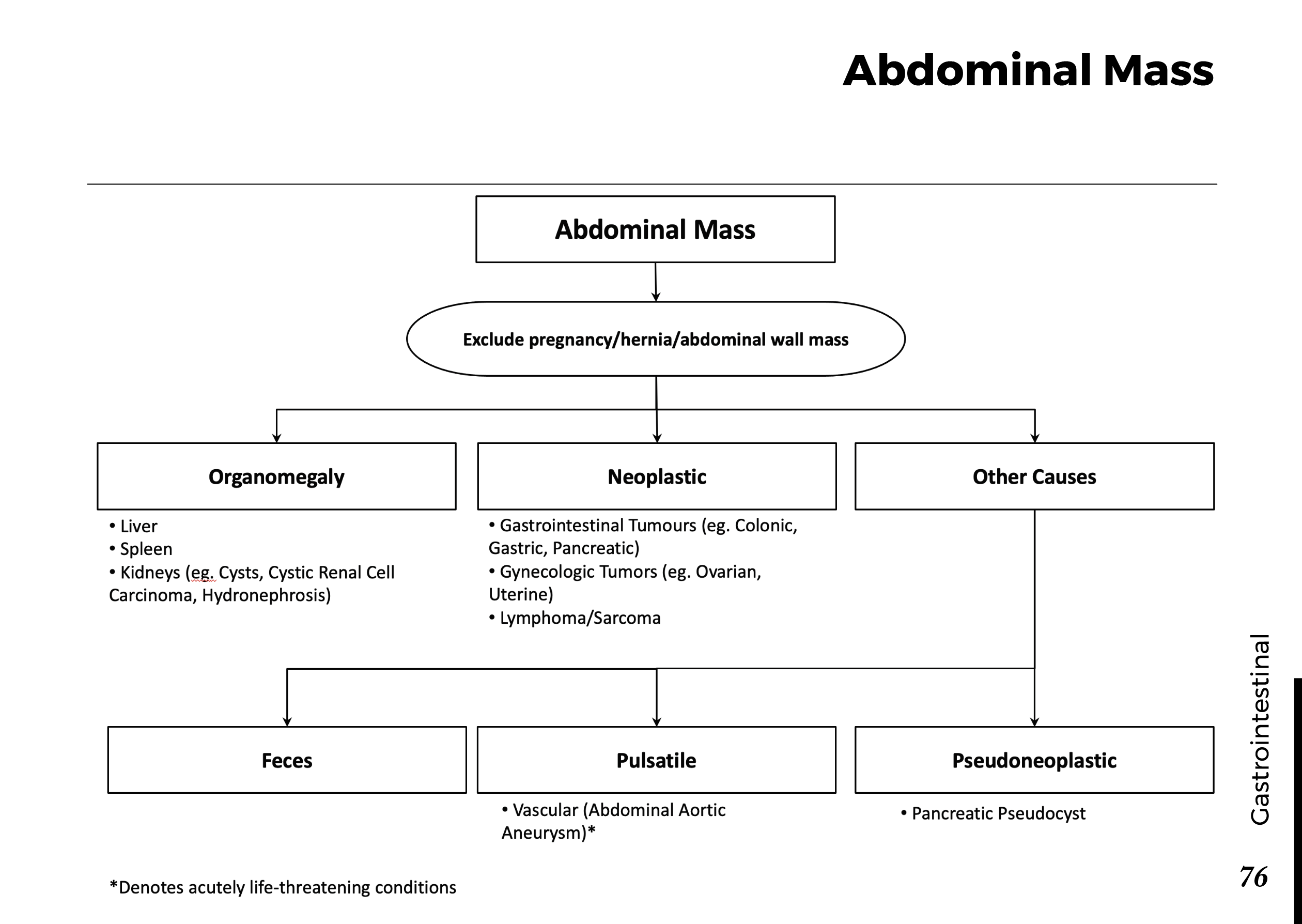
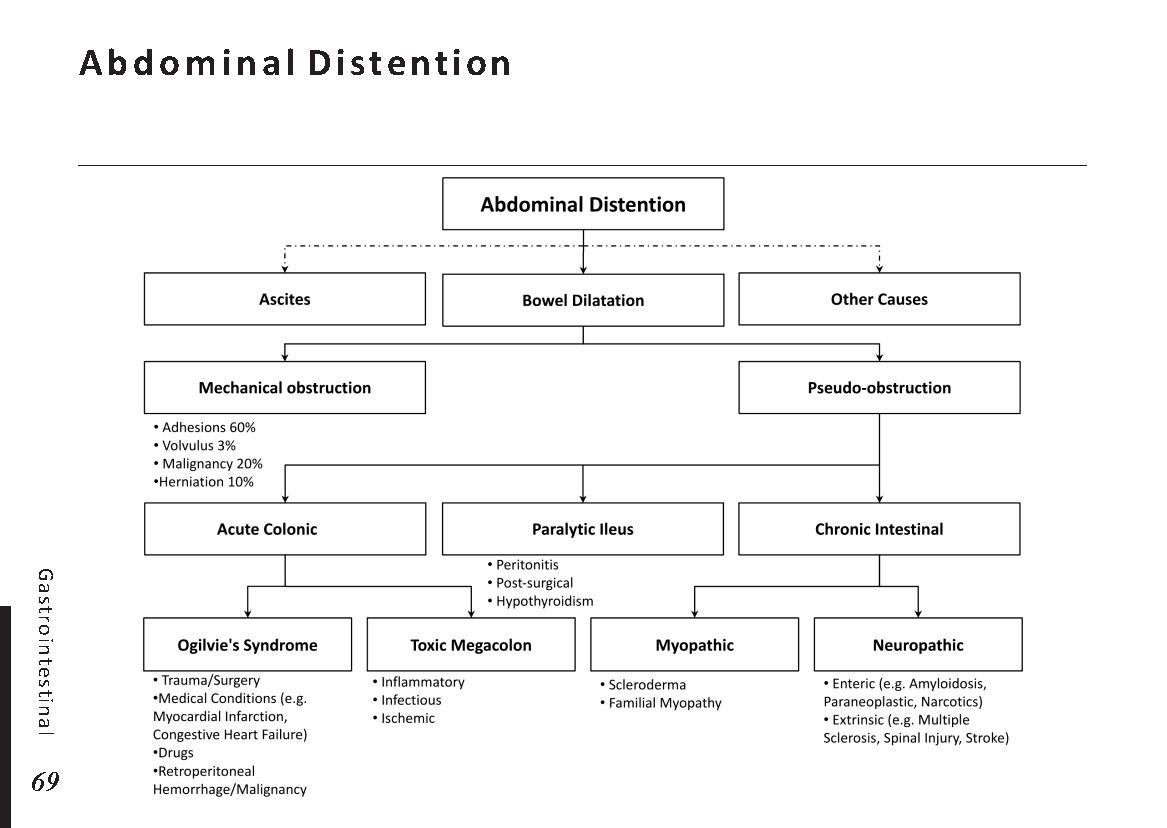
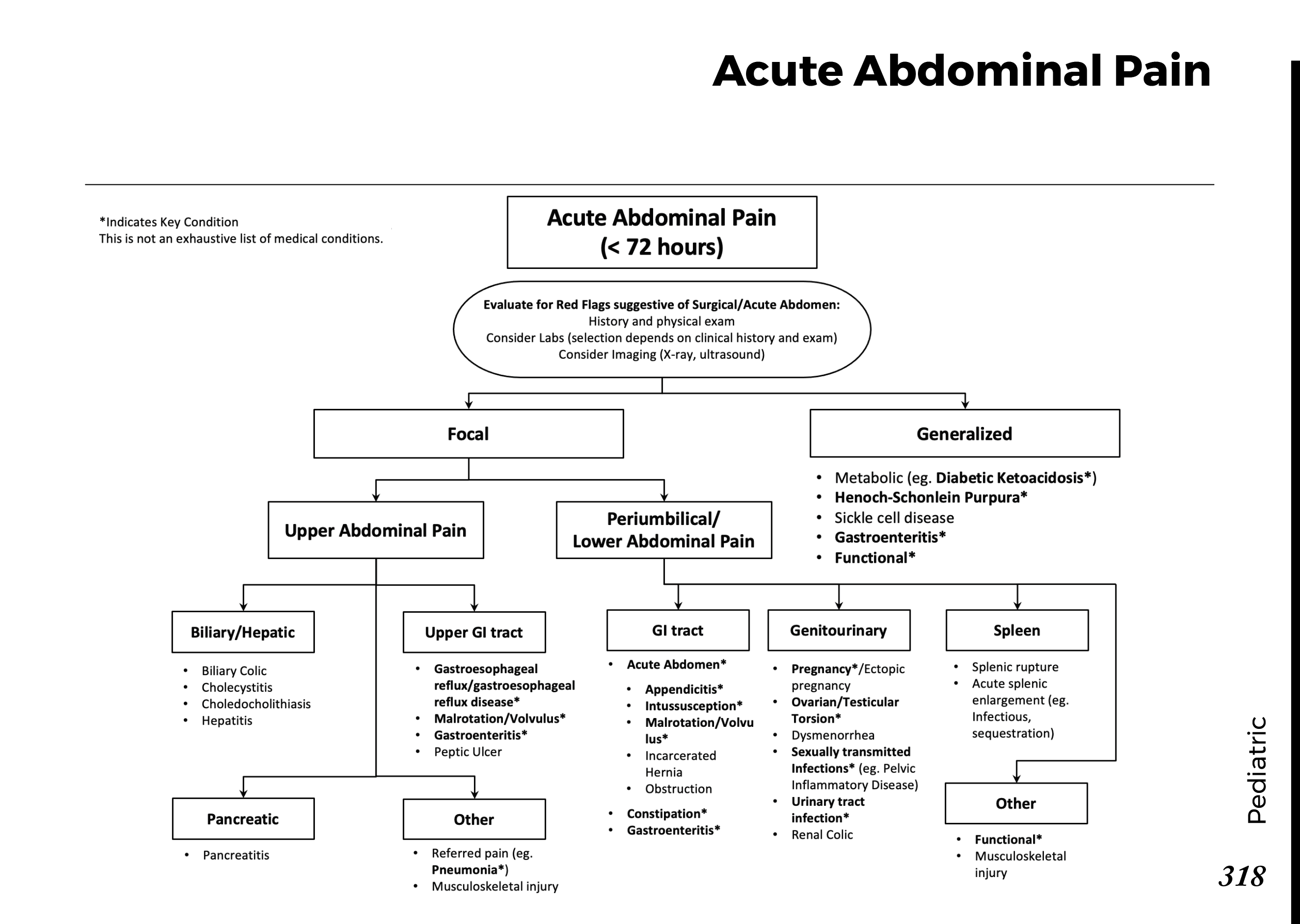
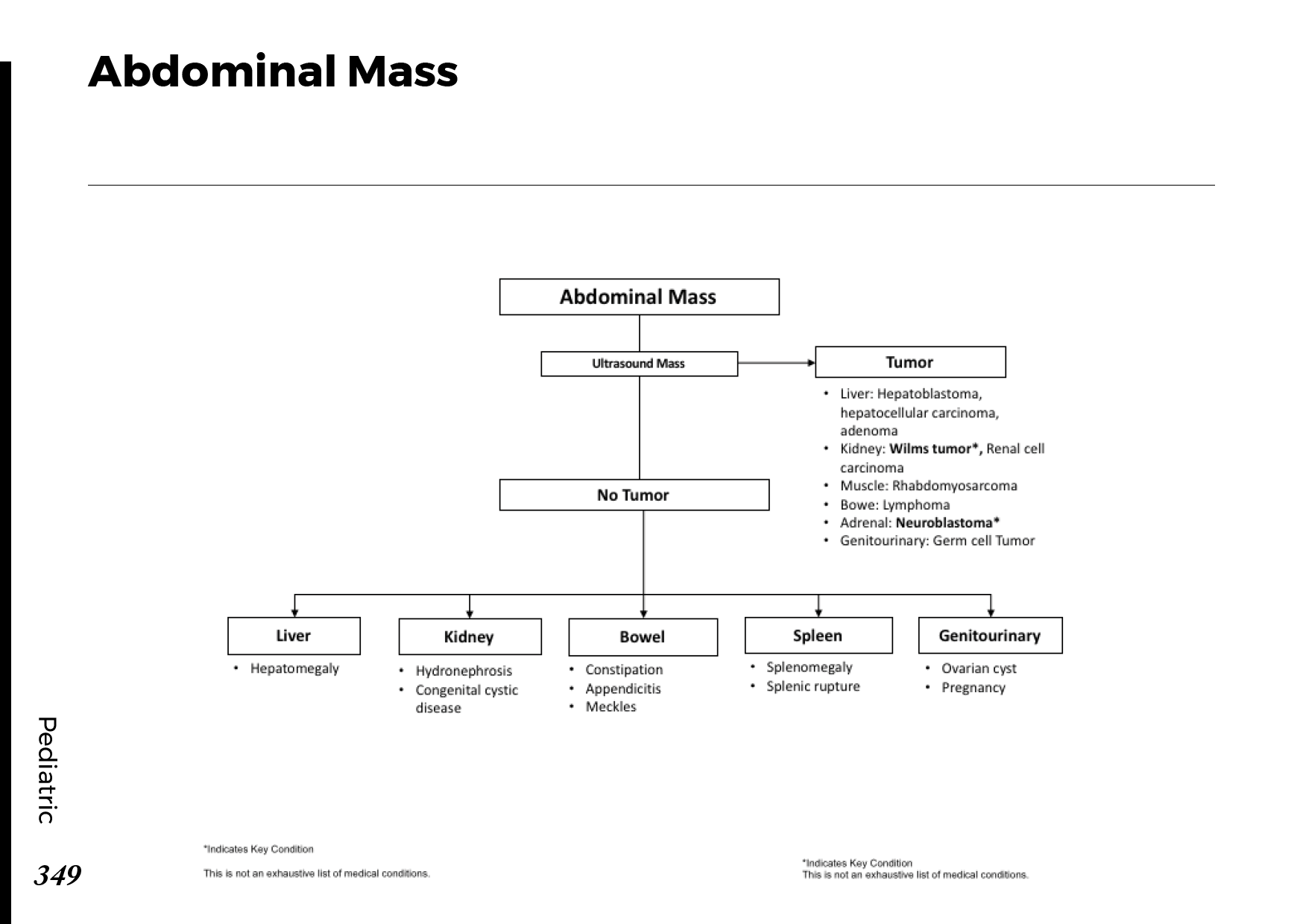
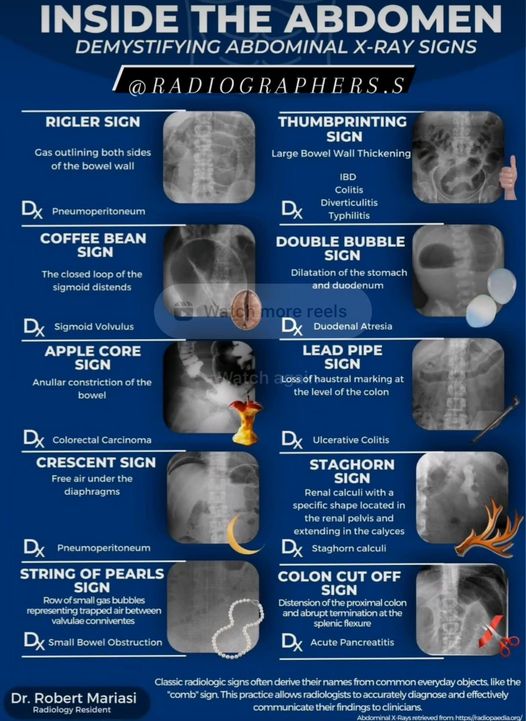
Common abdominal X-ray findings:
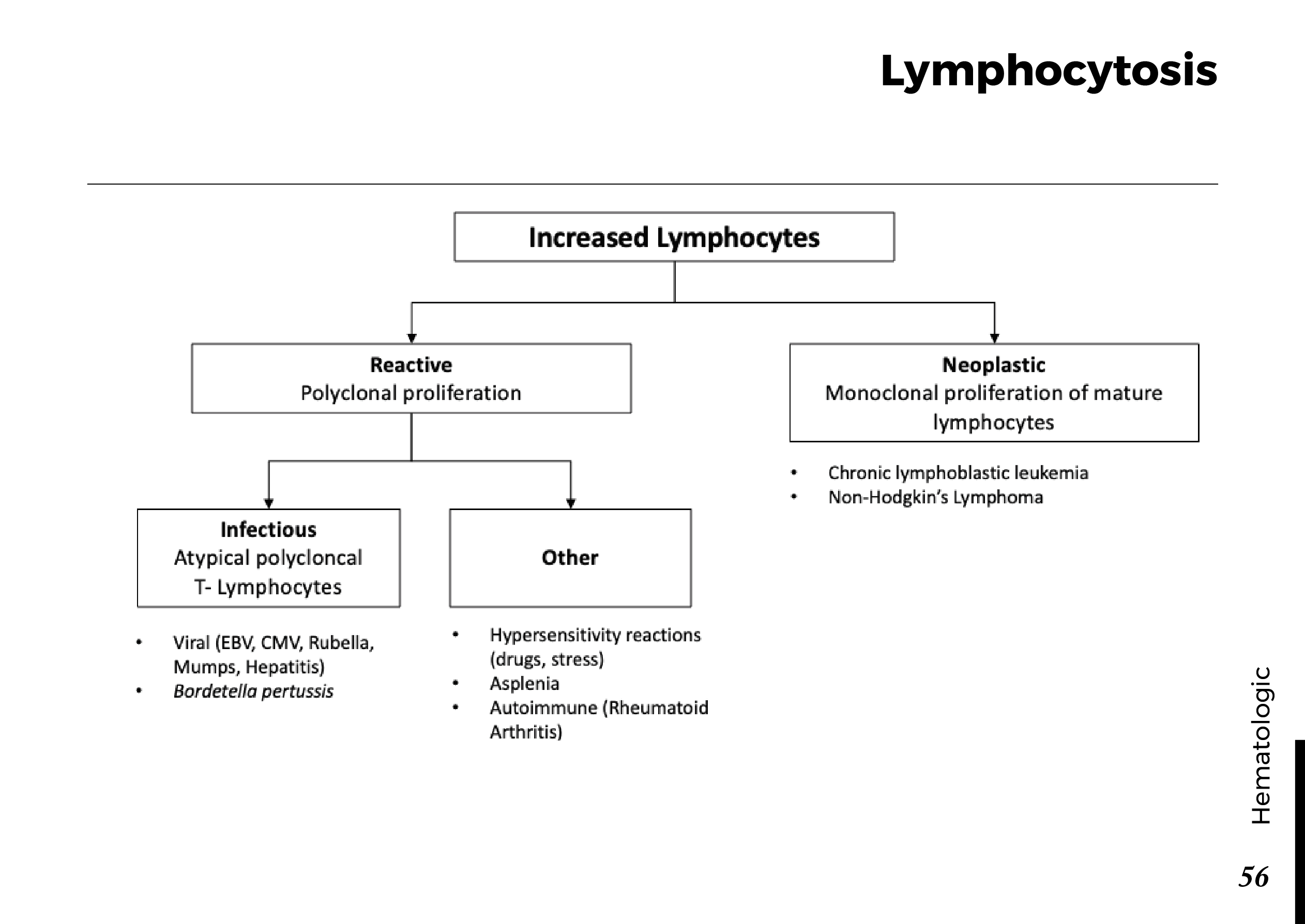
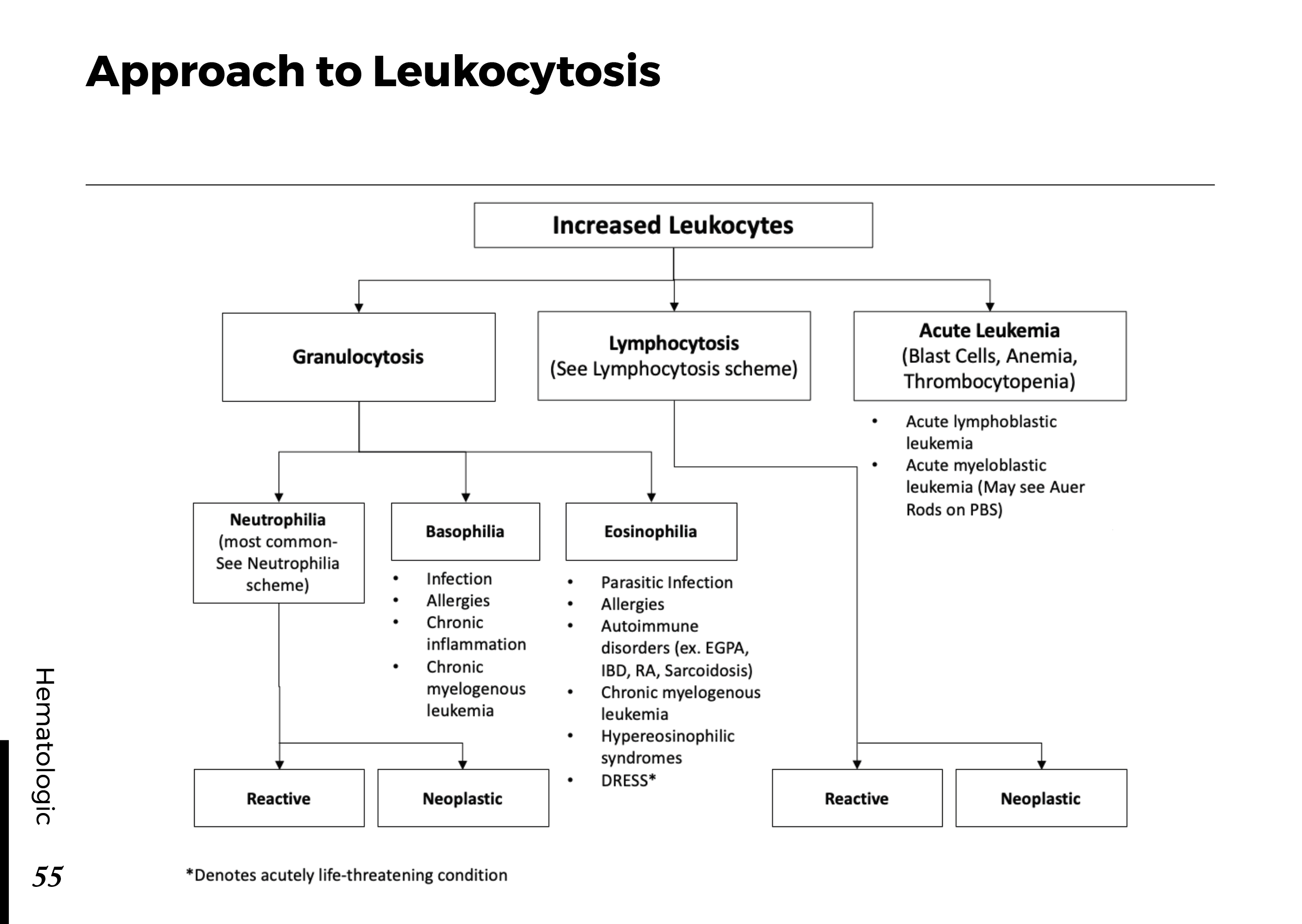
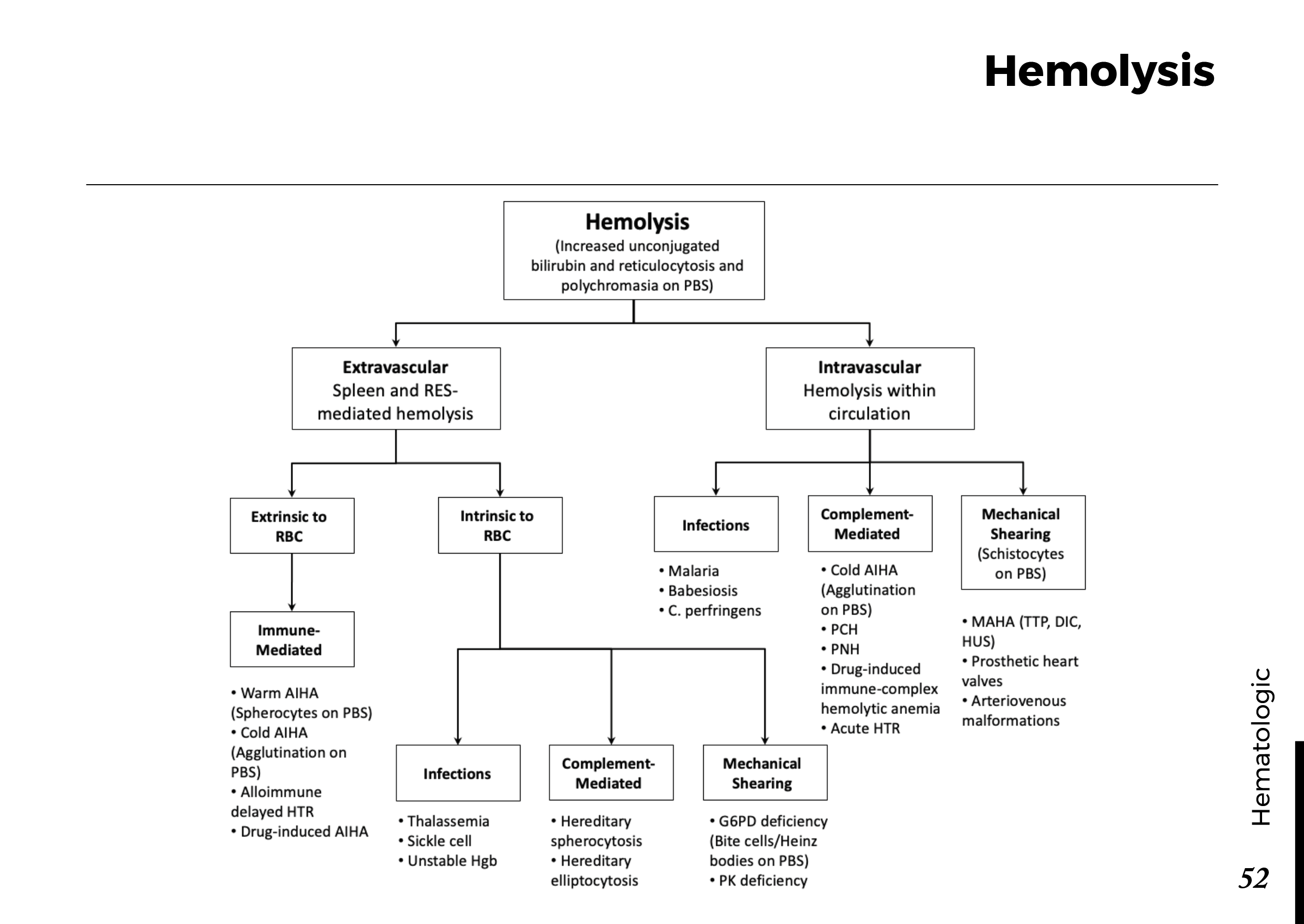
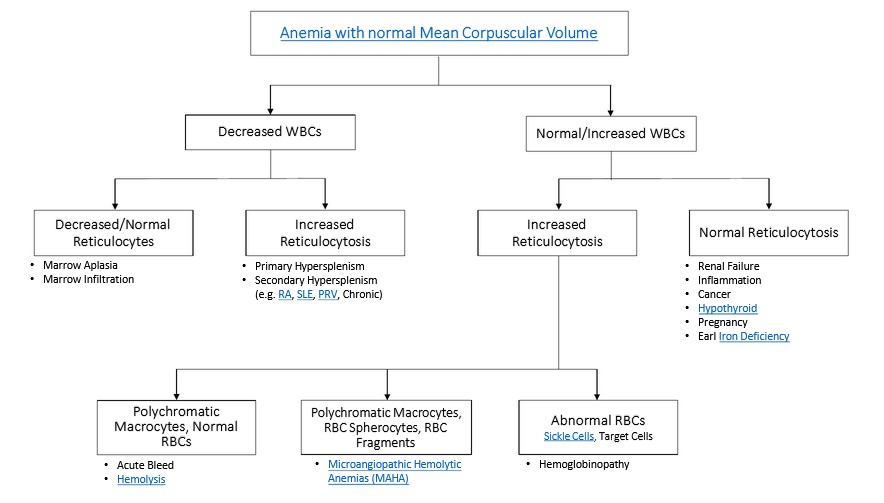
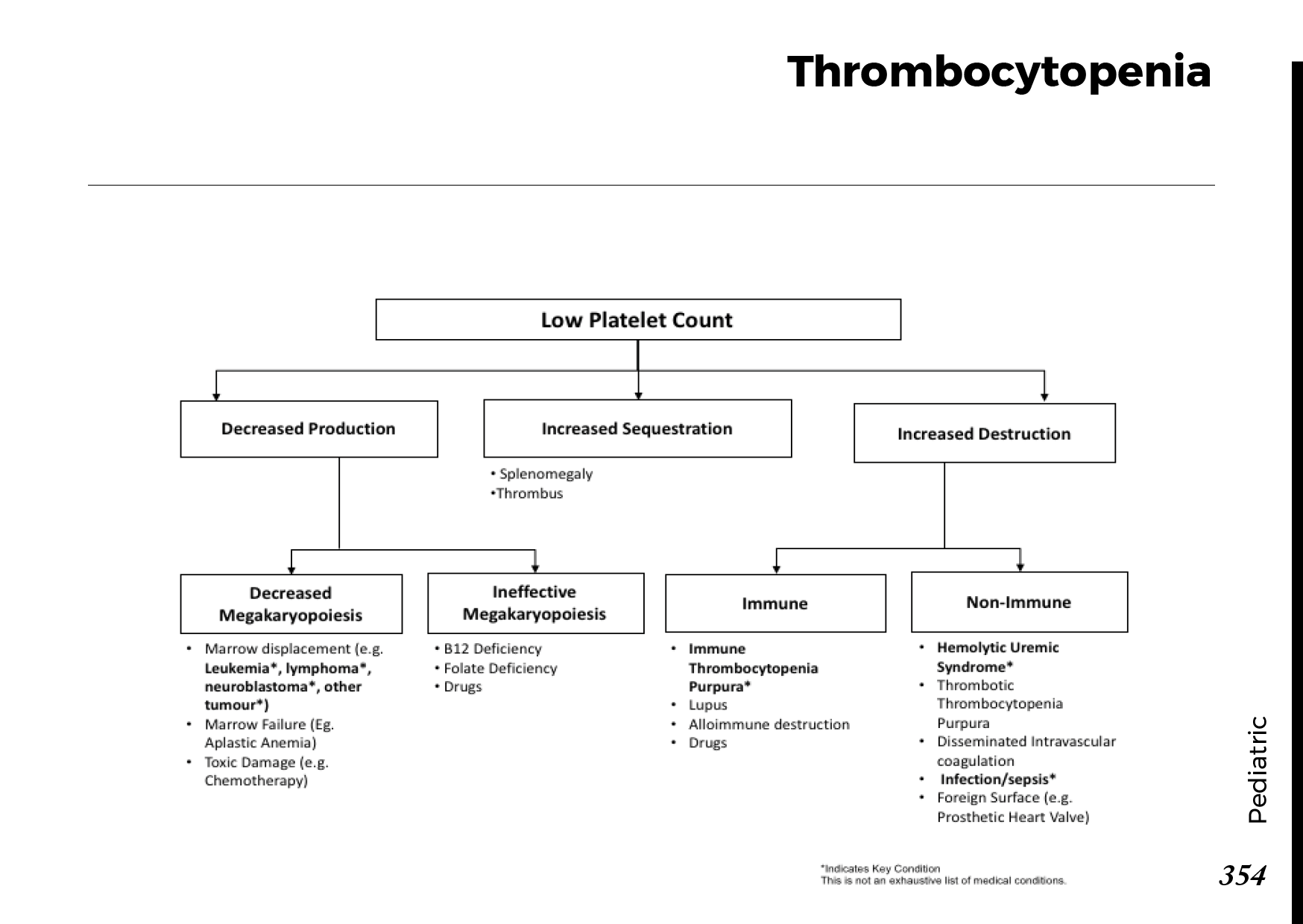
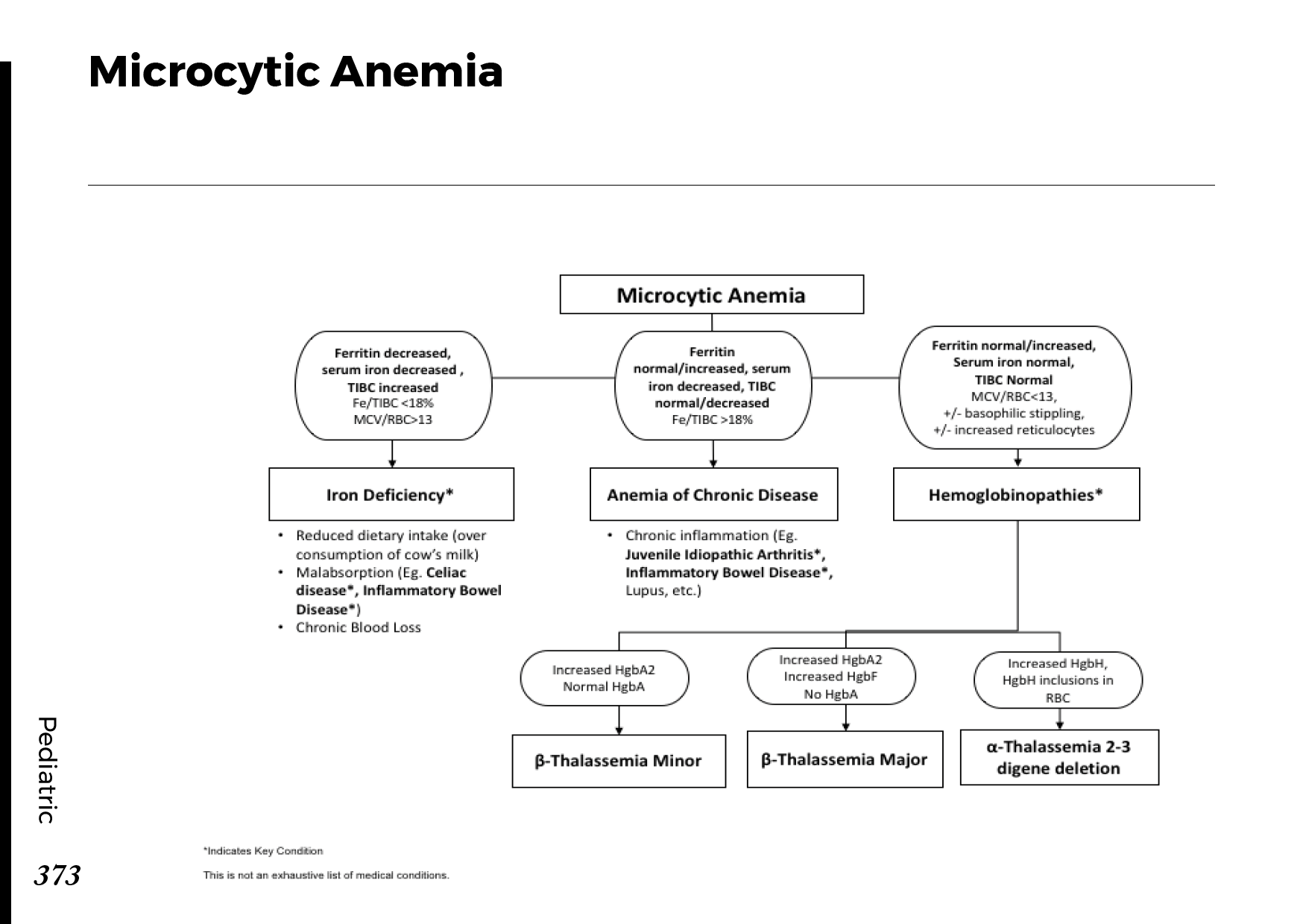
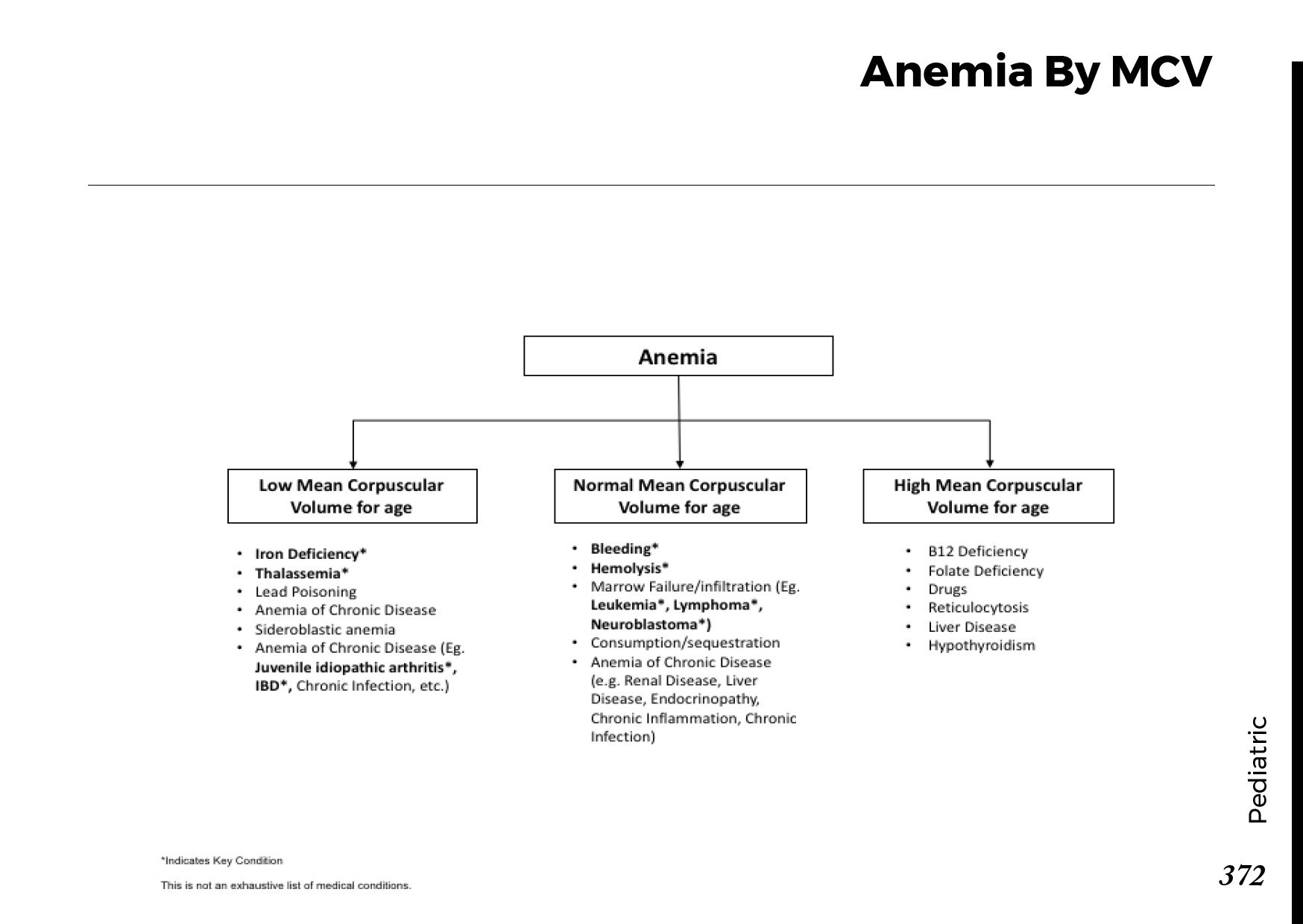
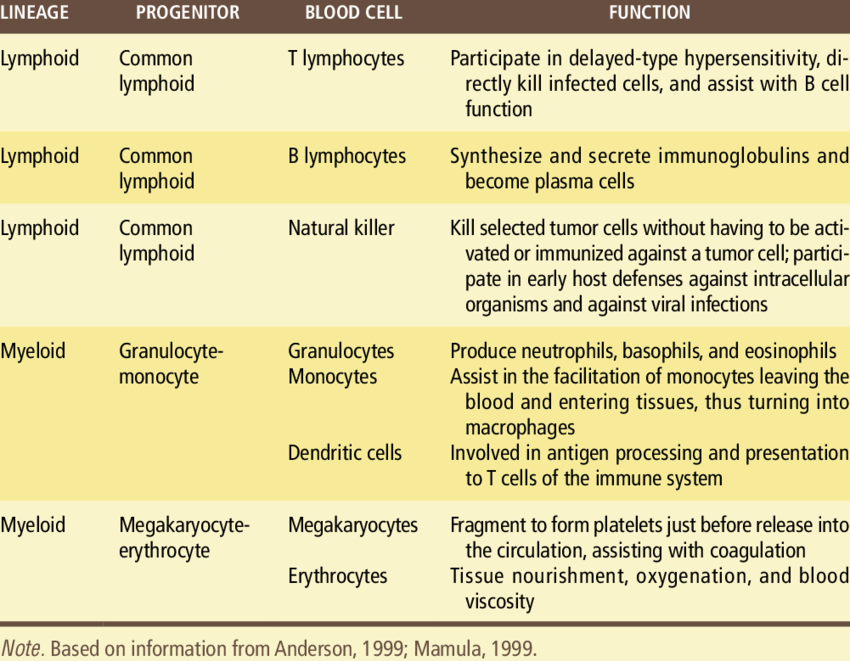
Blood cell types and their functions:
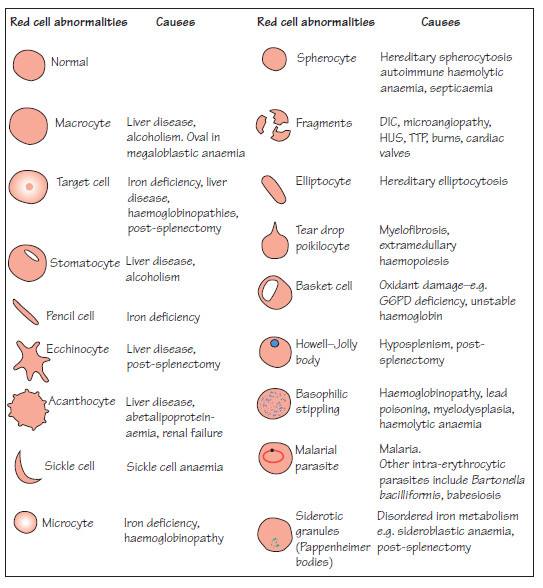
Common blood smear findings:
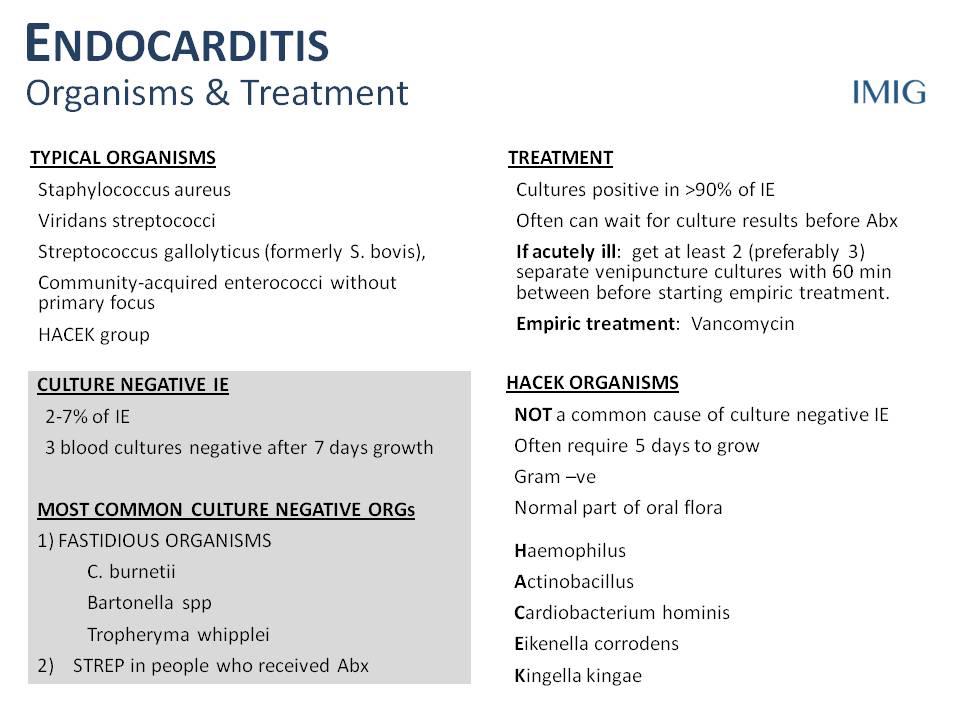
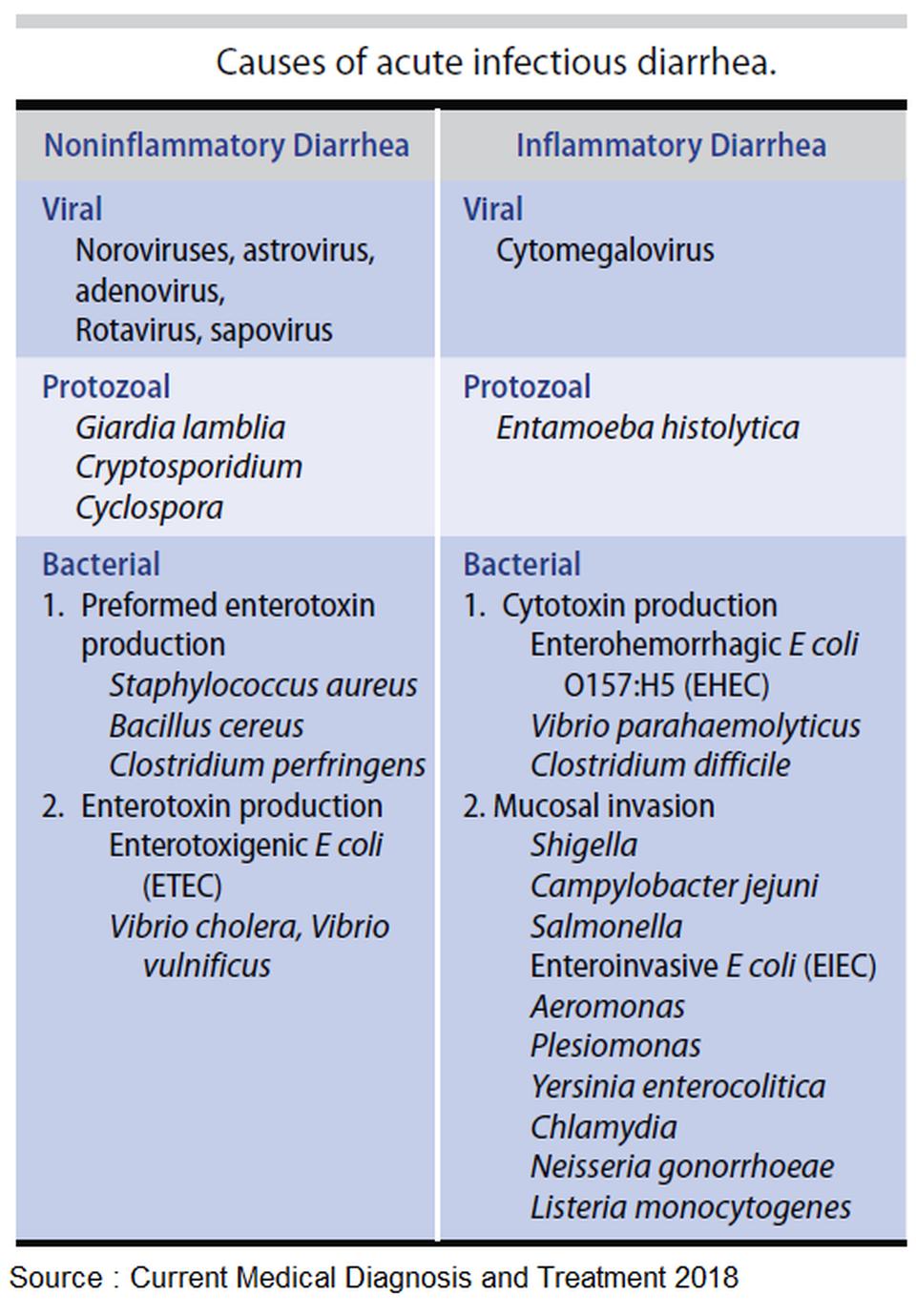
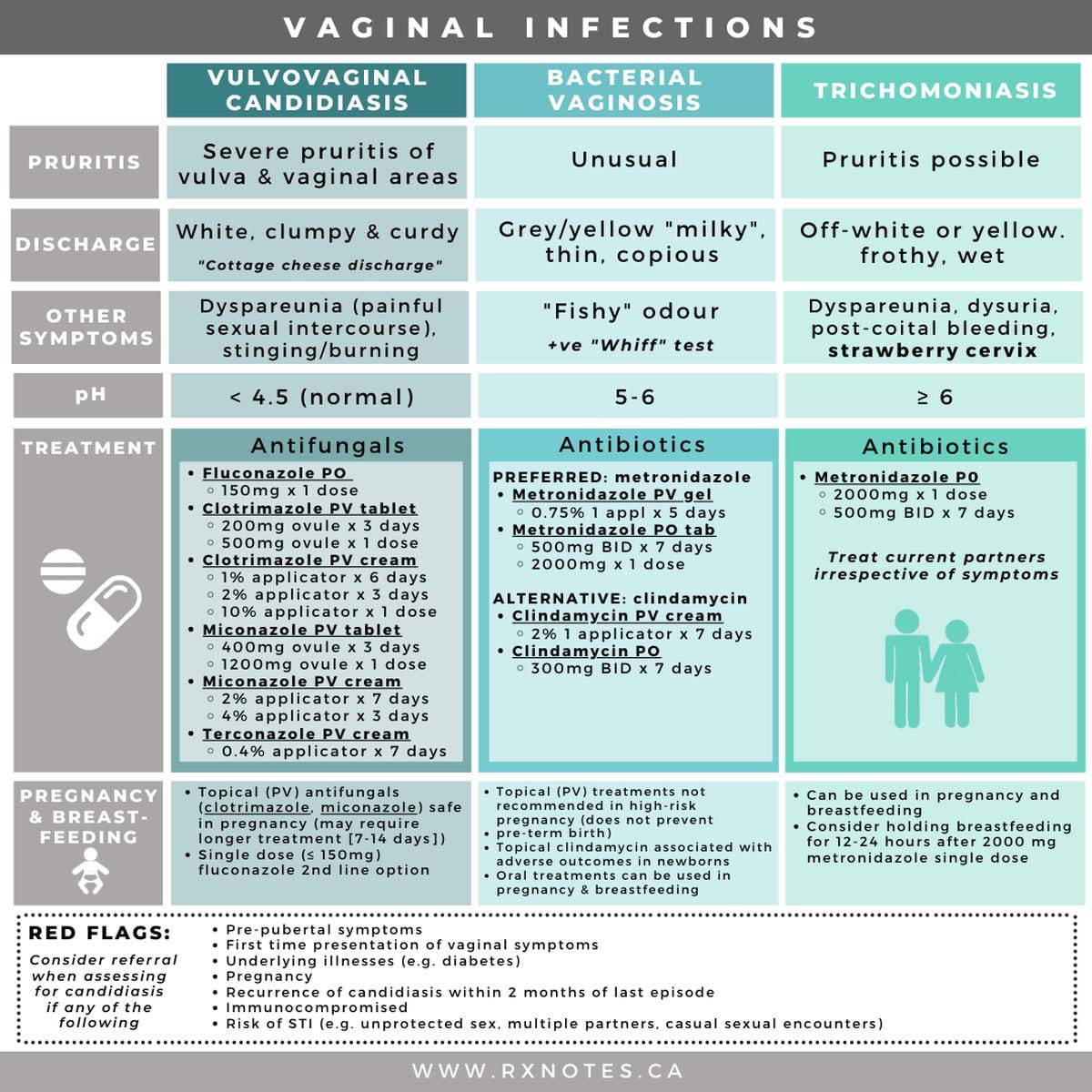
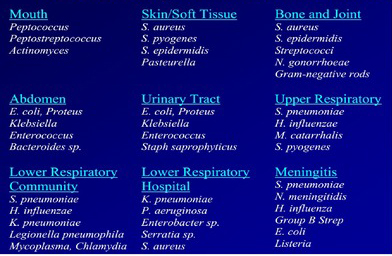
Common bacterial infections:
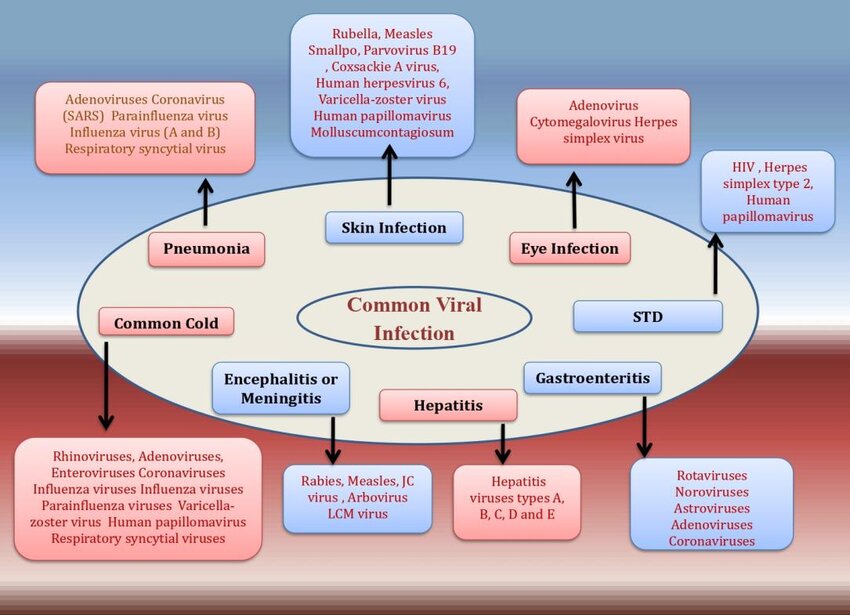
Common viral infections:
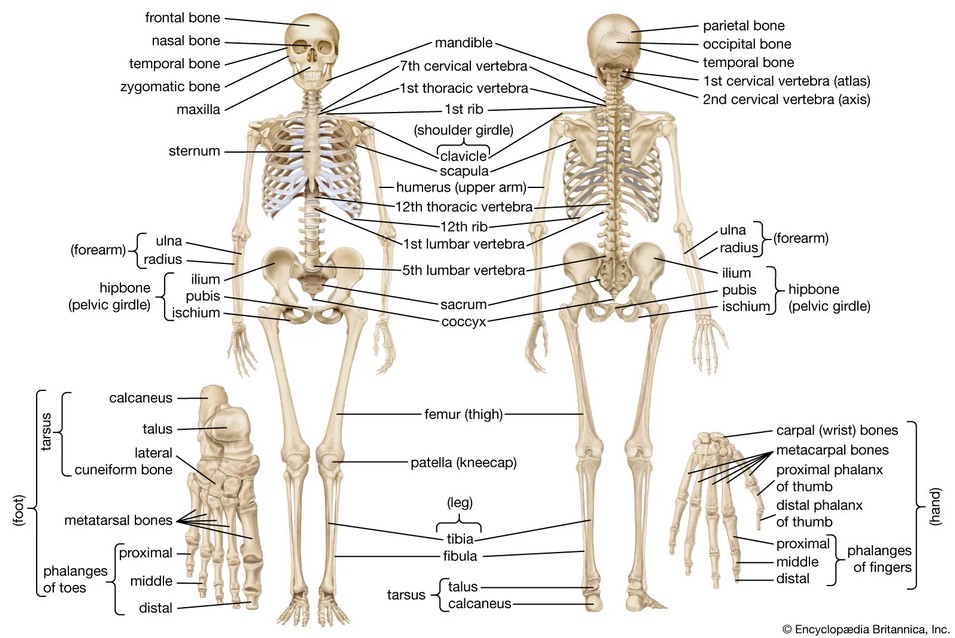
Bone anatomy:
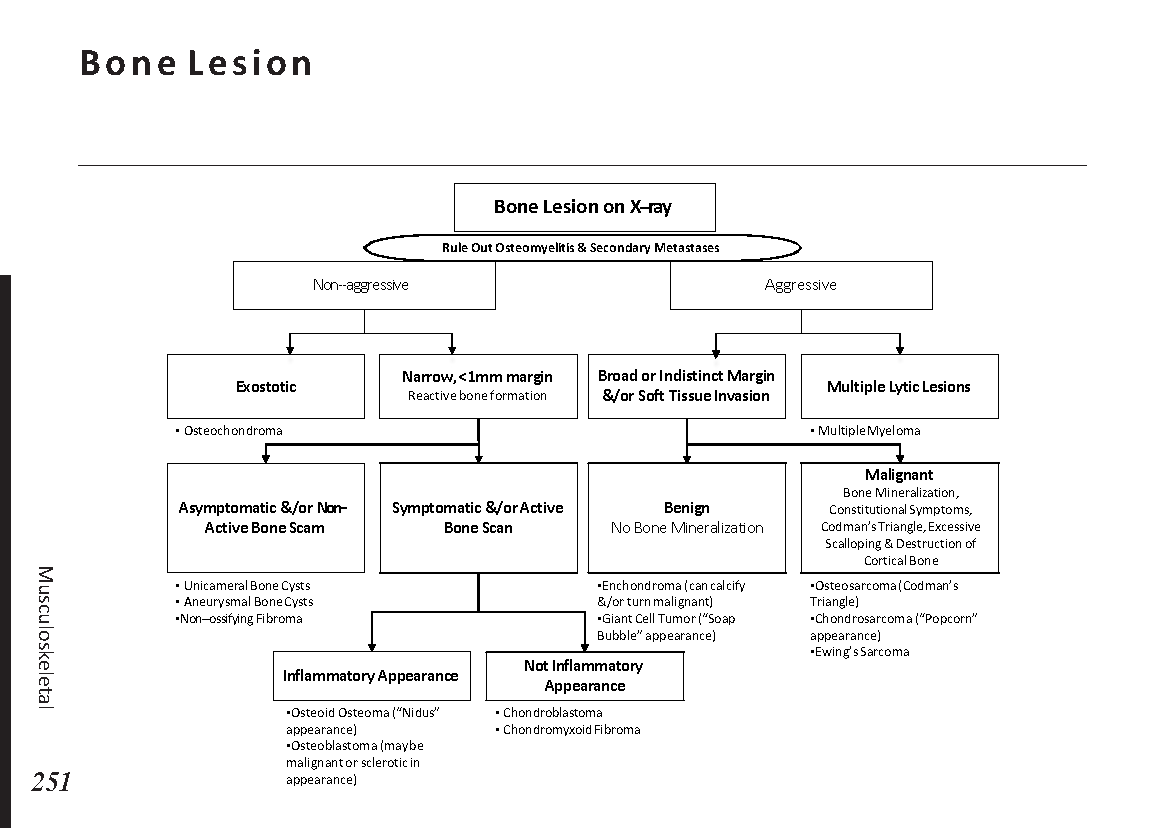
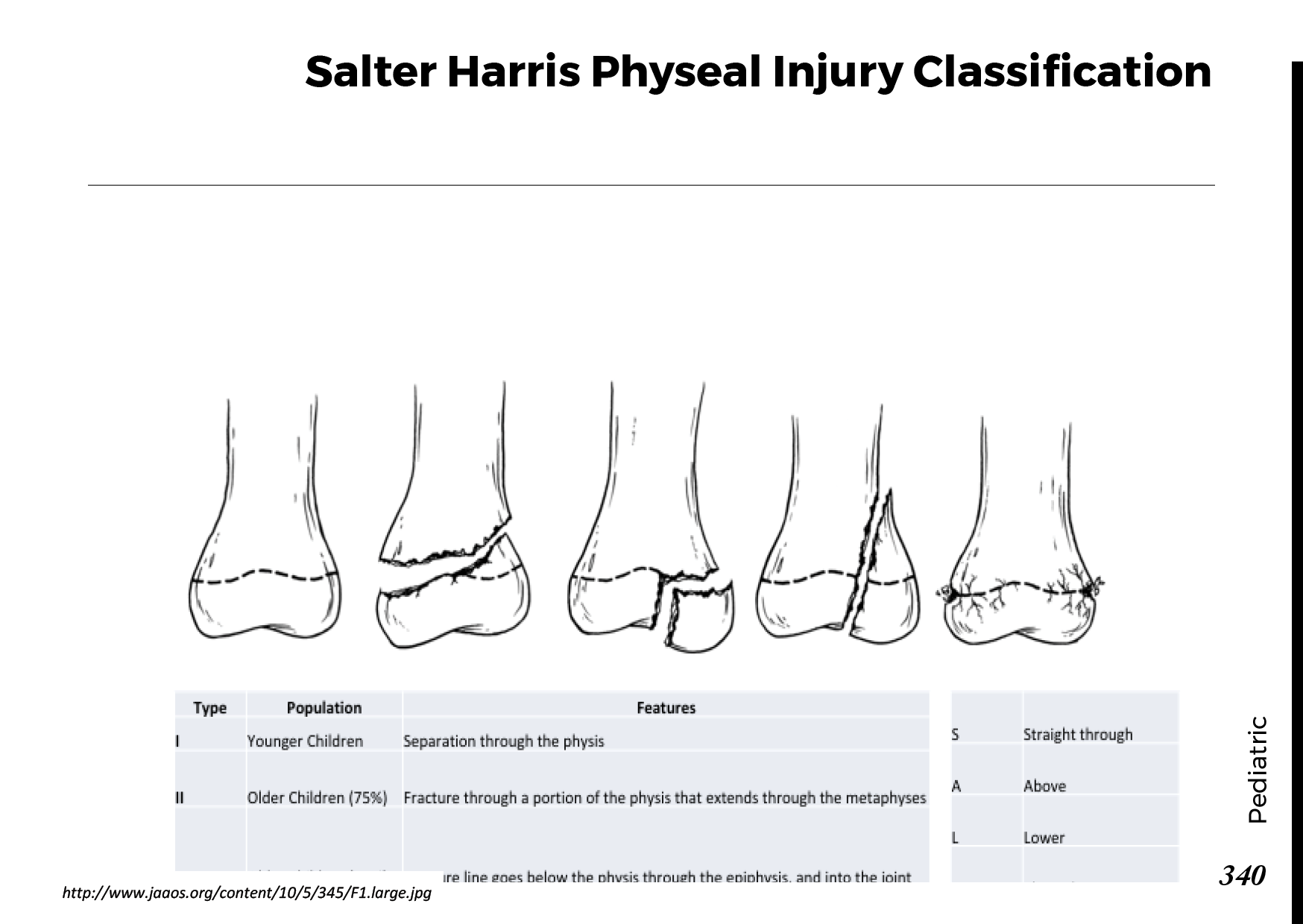
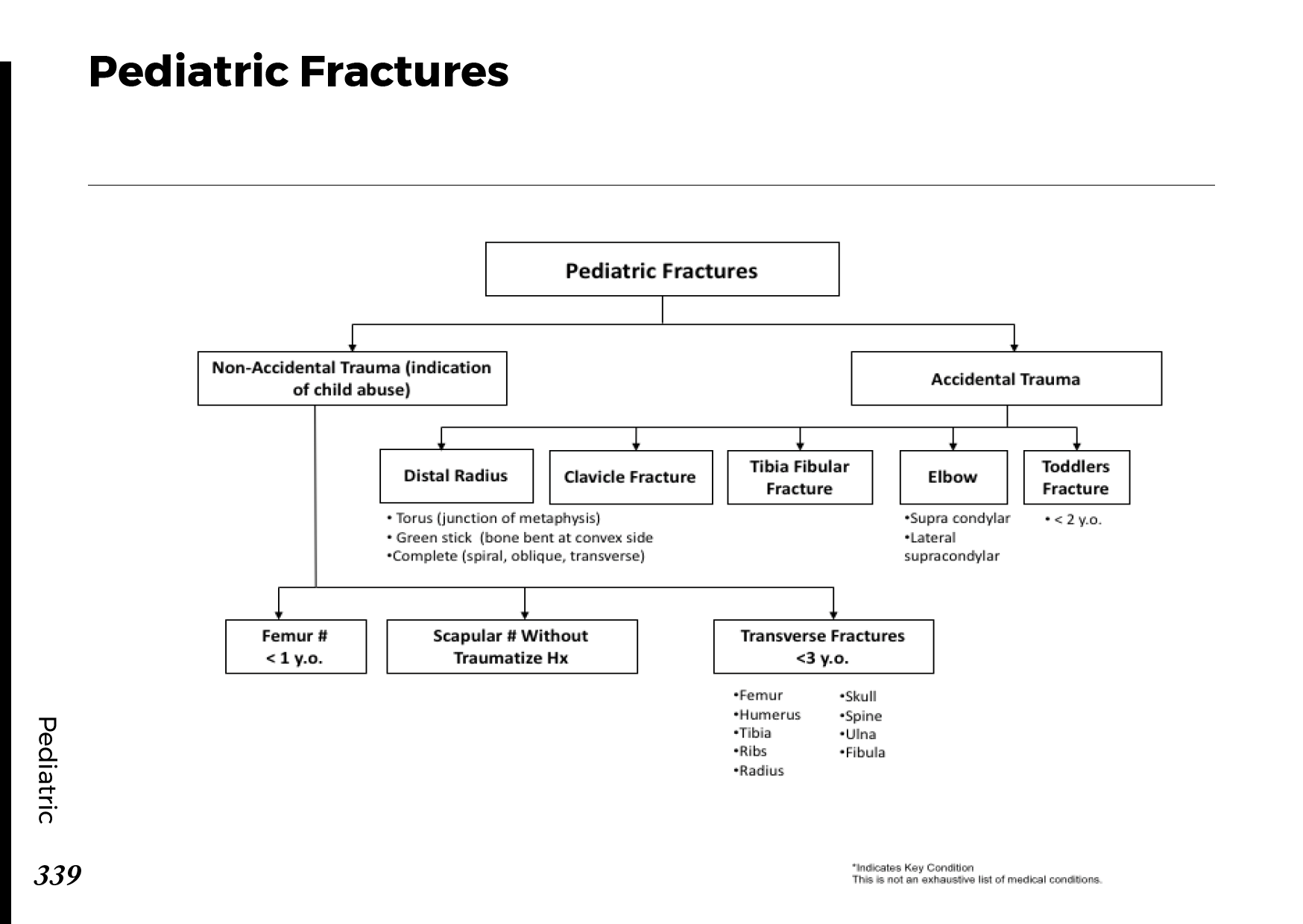
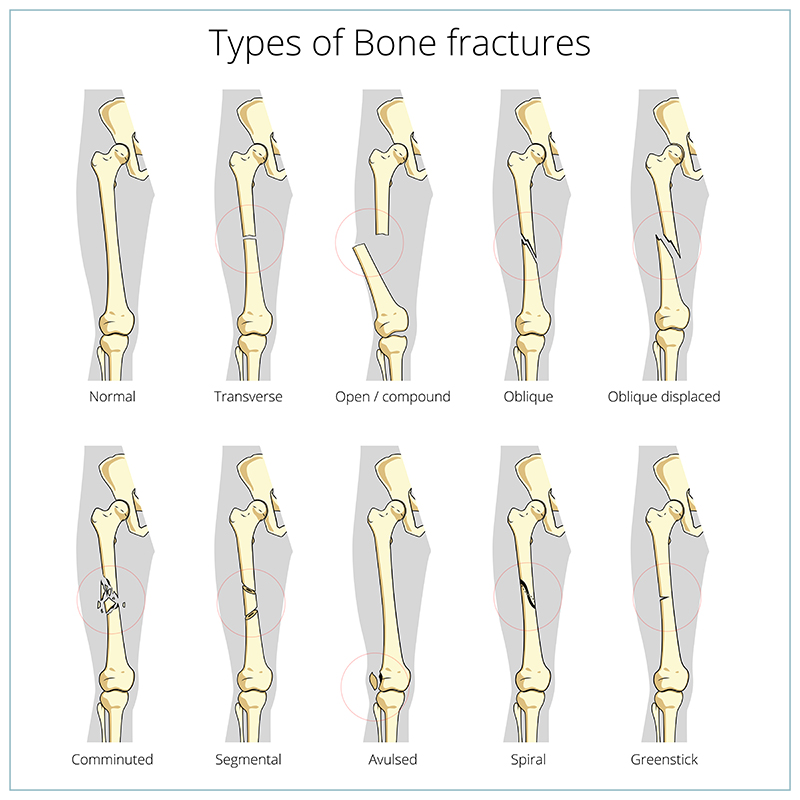
Common bone fractures:
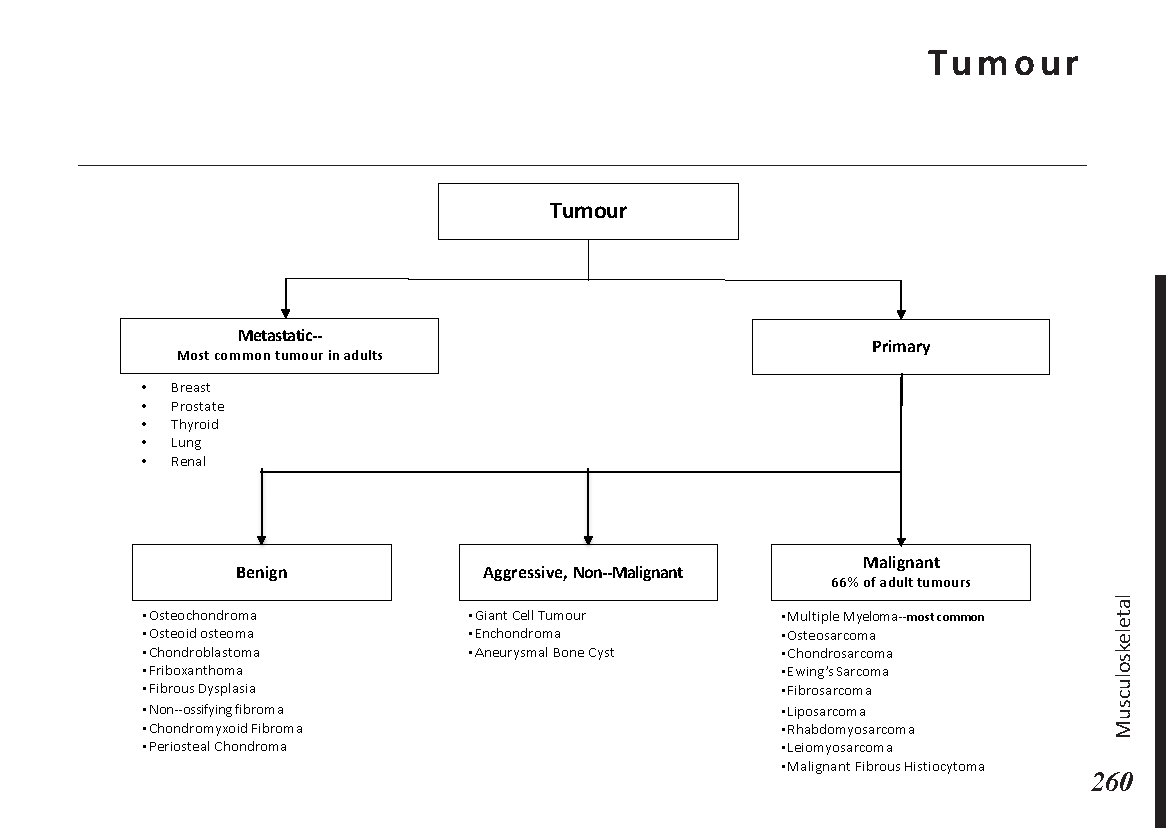
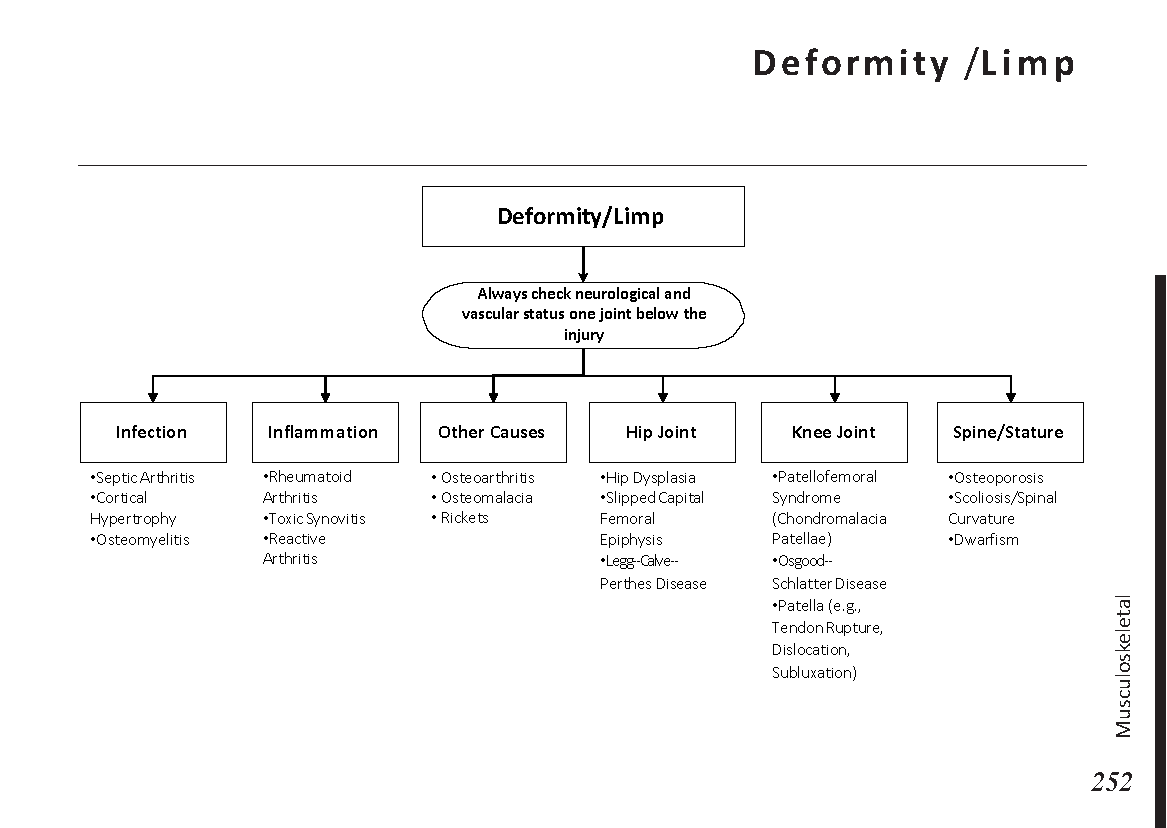
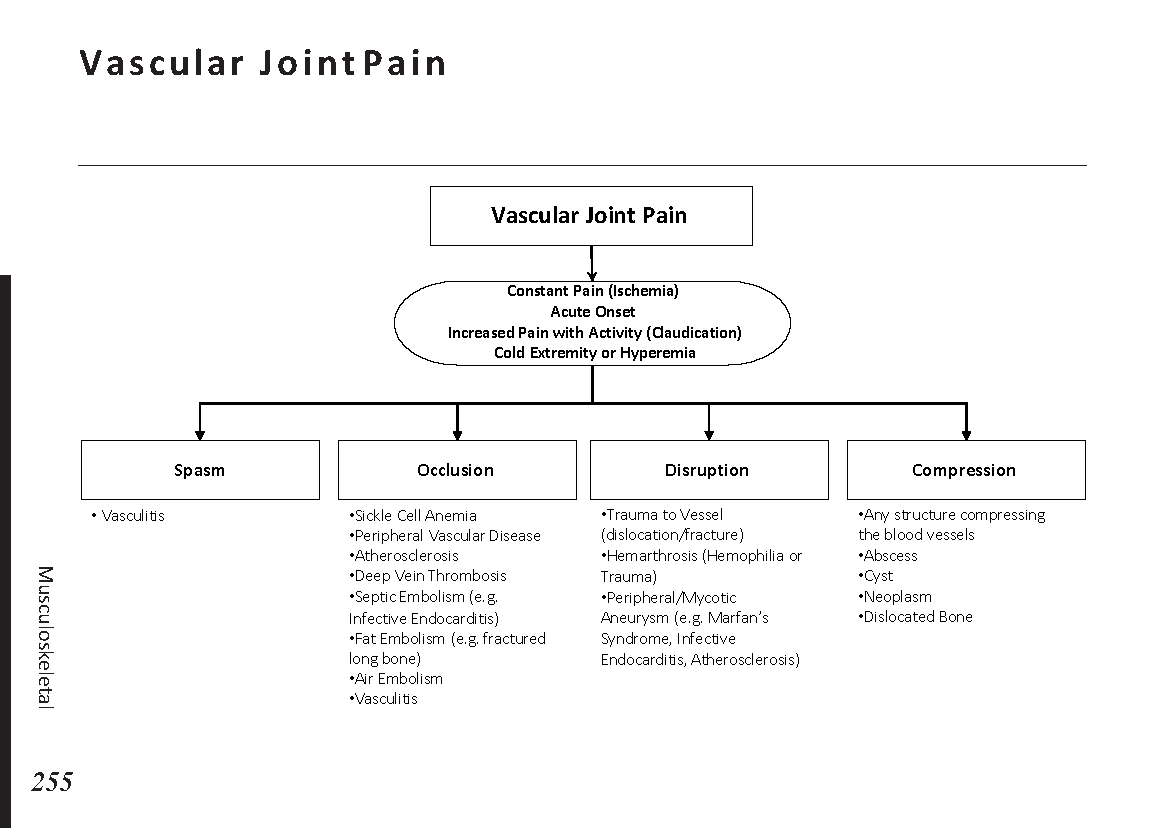
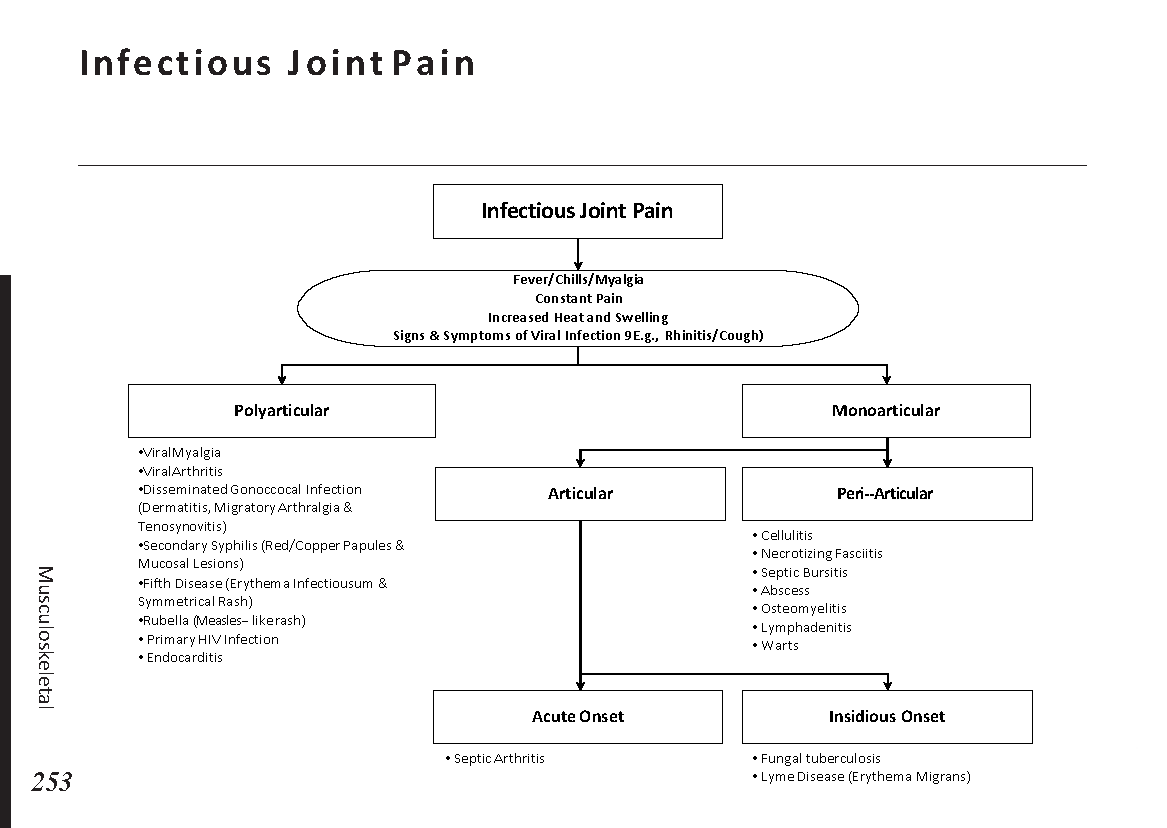
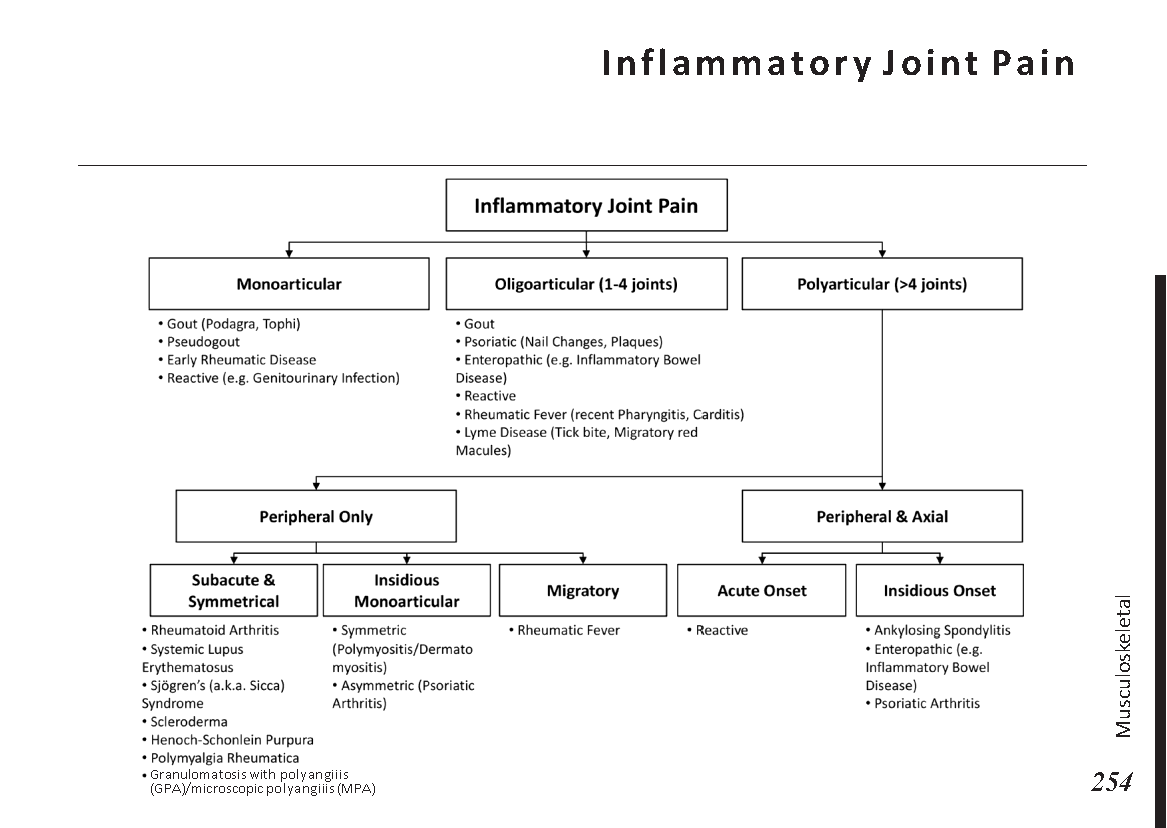
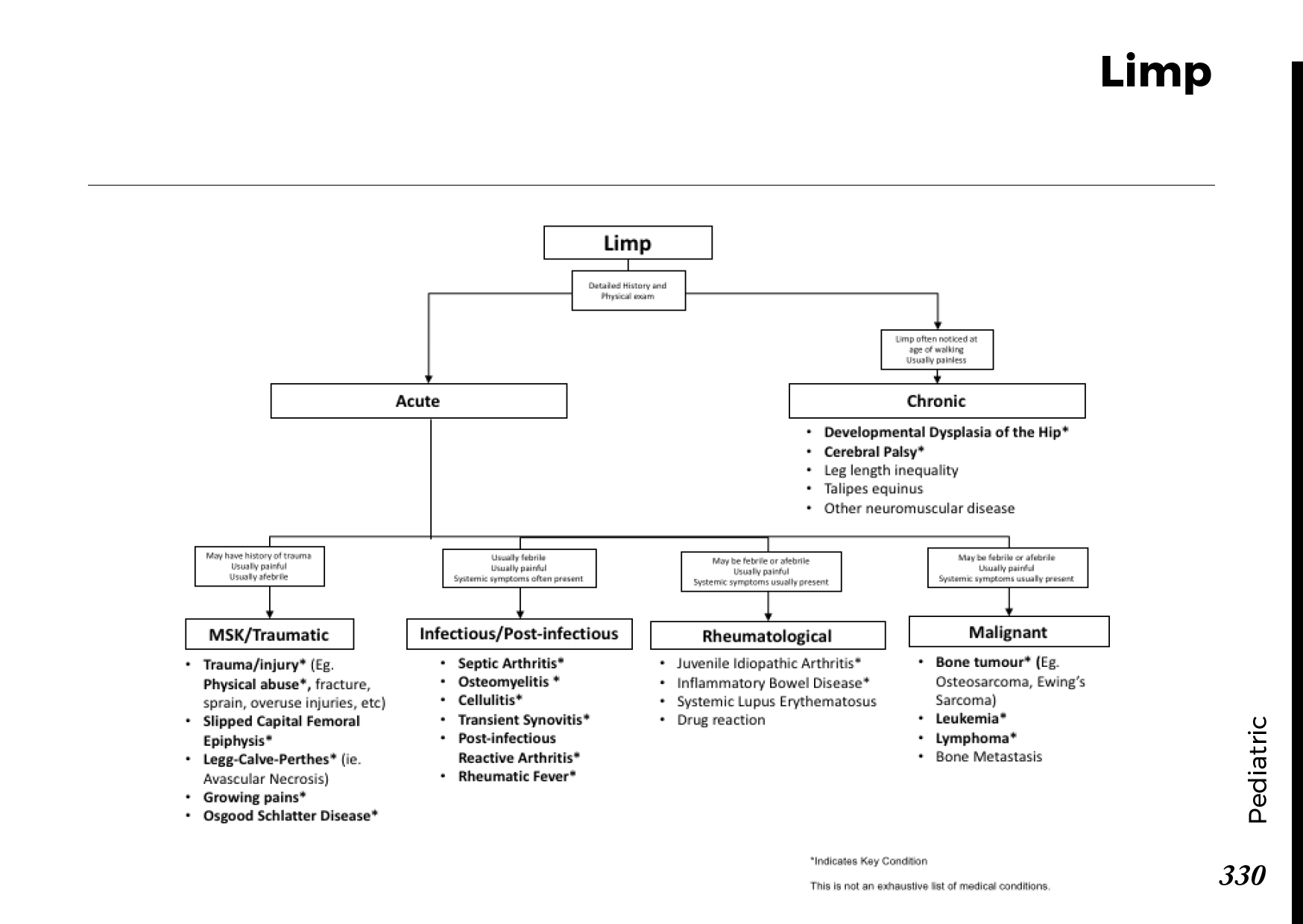
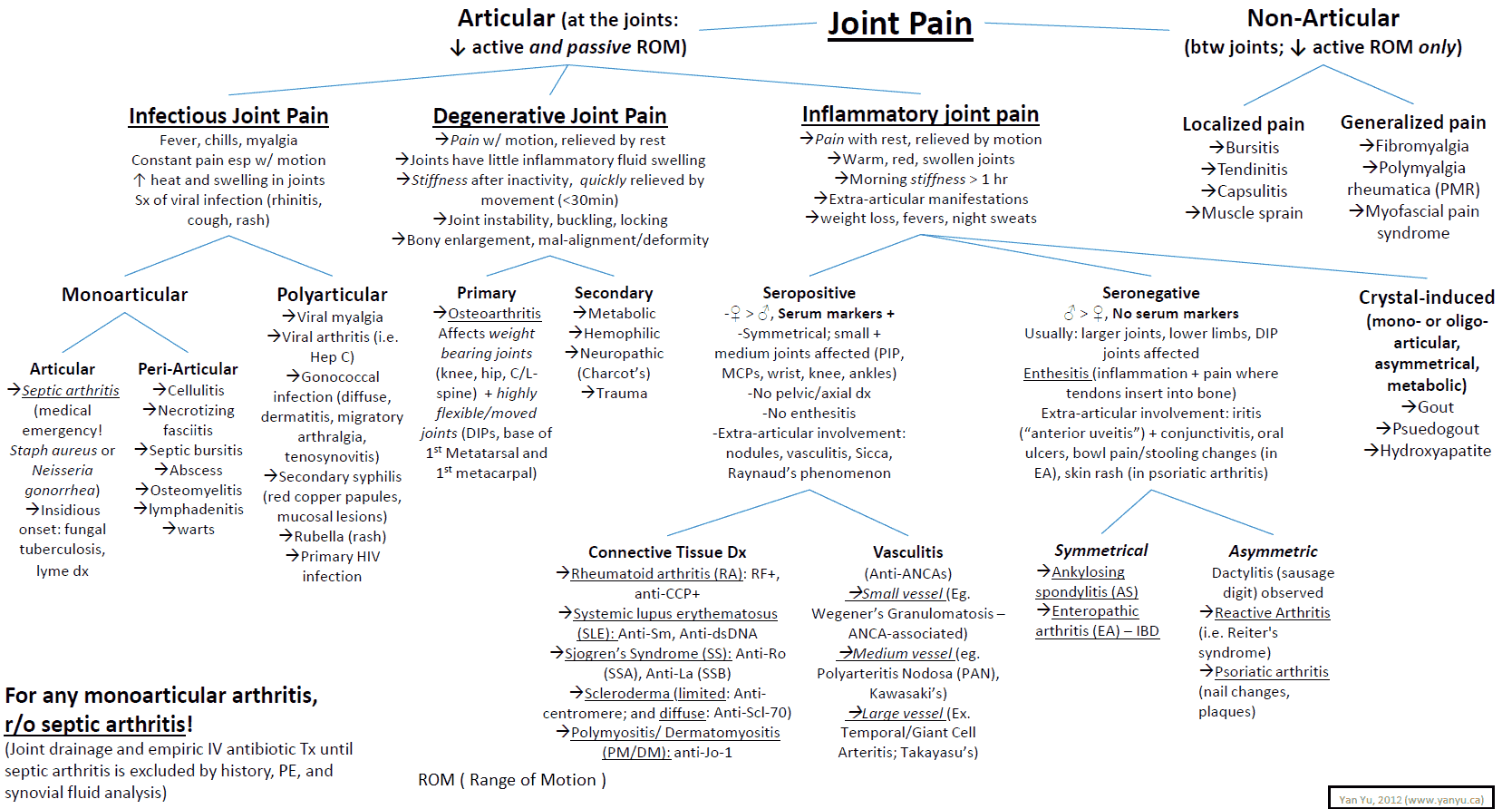
Joint pain differential diagnosis:
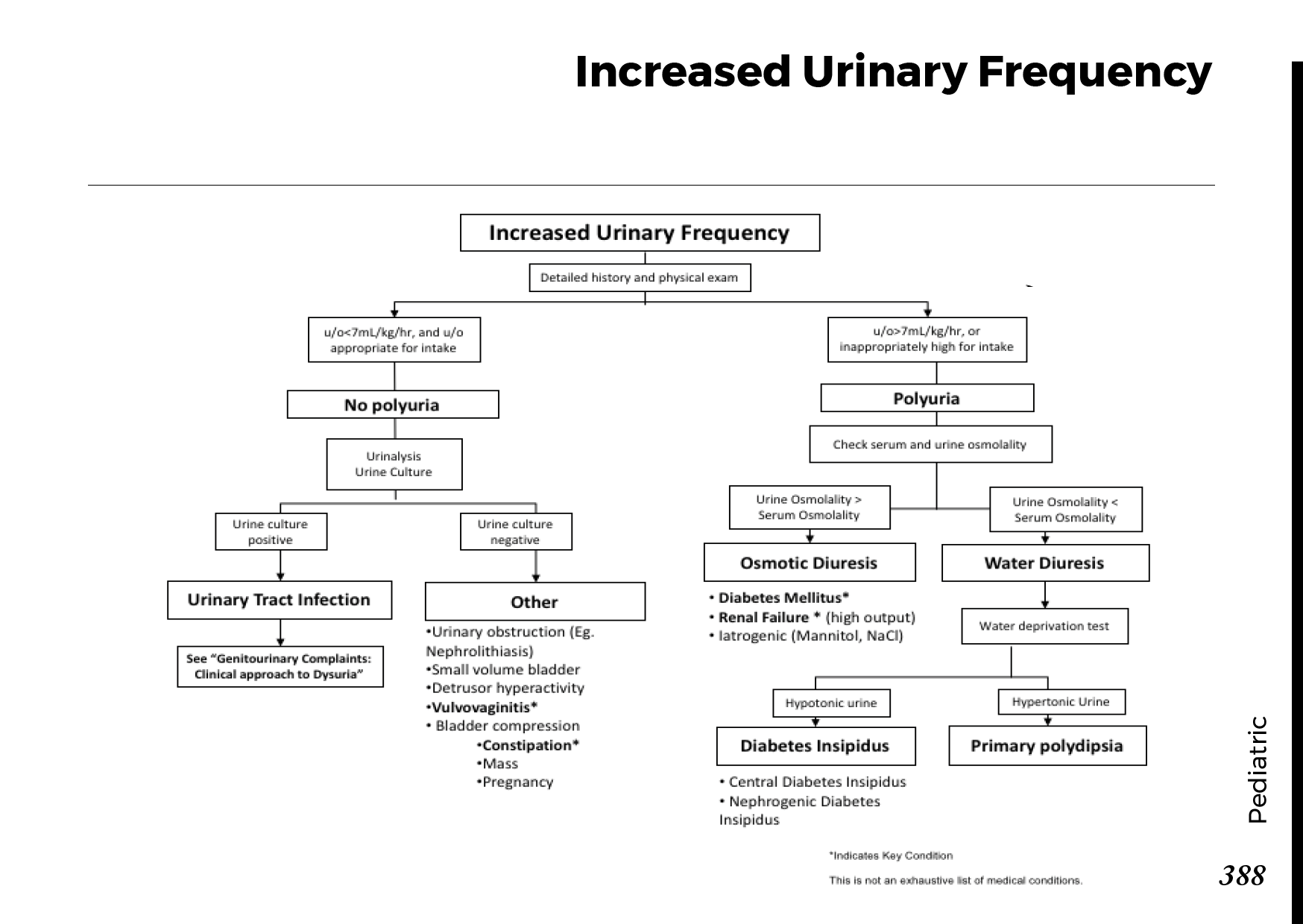
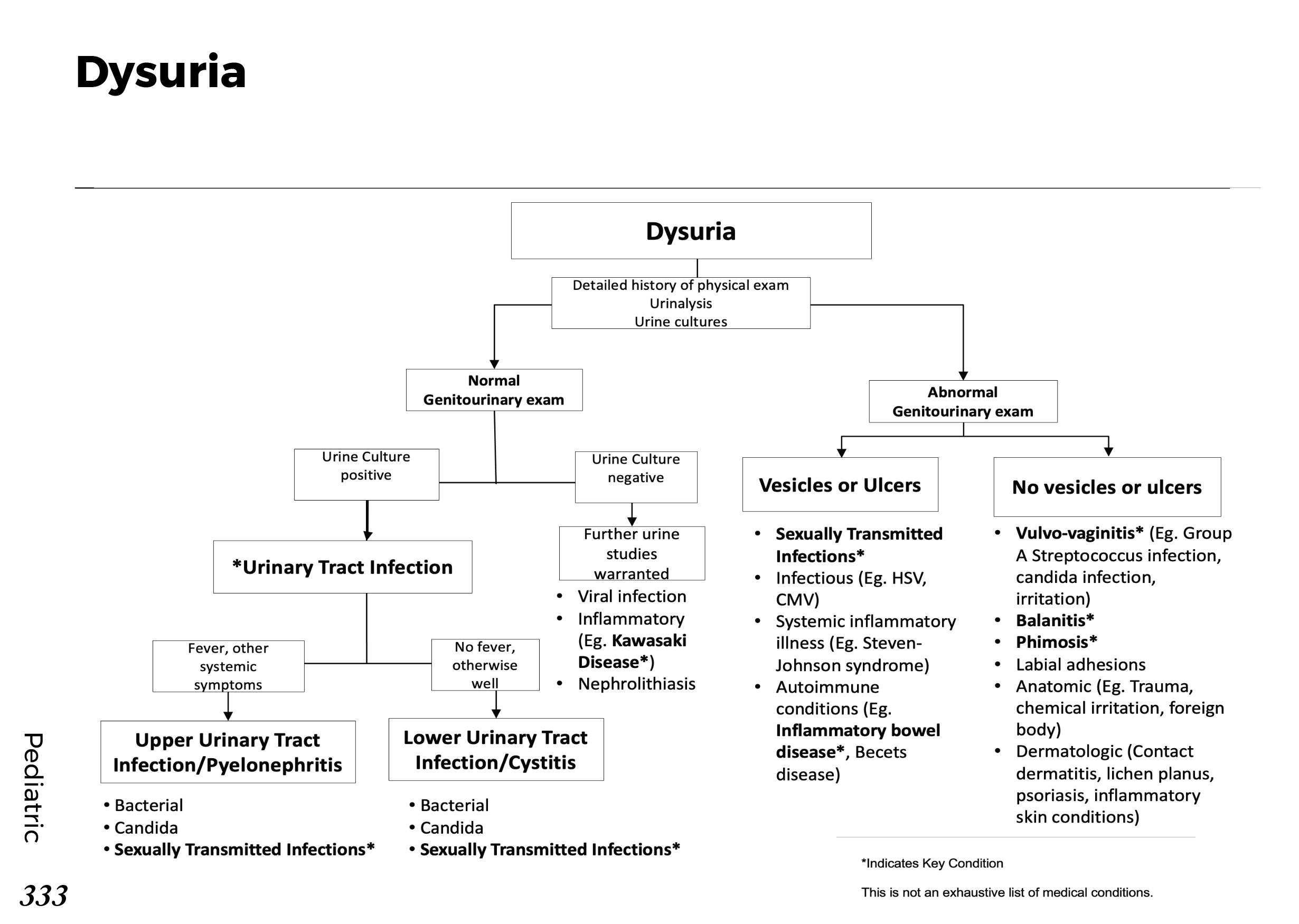
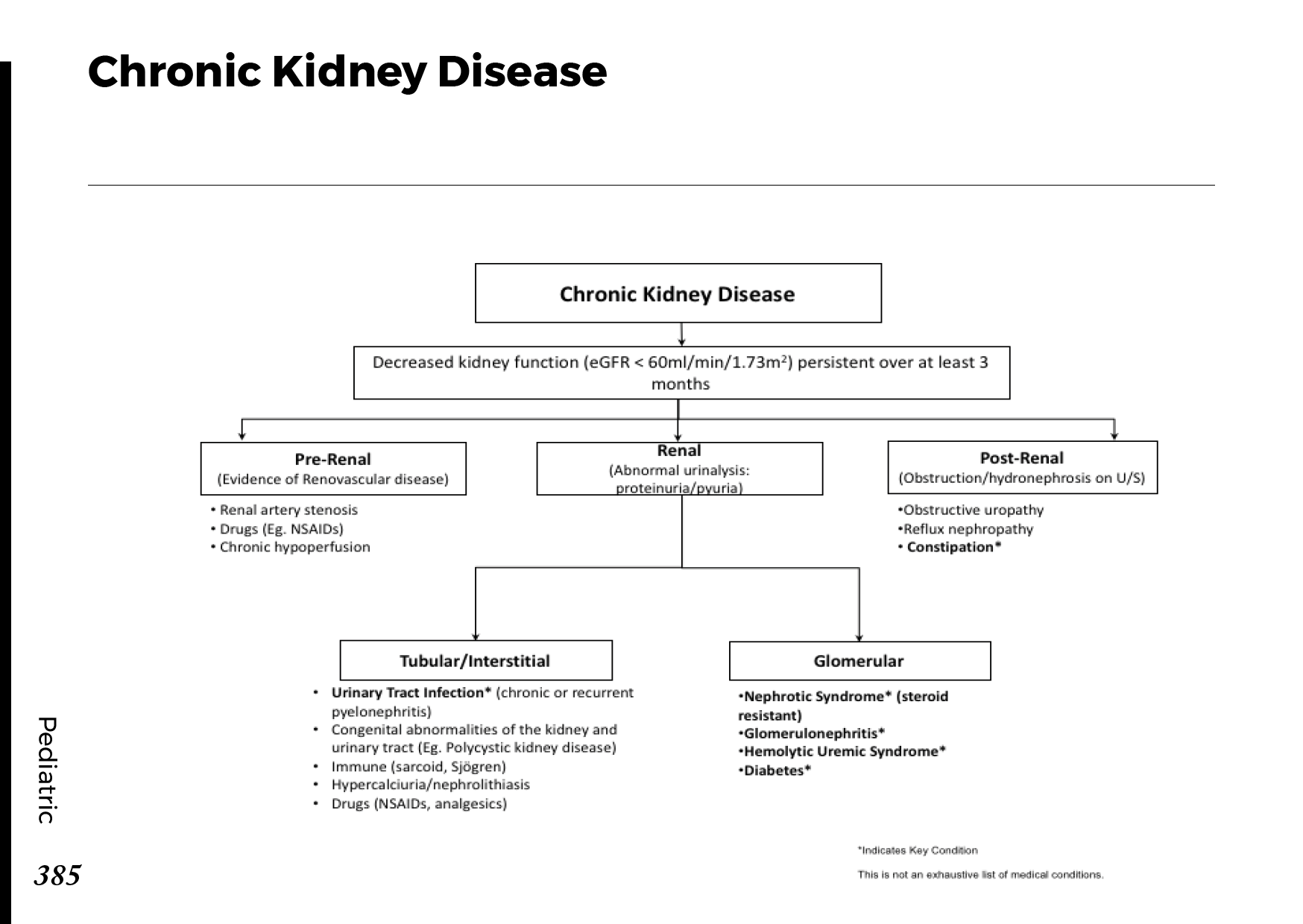
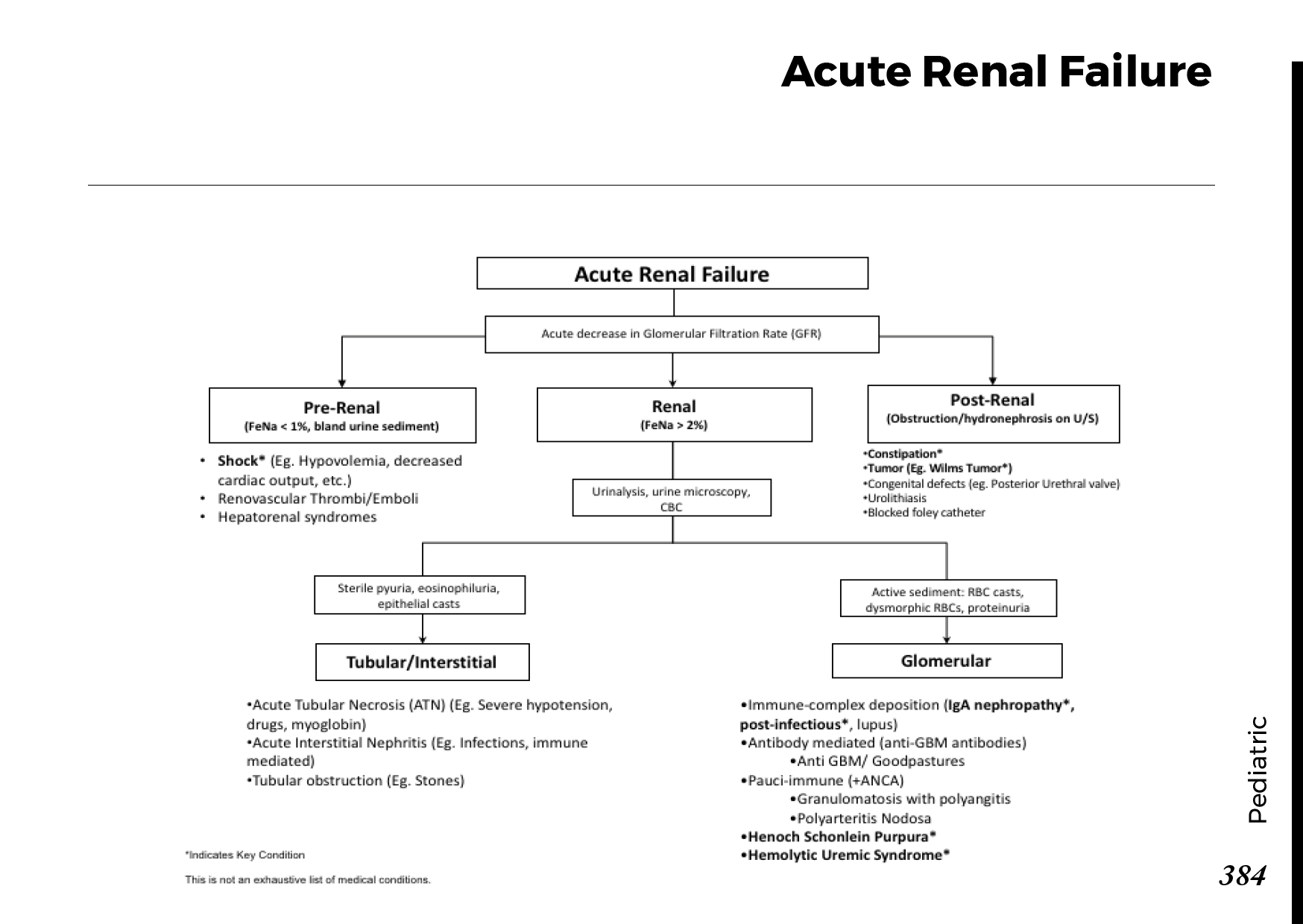
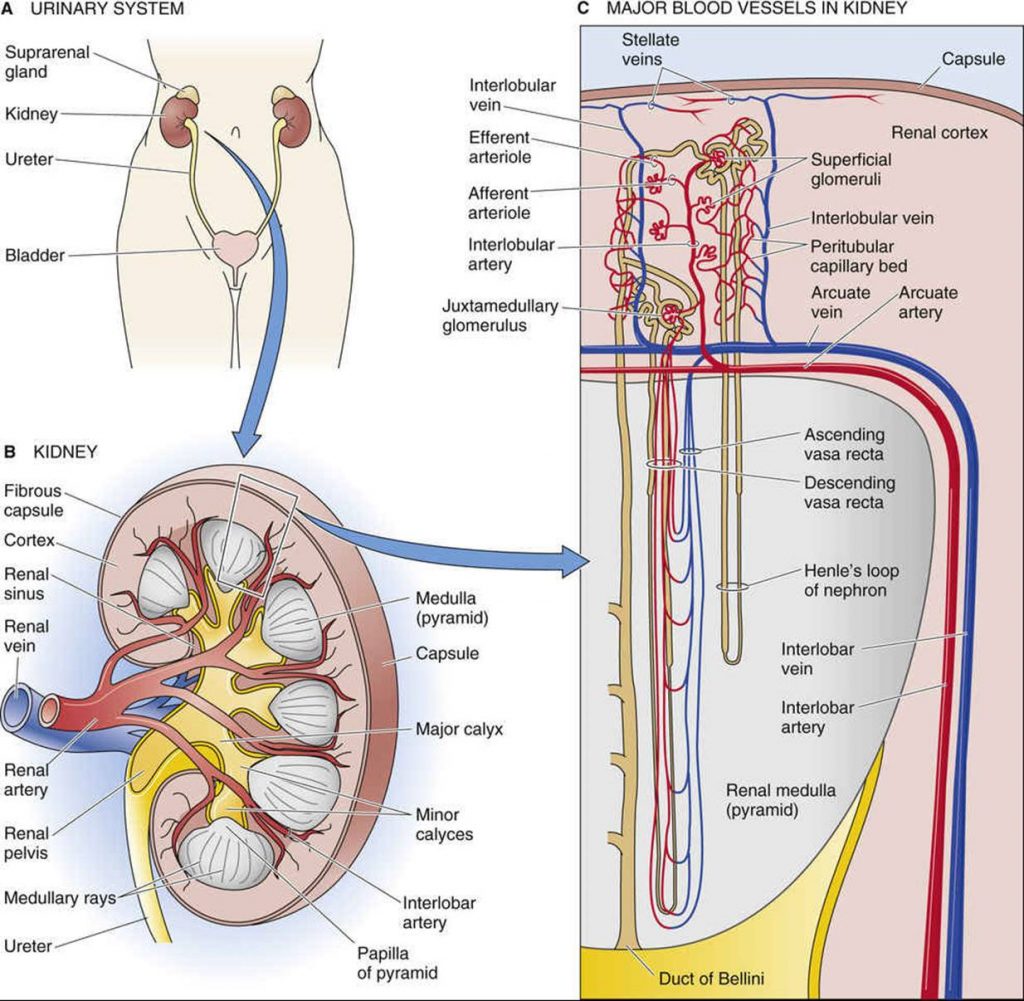
Urinary system anatomy:
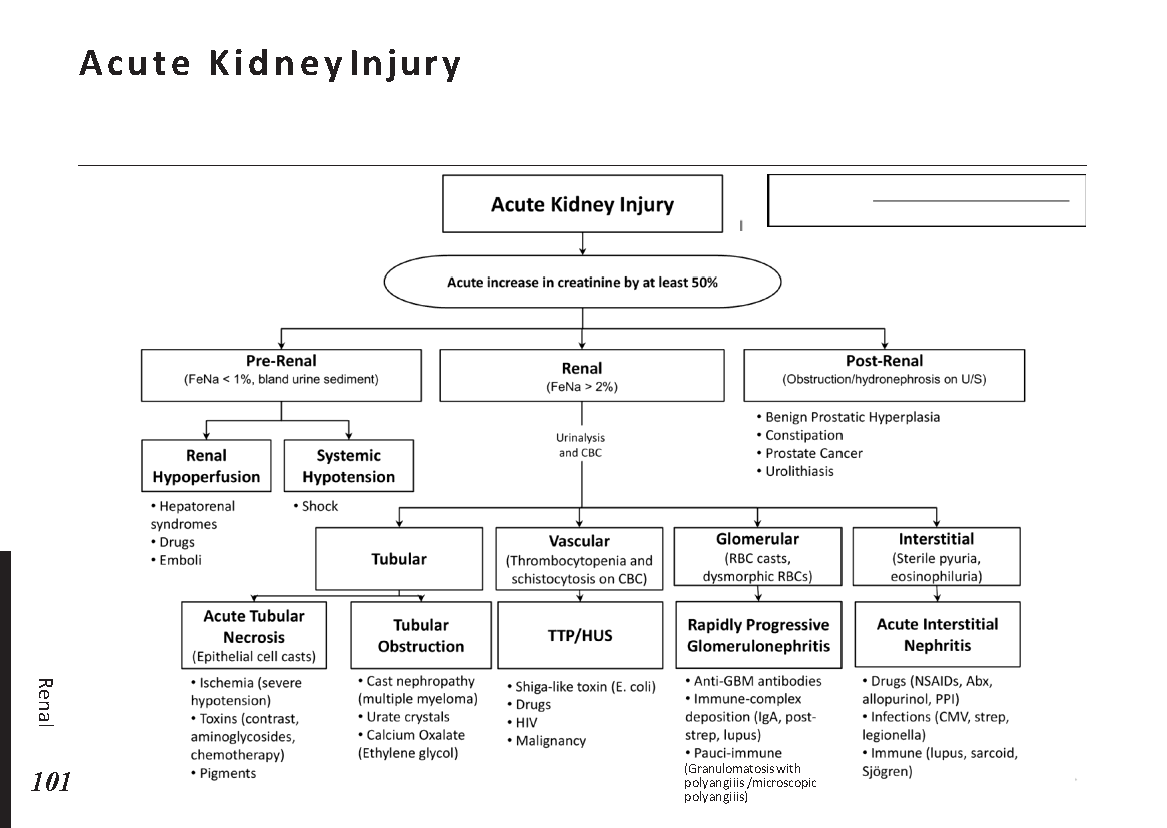
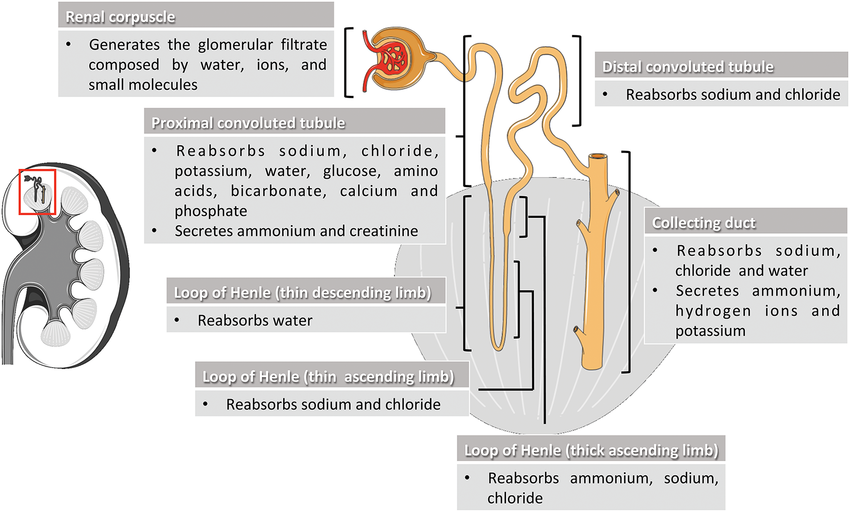
Nephron Function:
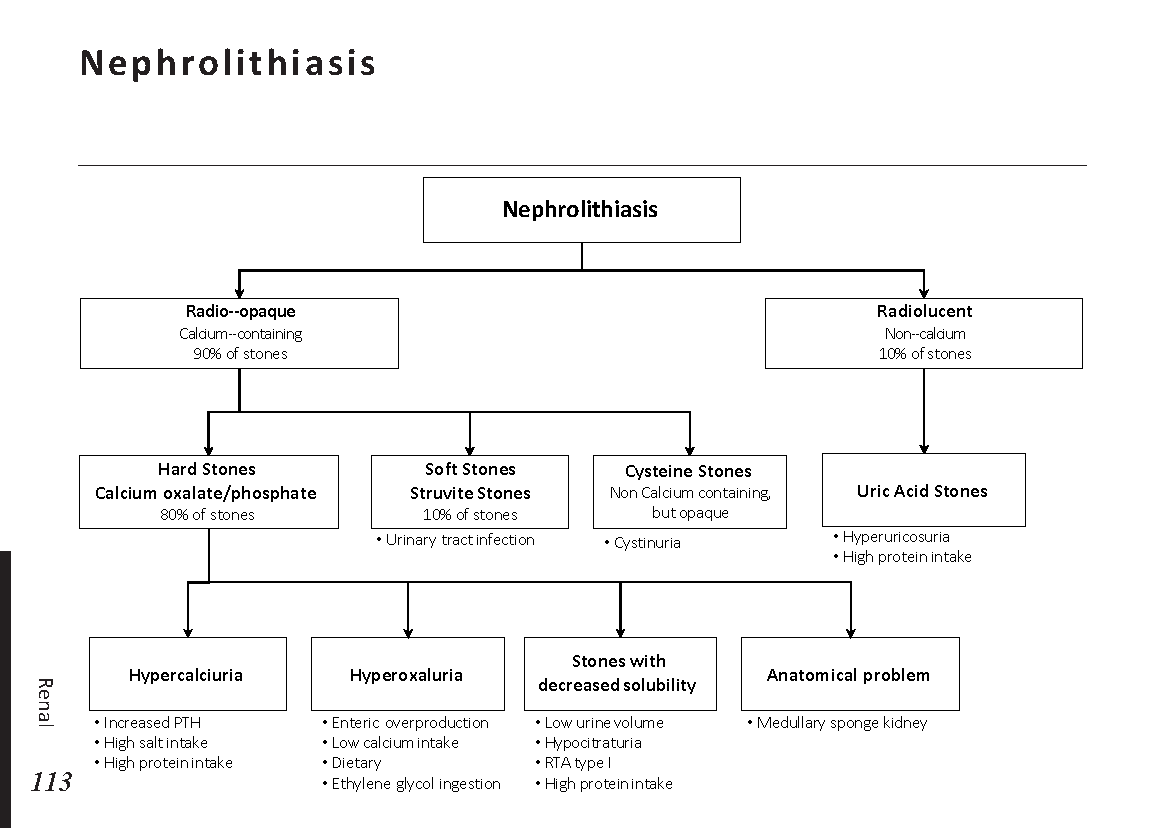
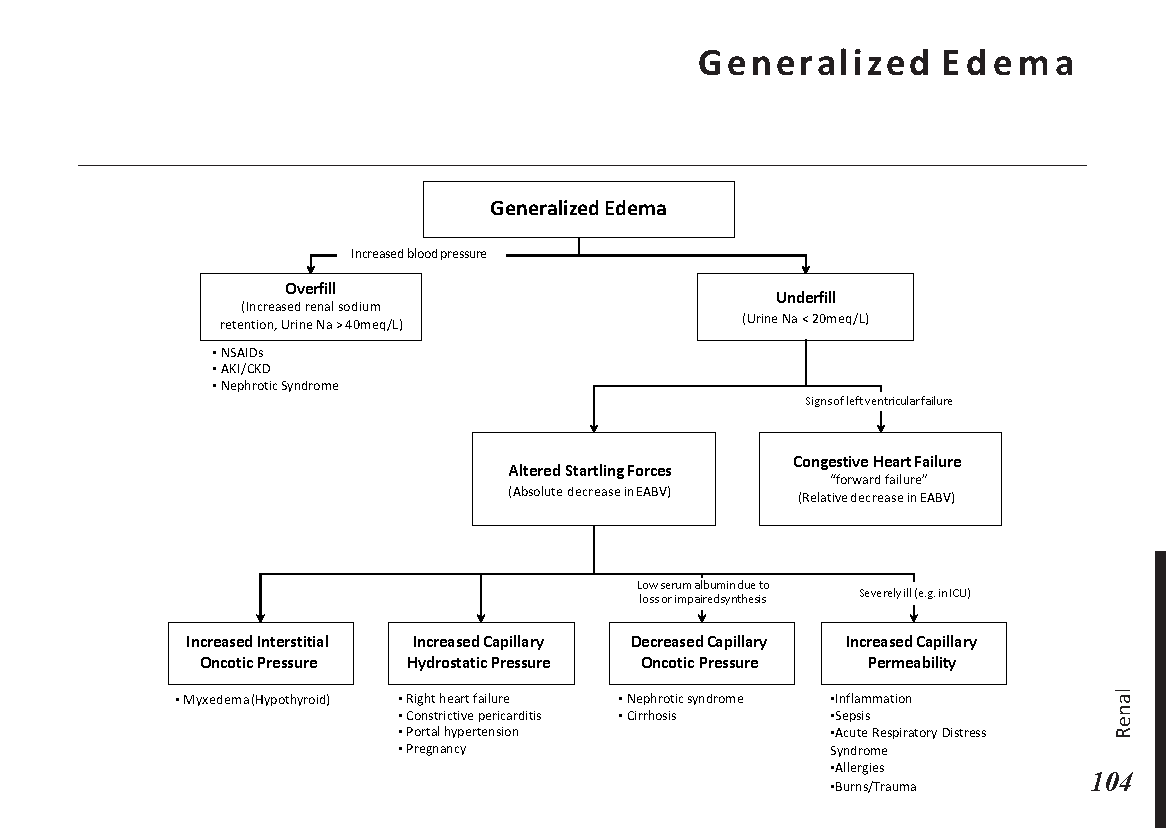
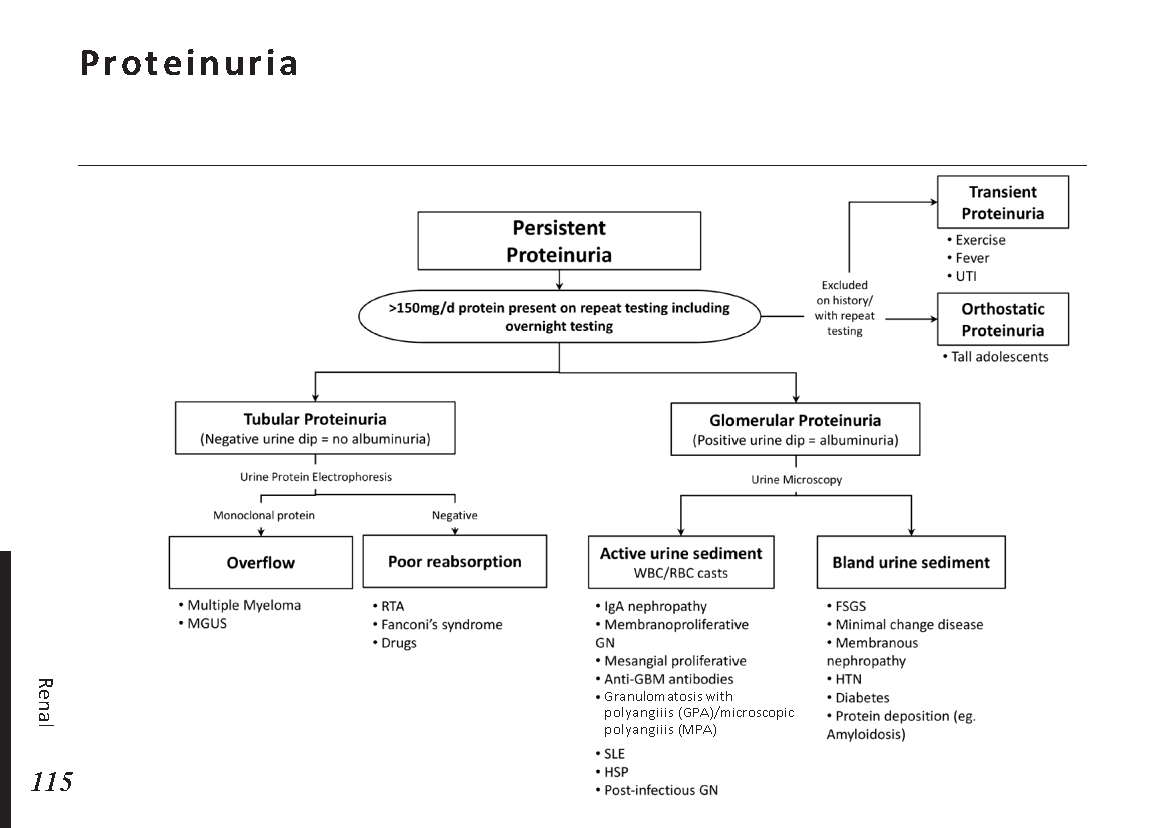
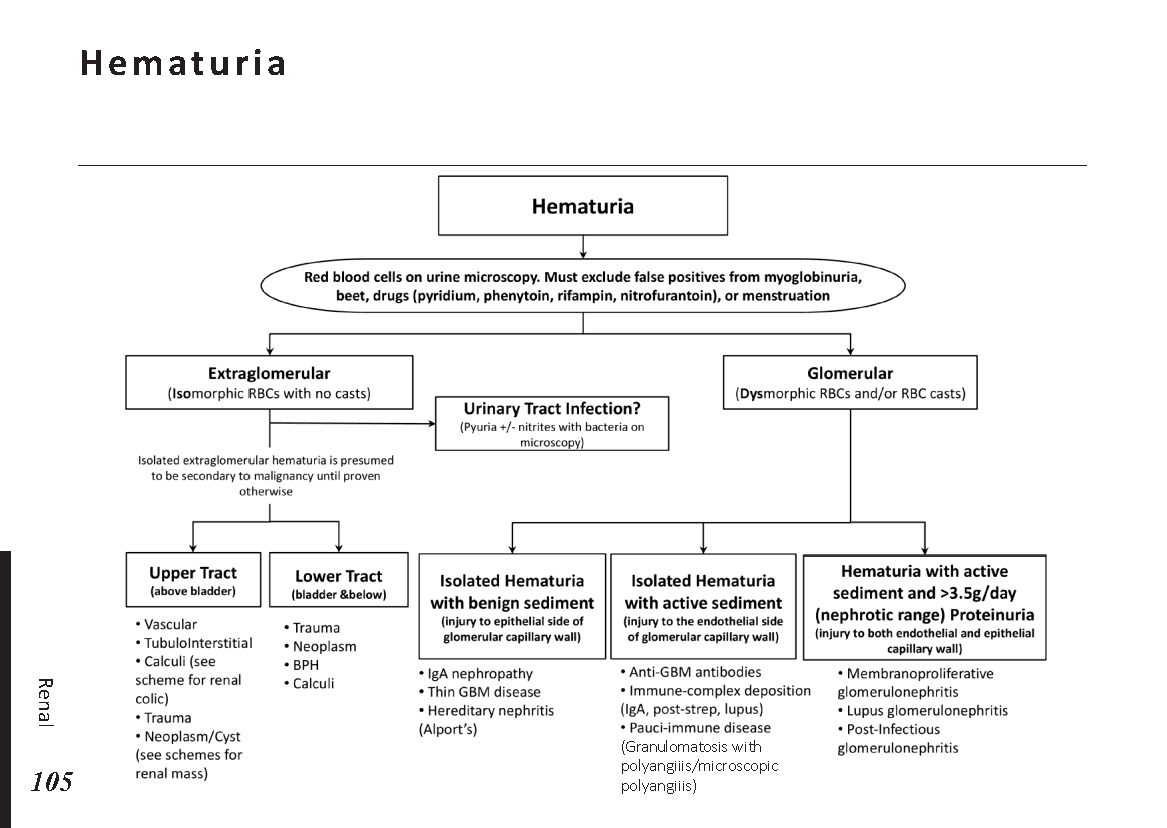
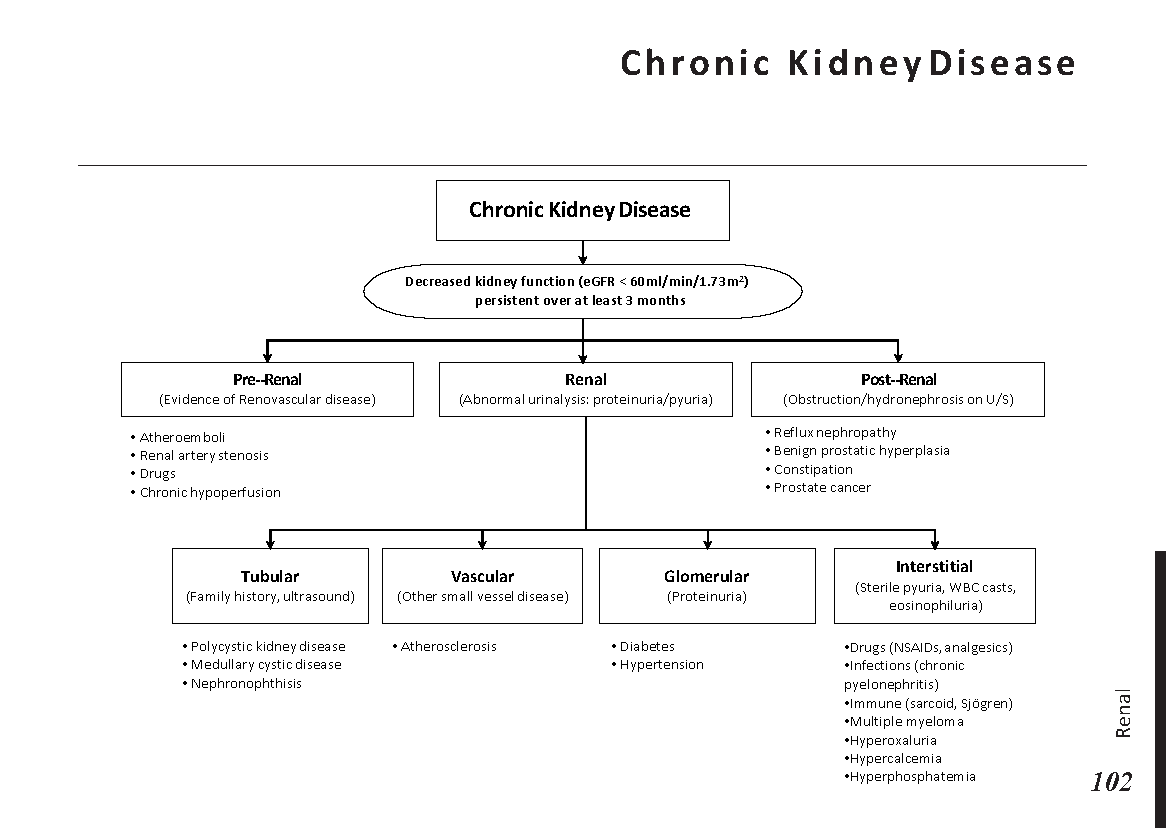
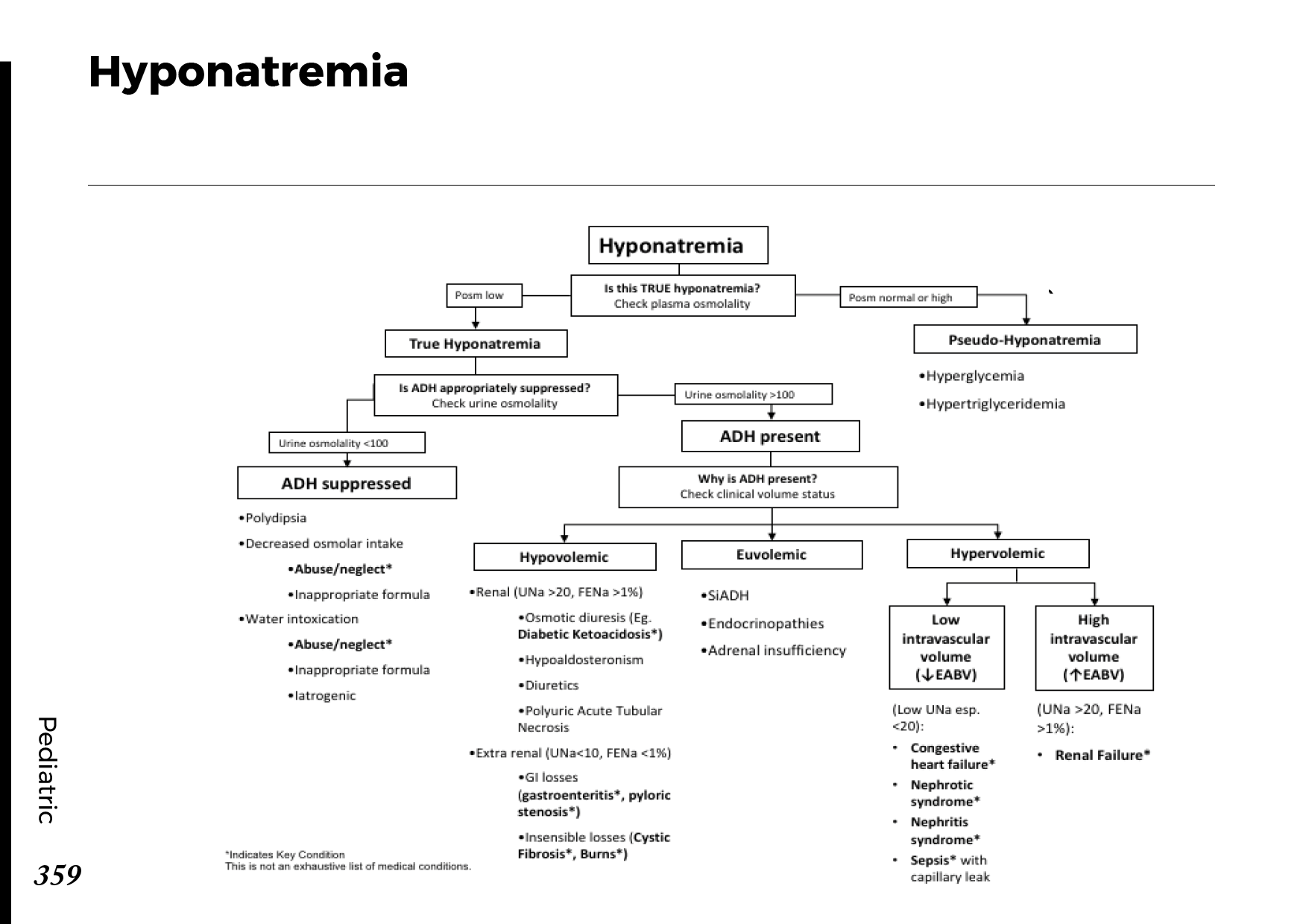
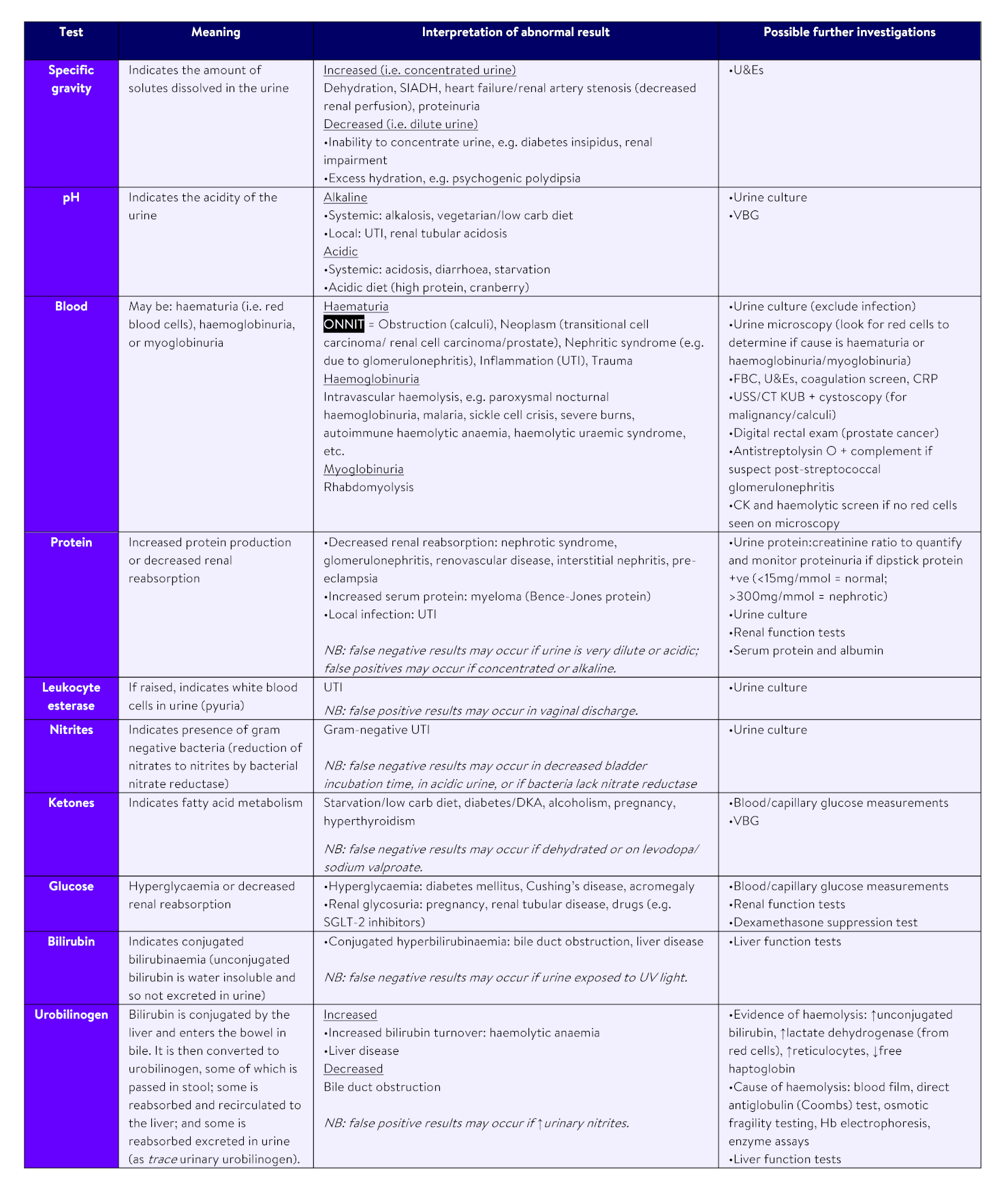
Interpretation of common urinalysis results:
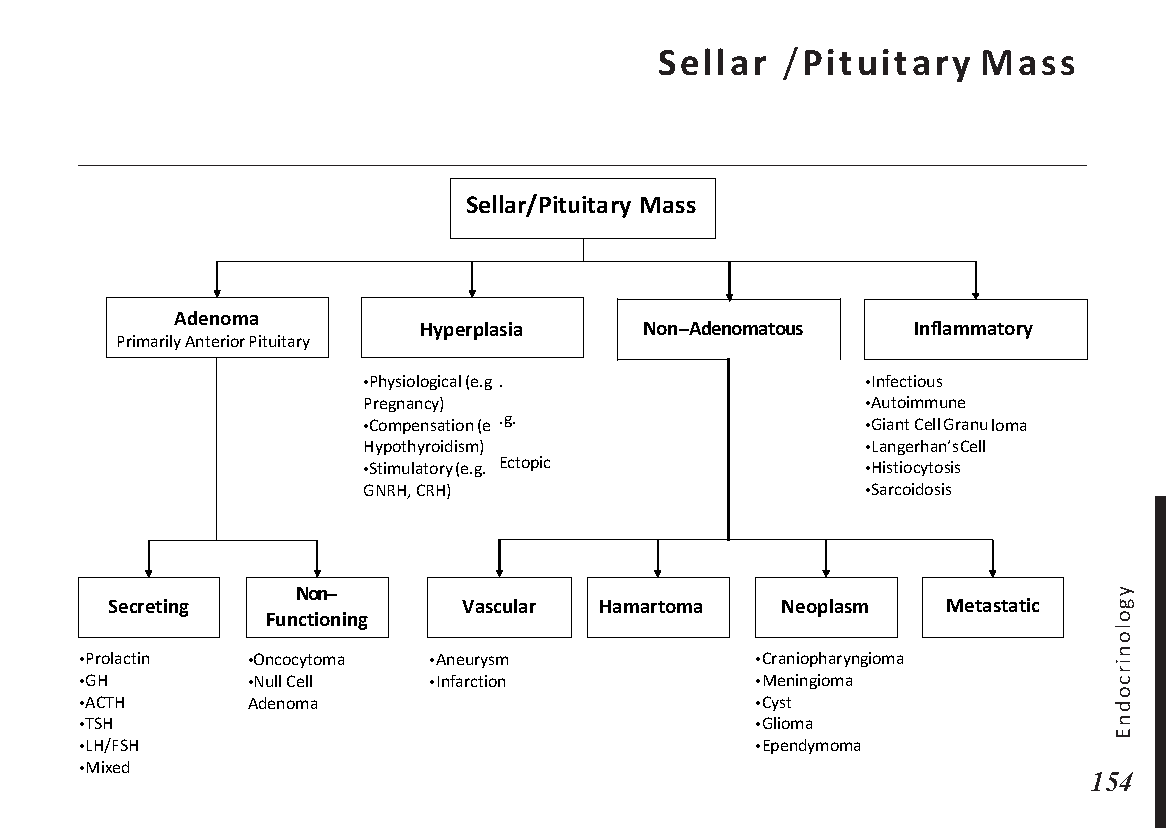
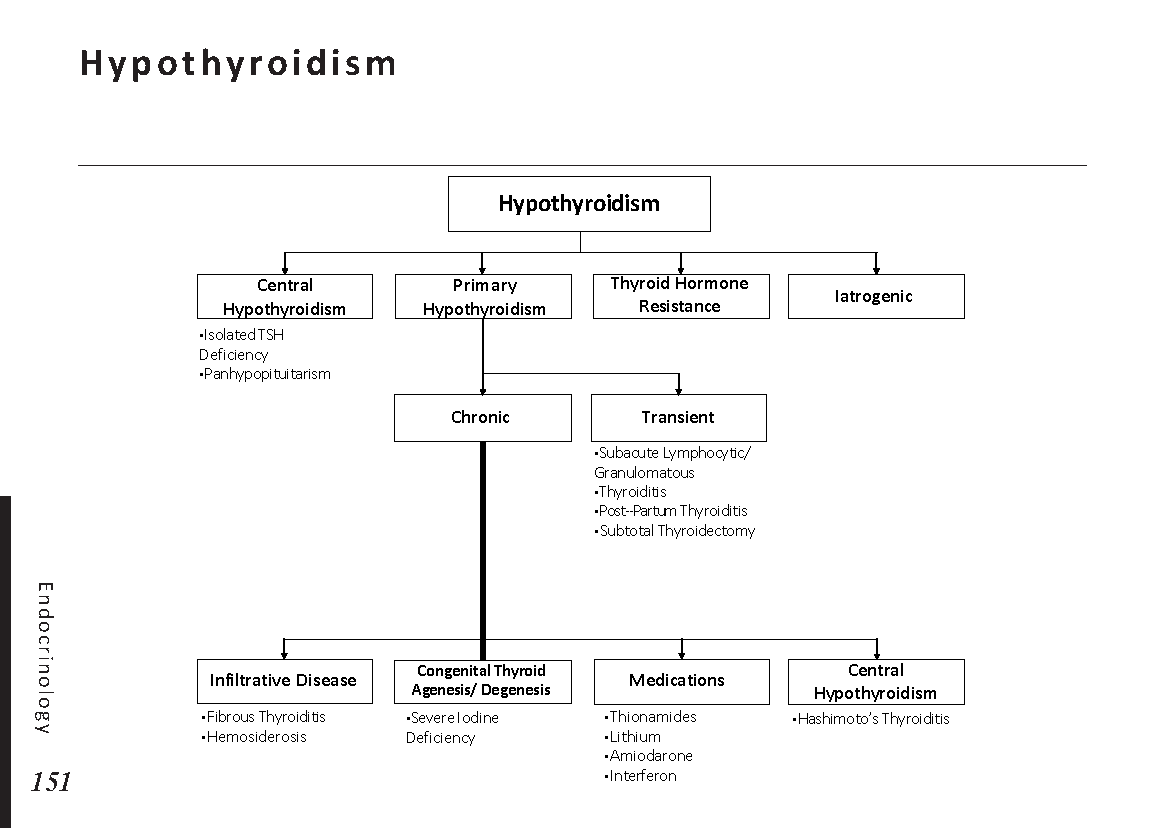
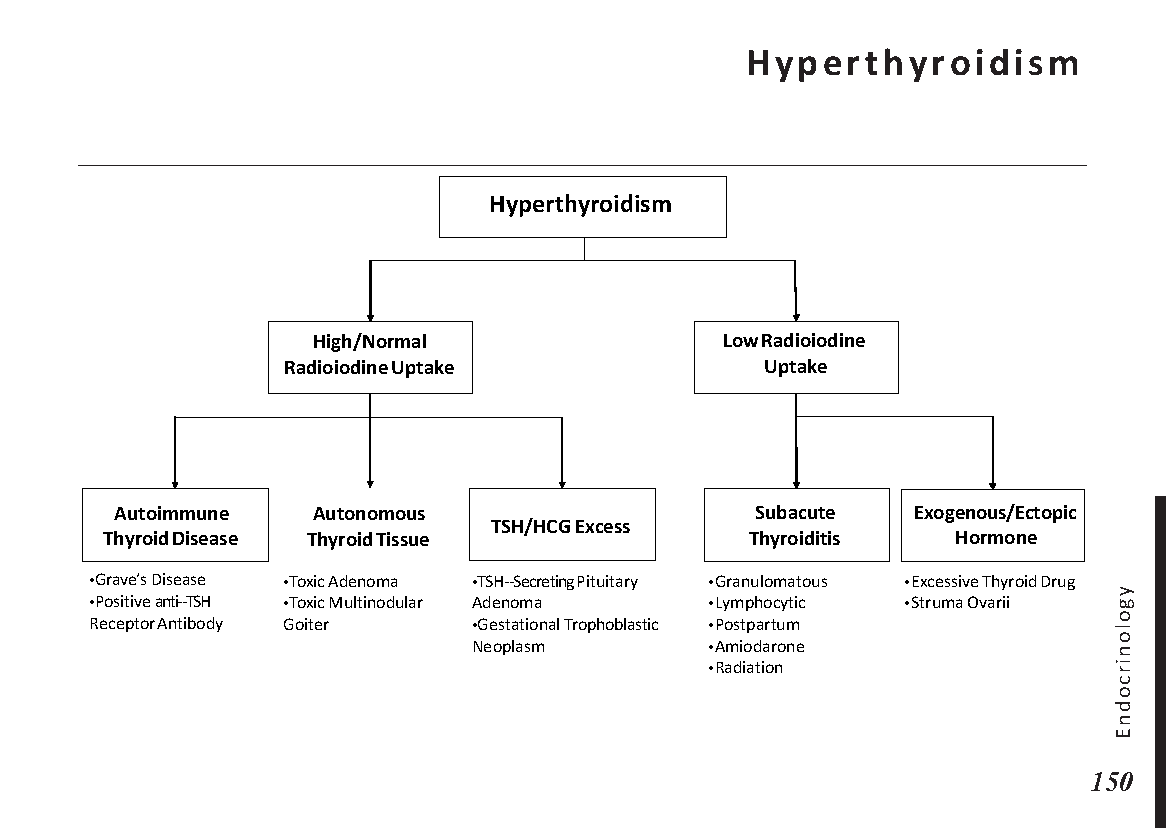
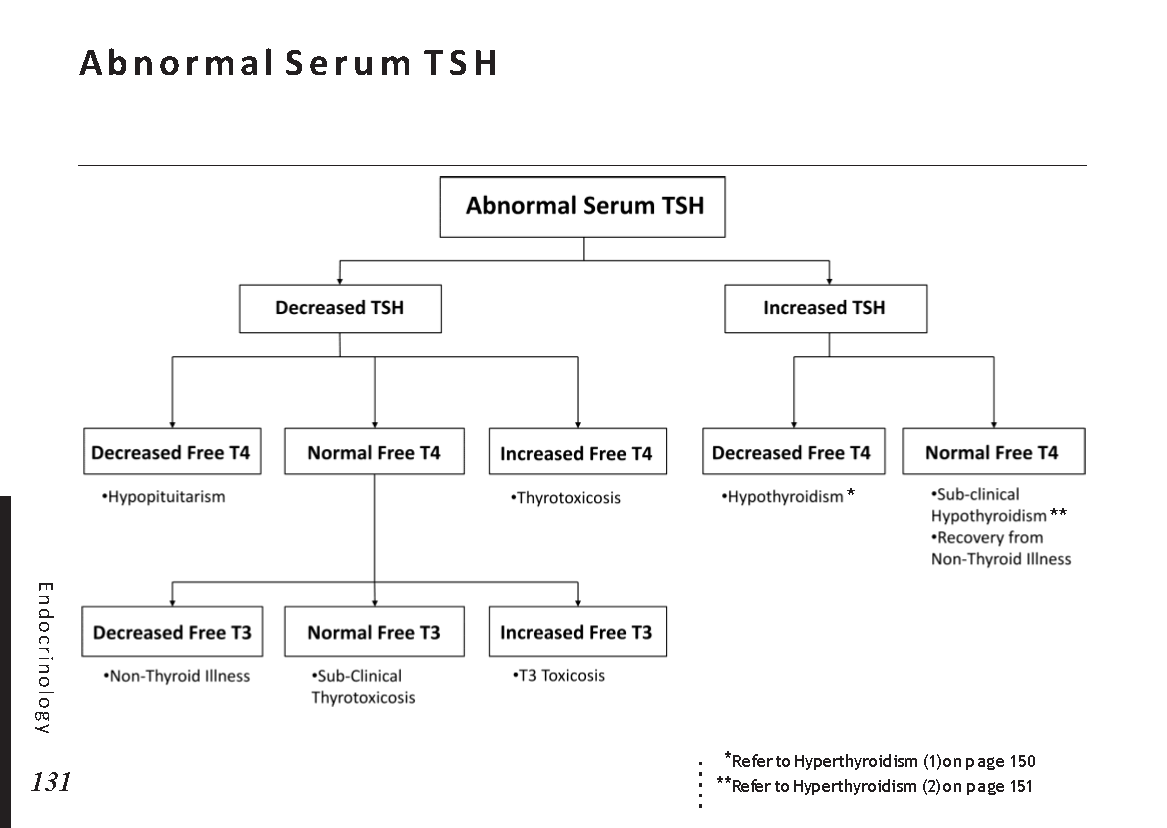
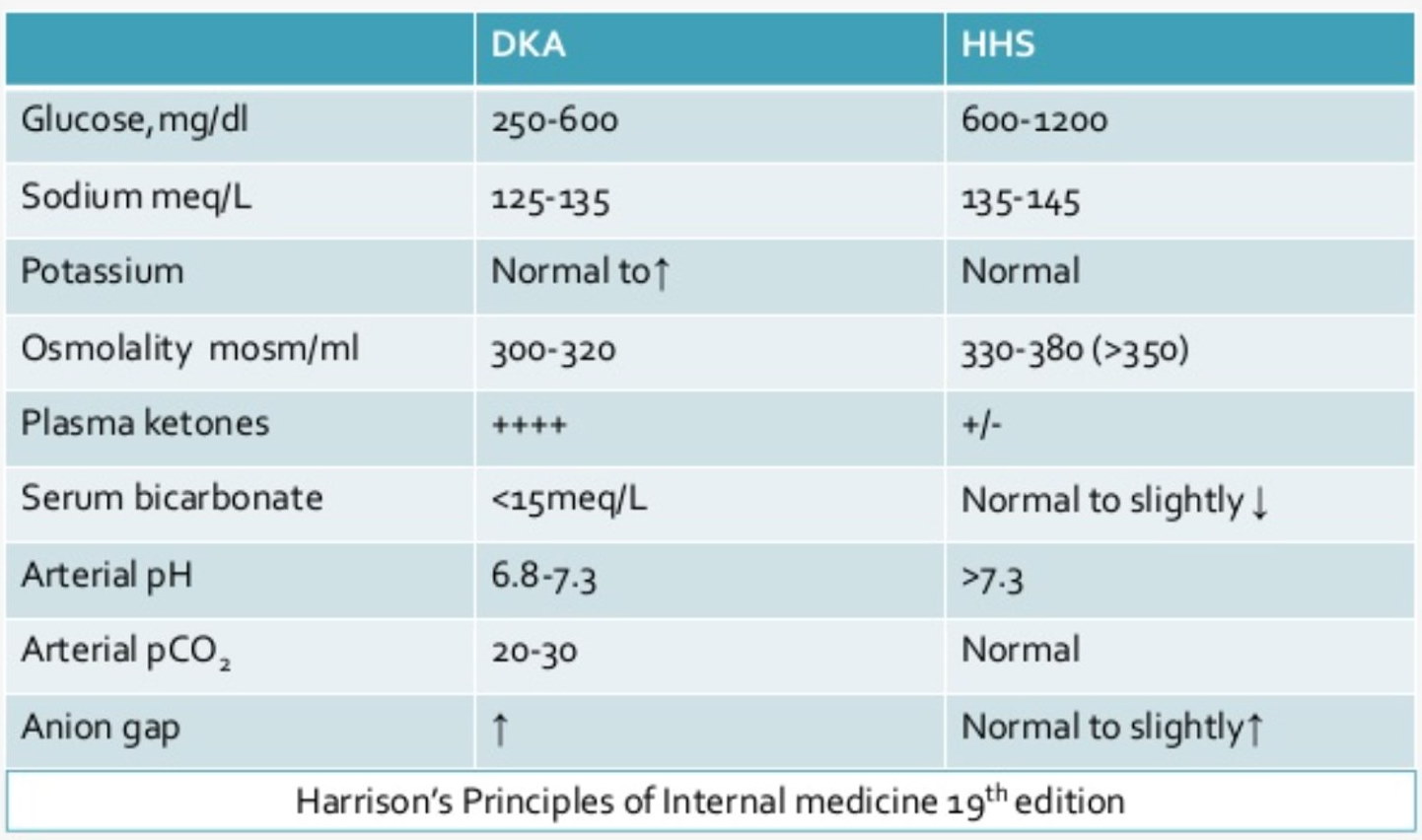
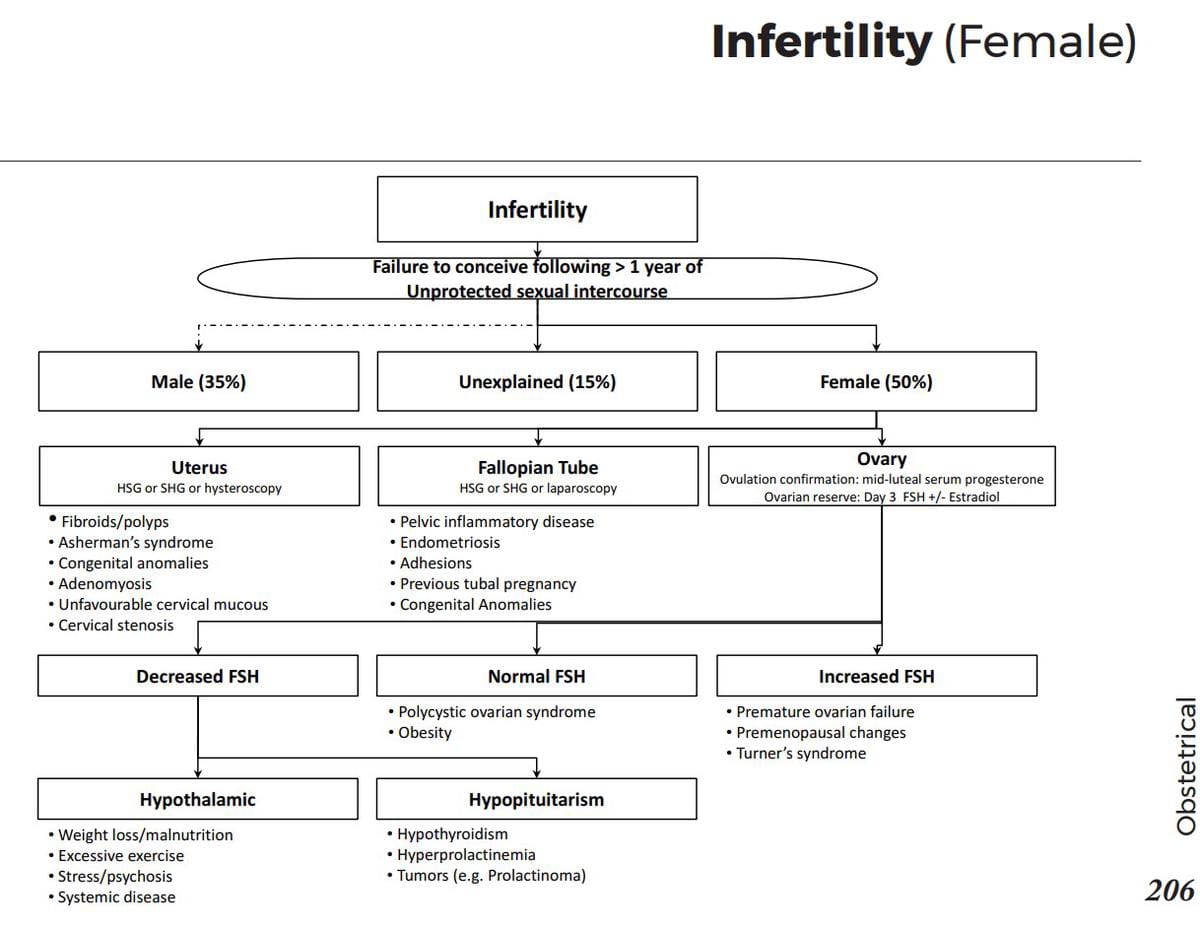
Endocrine glands and their hormones:
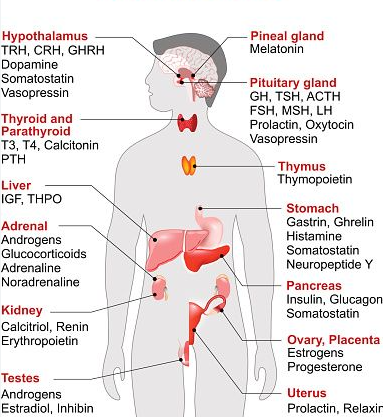
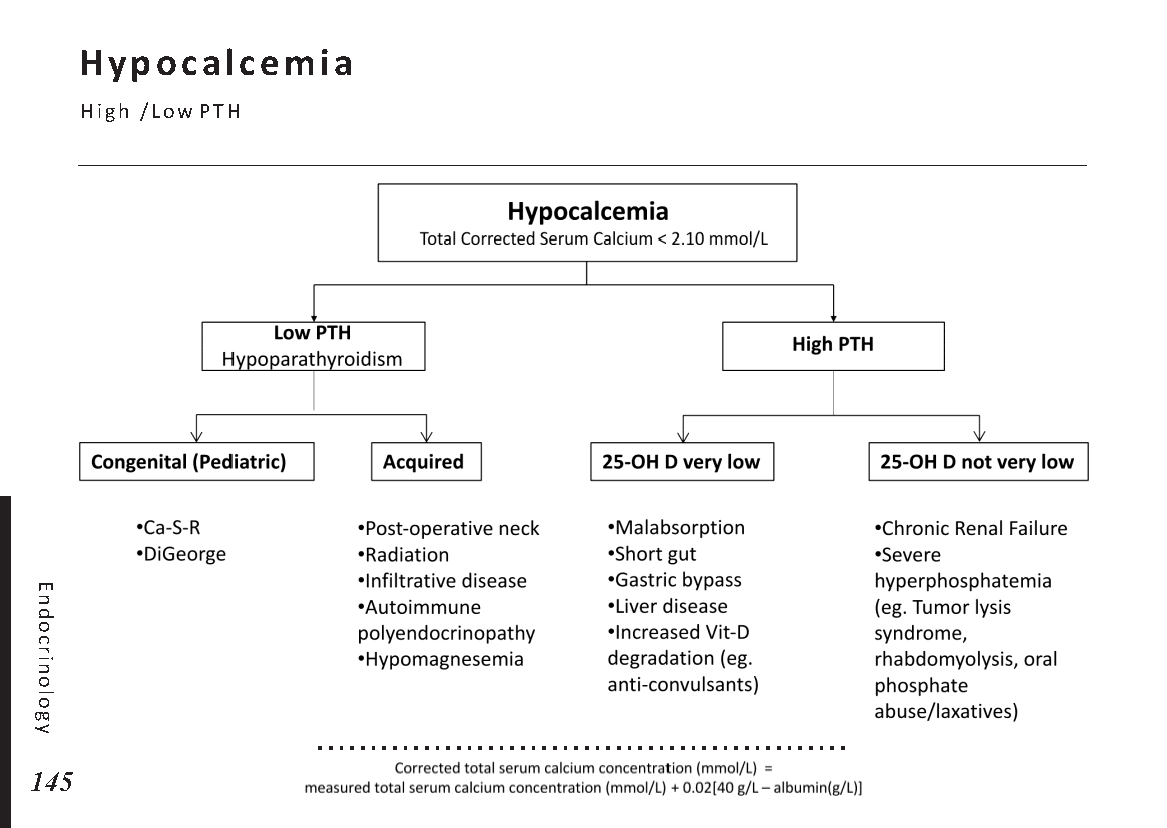
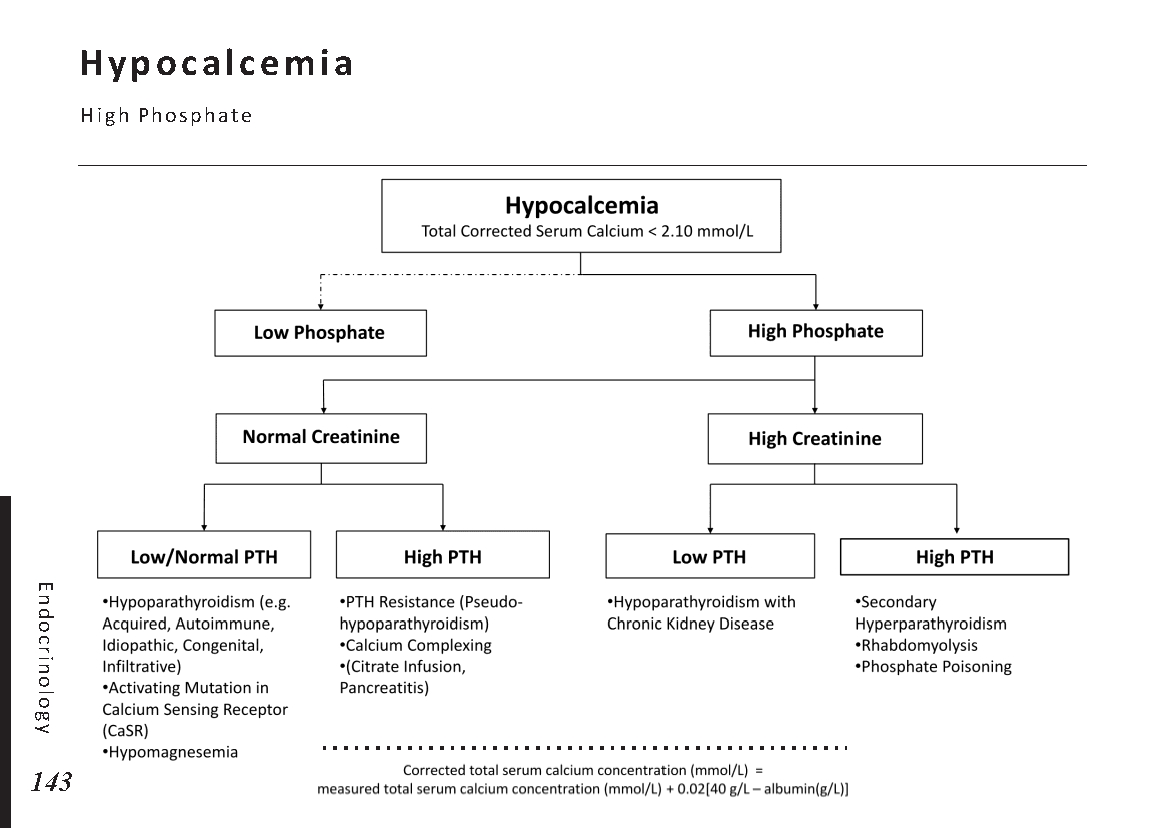
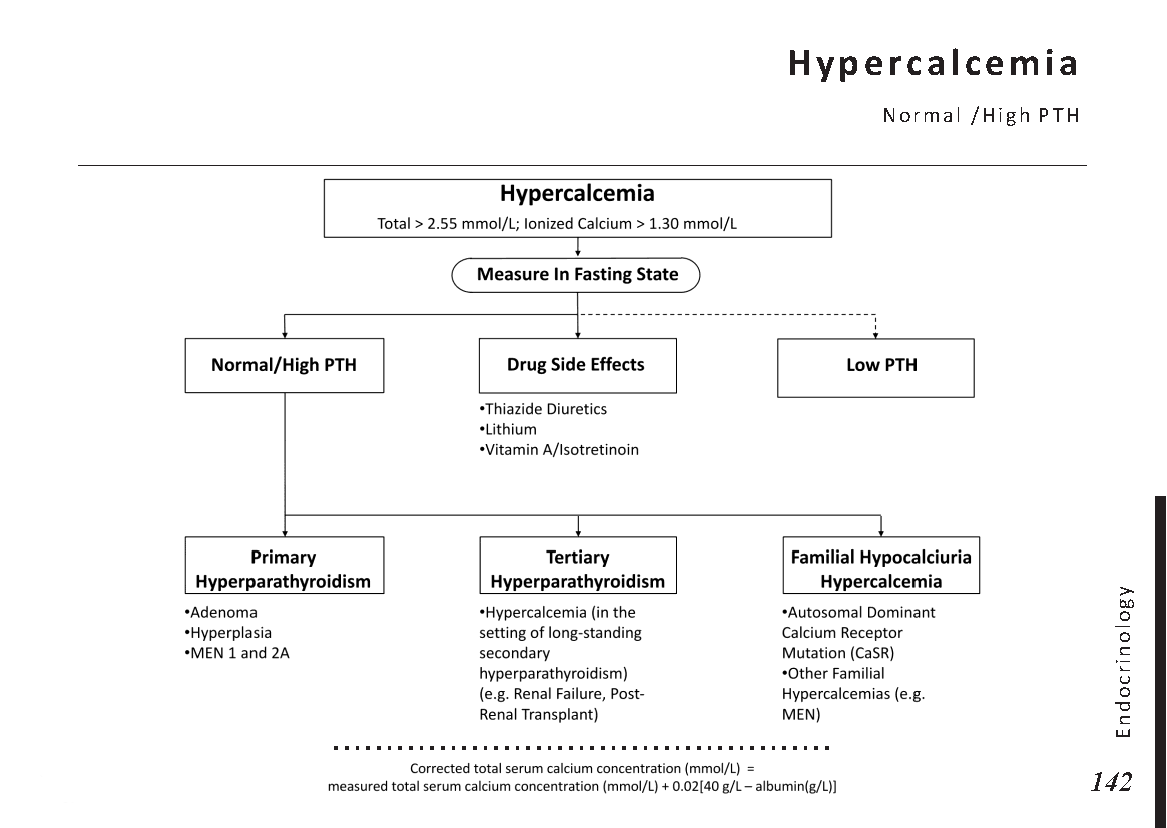
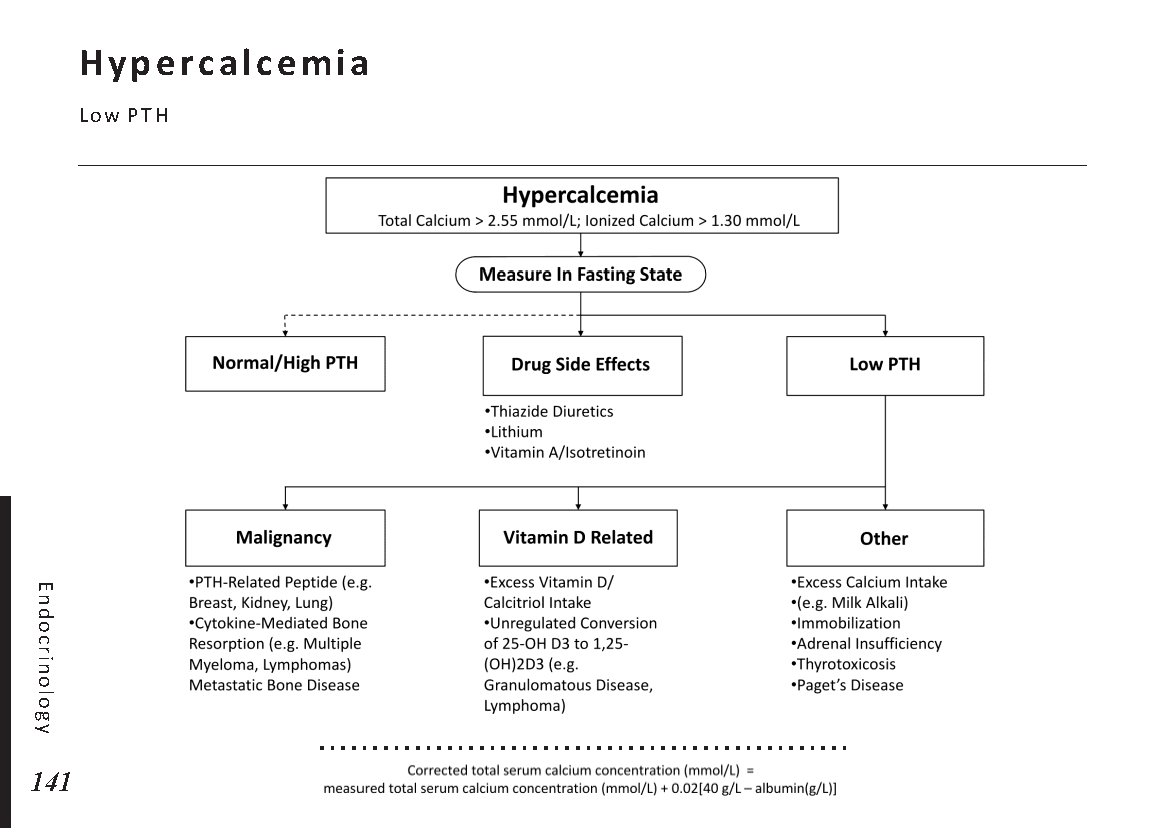
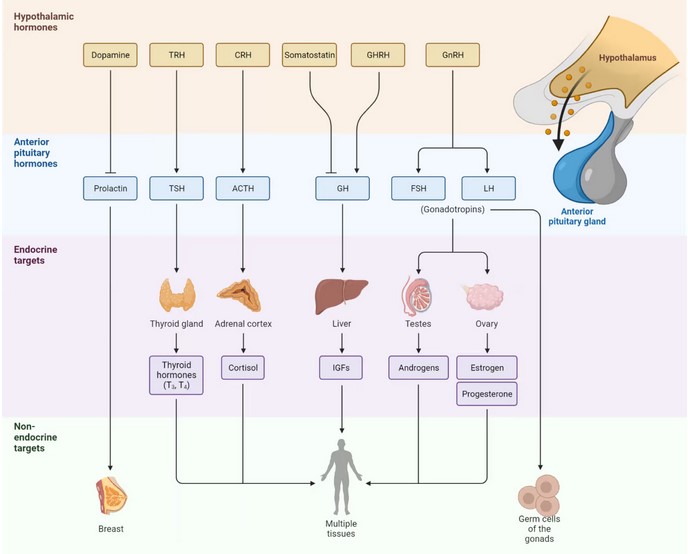
Hormonal pathways and feedback mechanisms:
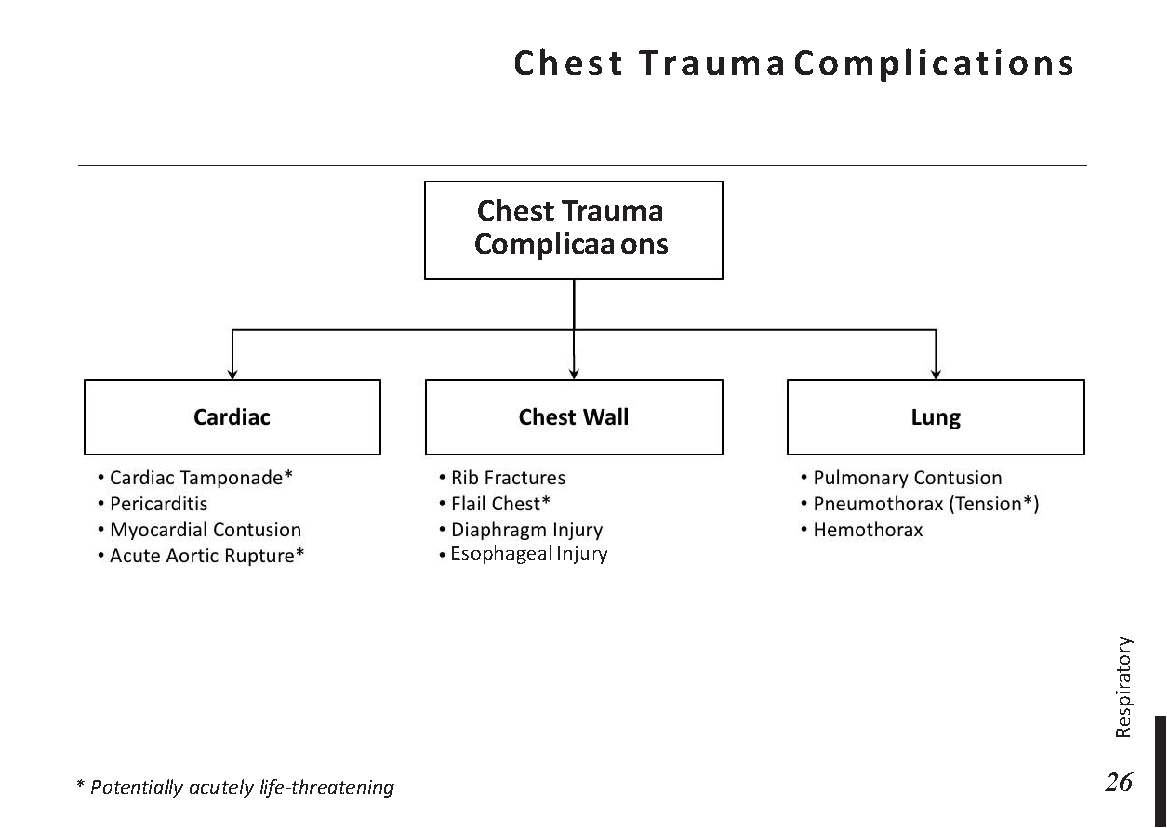
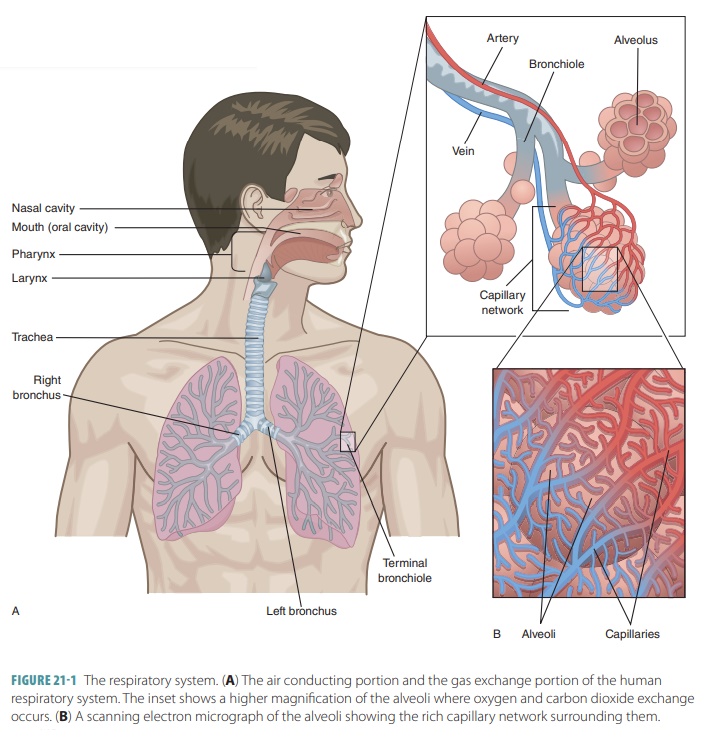
Lung anatomy and physiology:
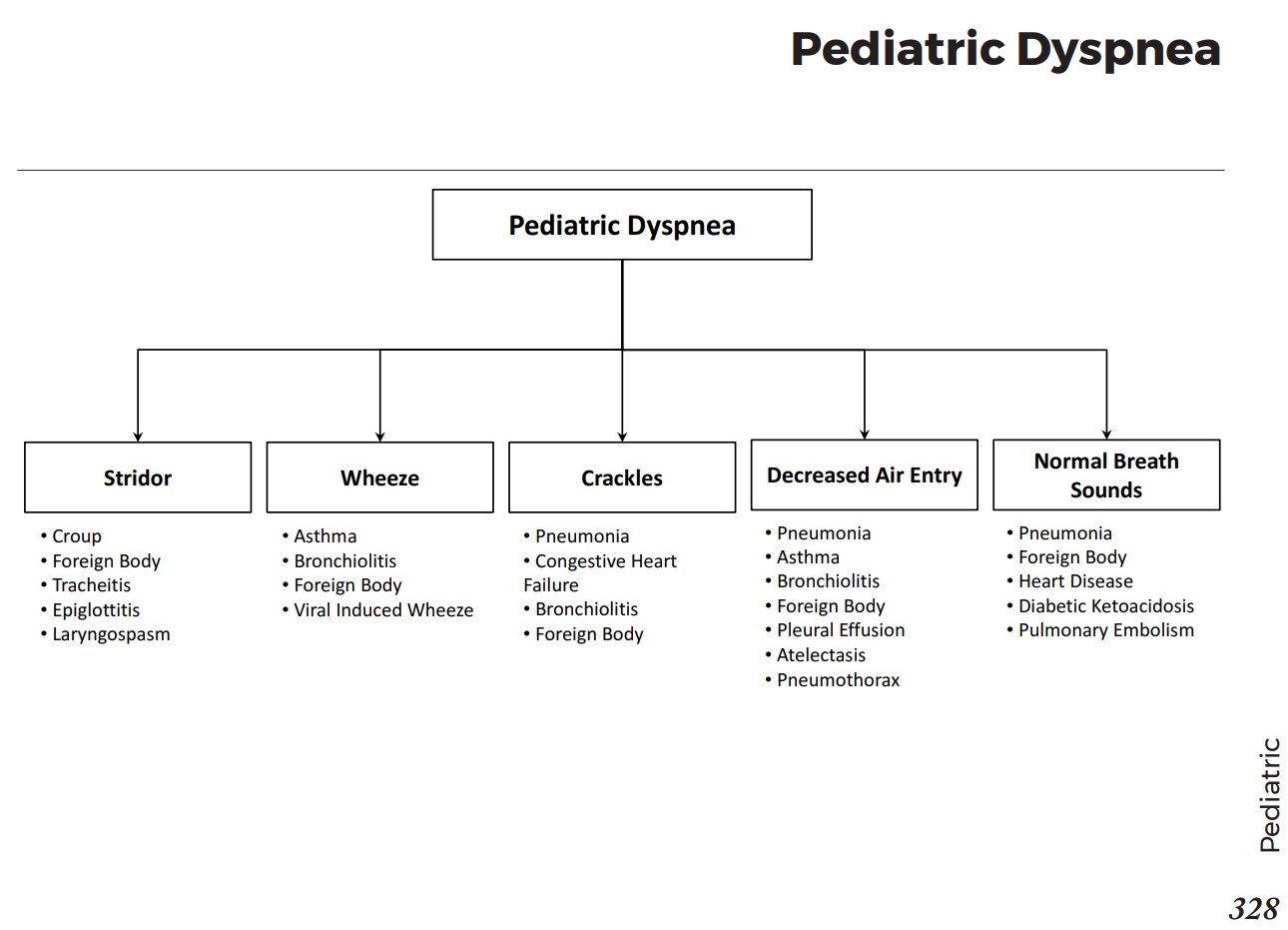
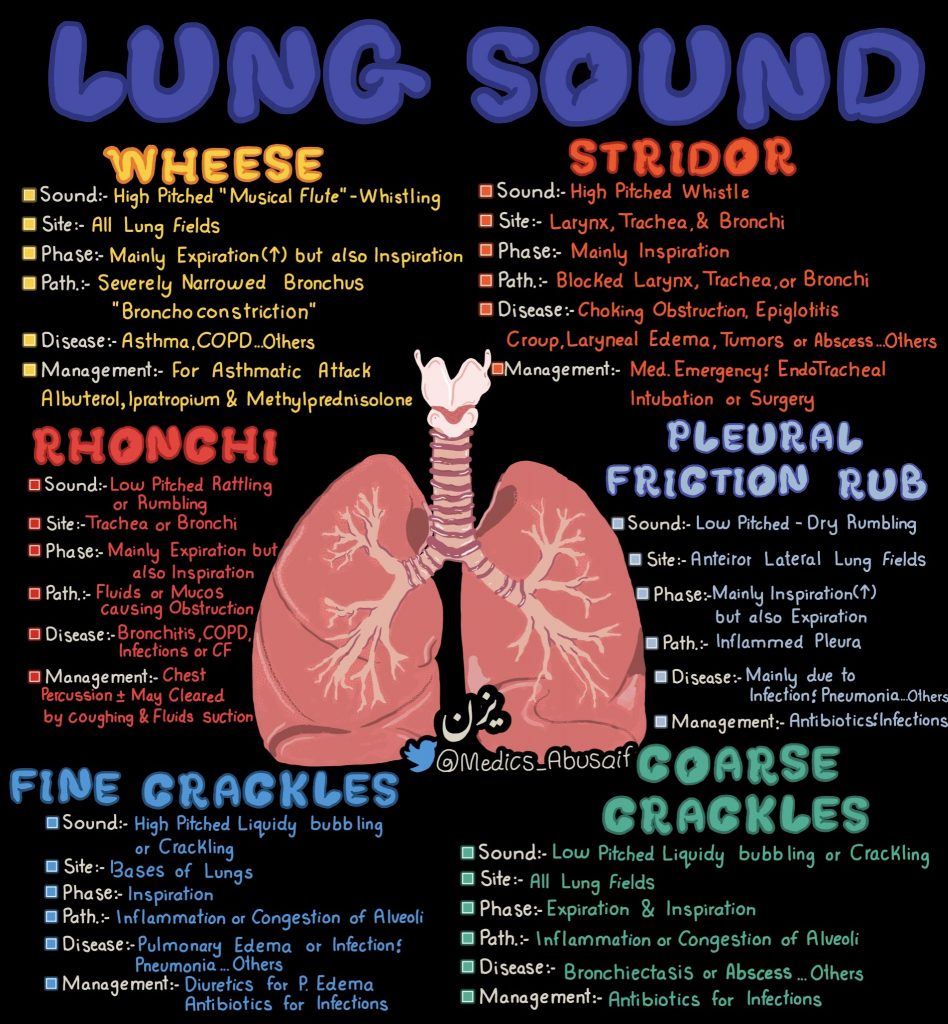
Abnormal lung sounds:
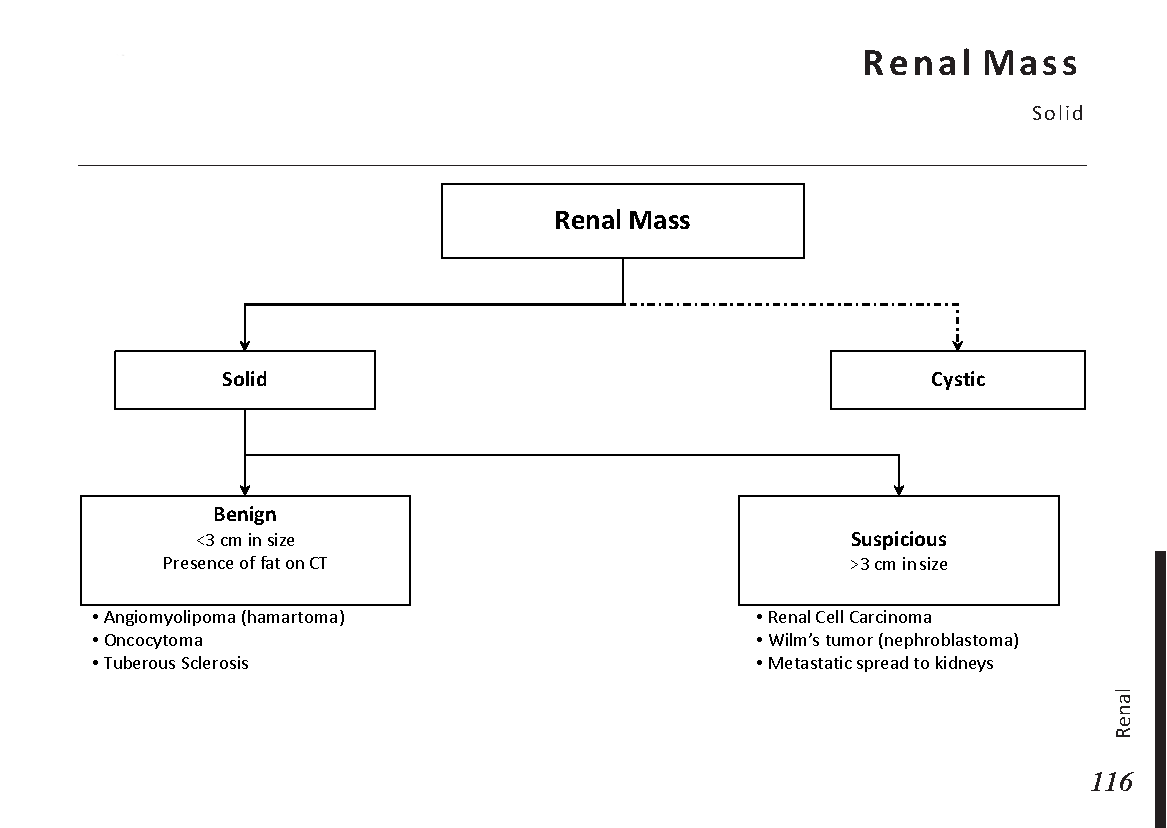
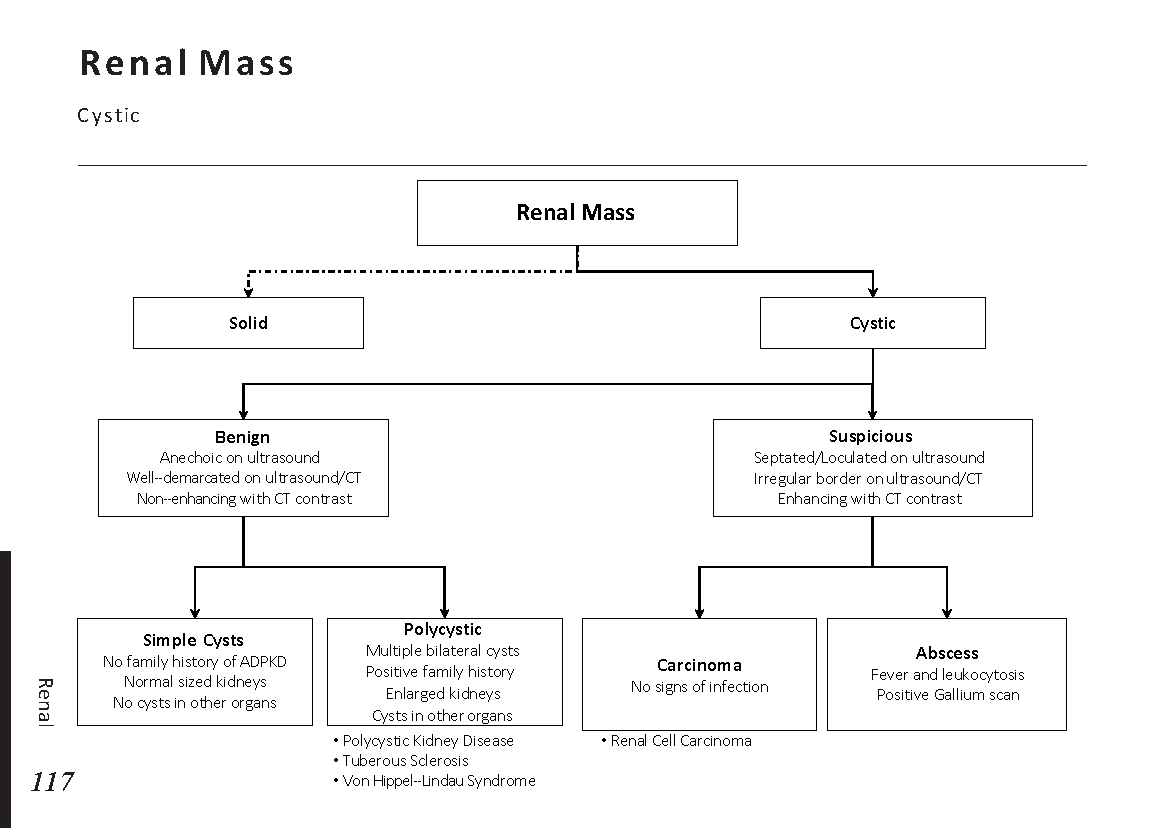
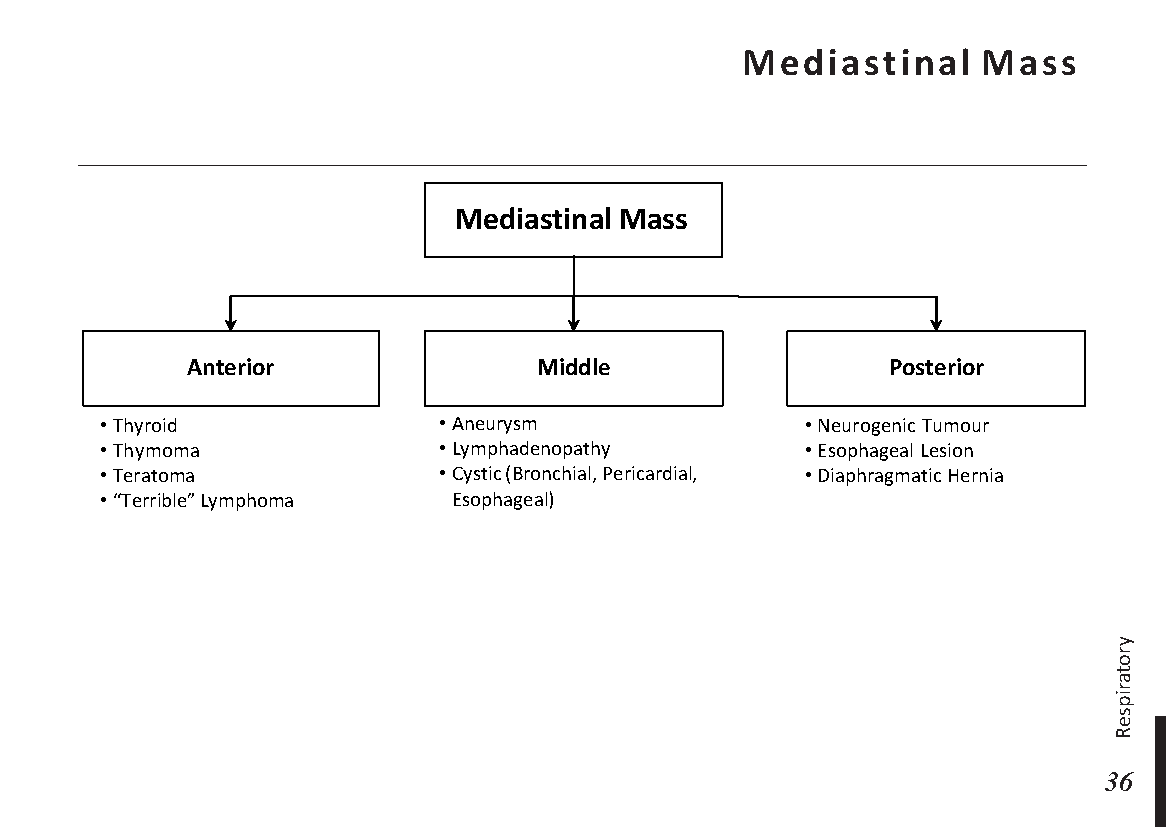
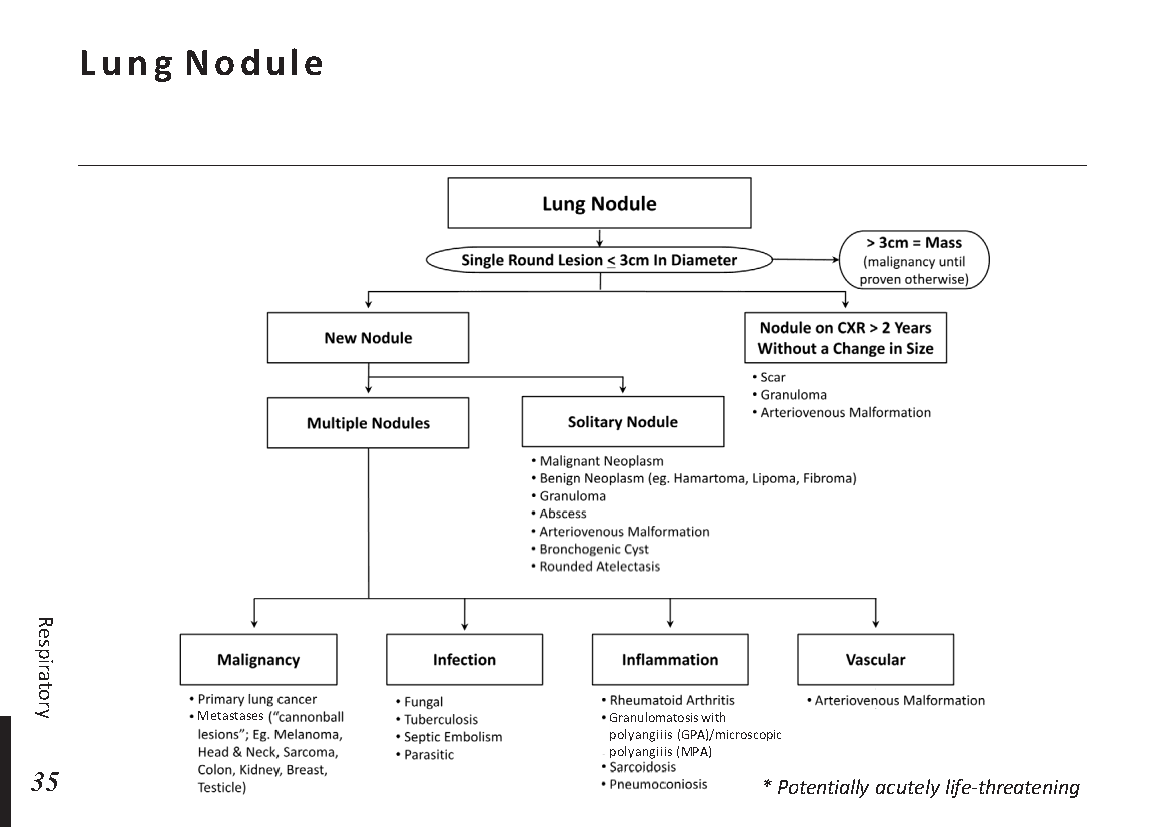
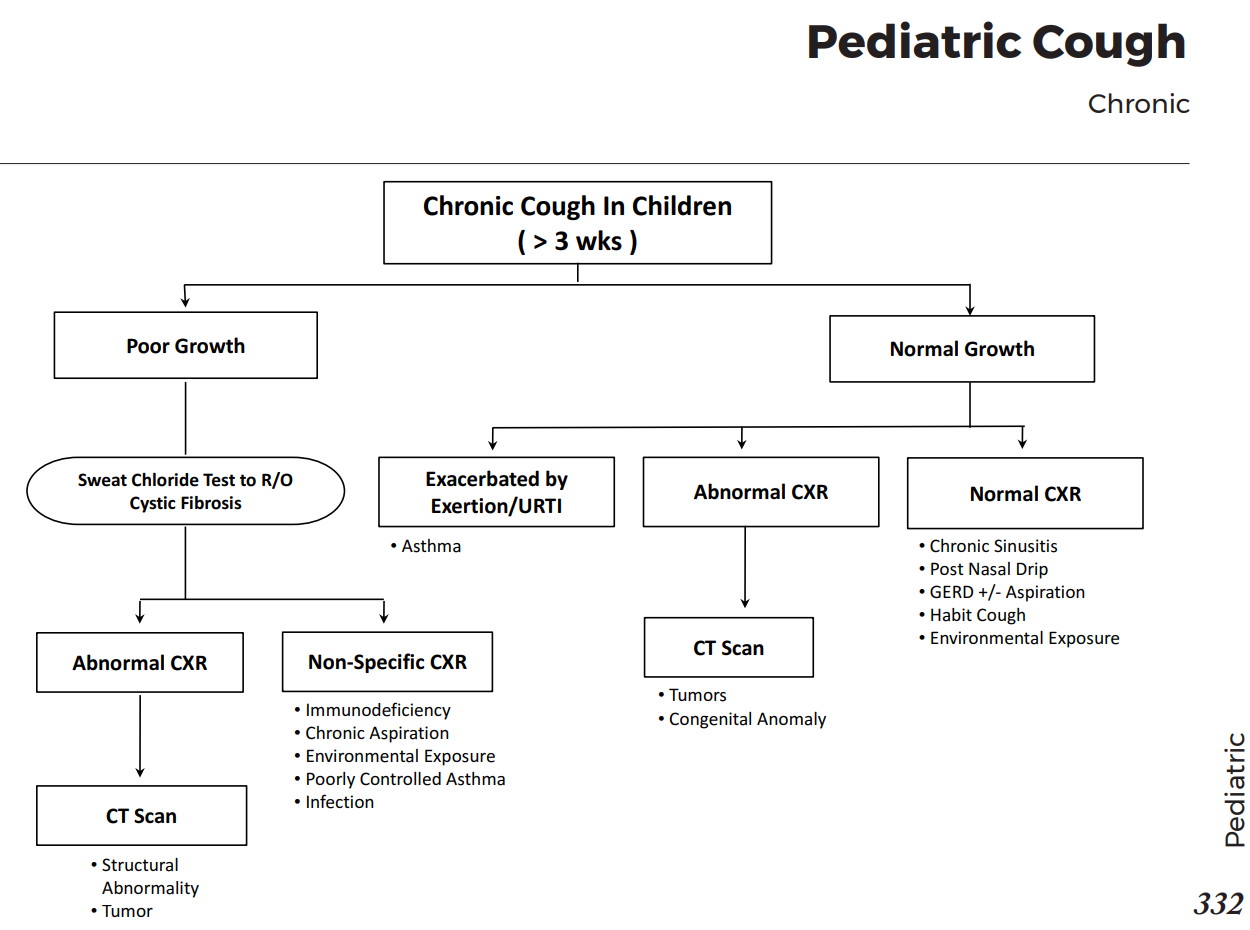
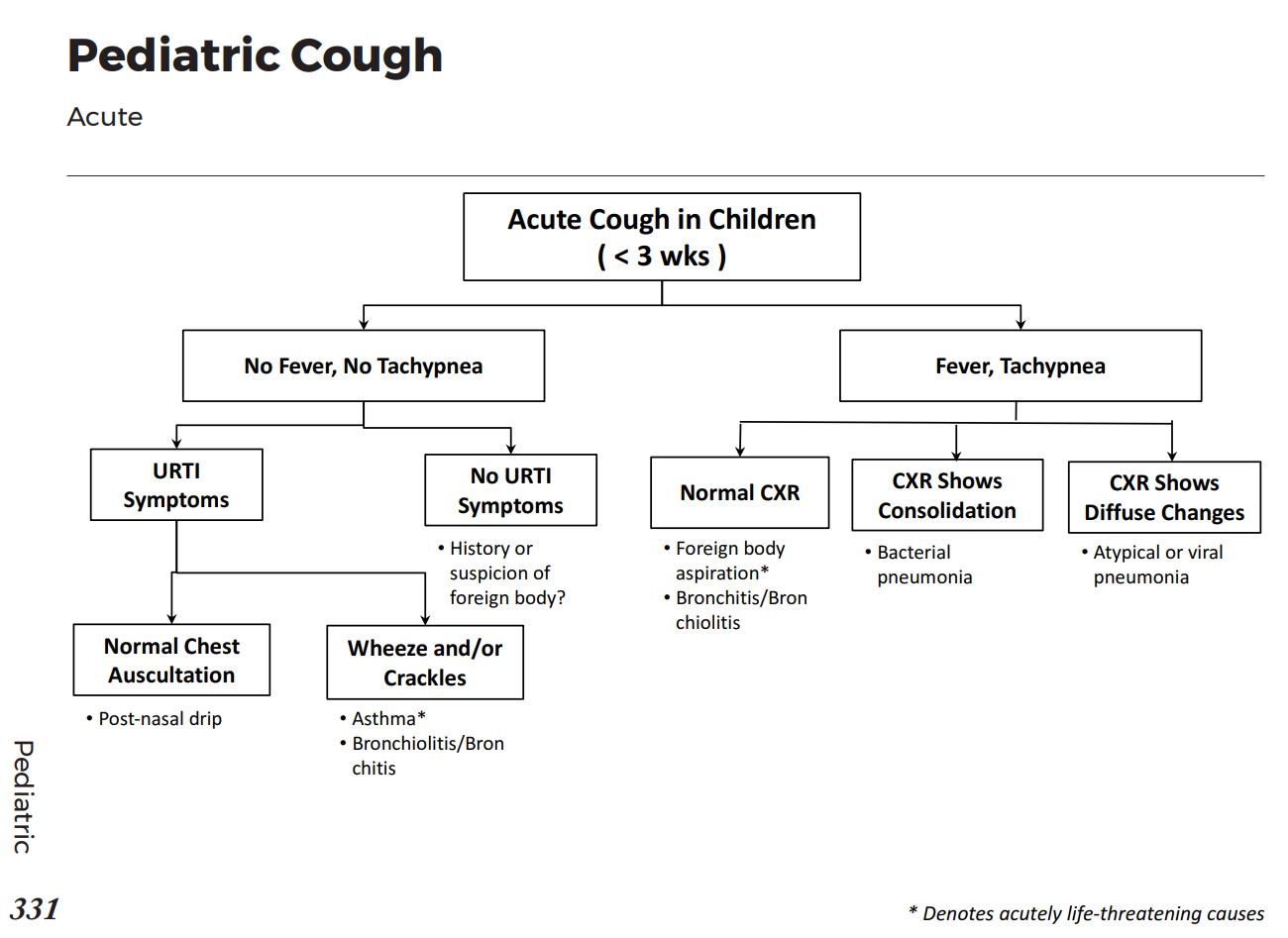
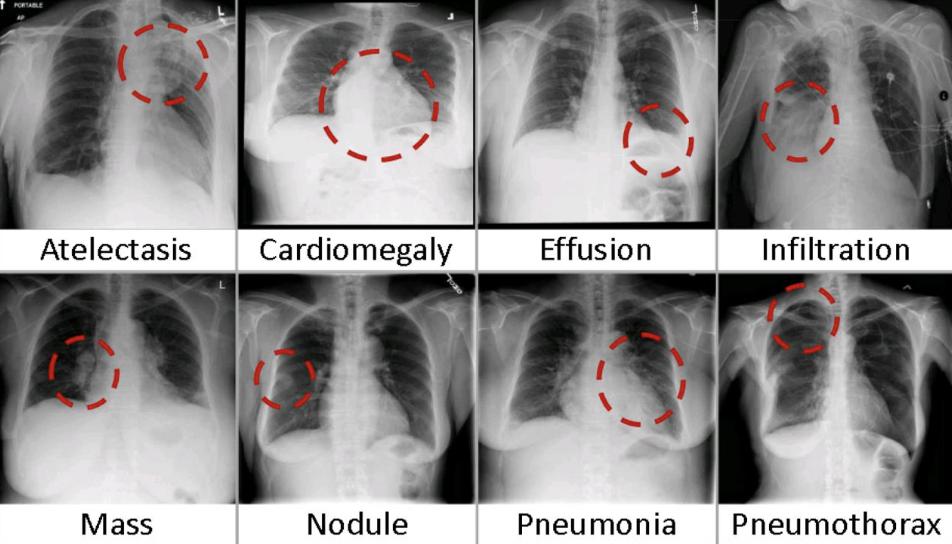
Common X-ray Findings:
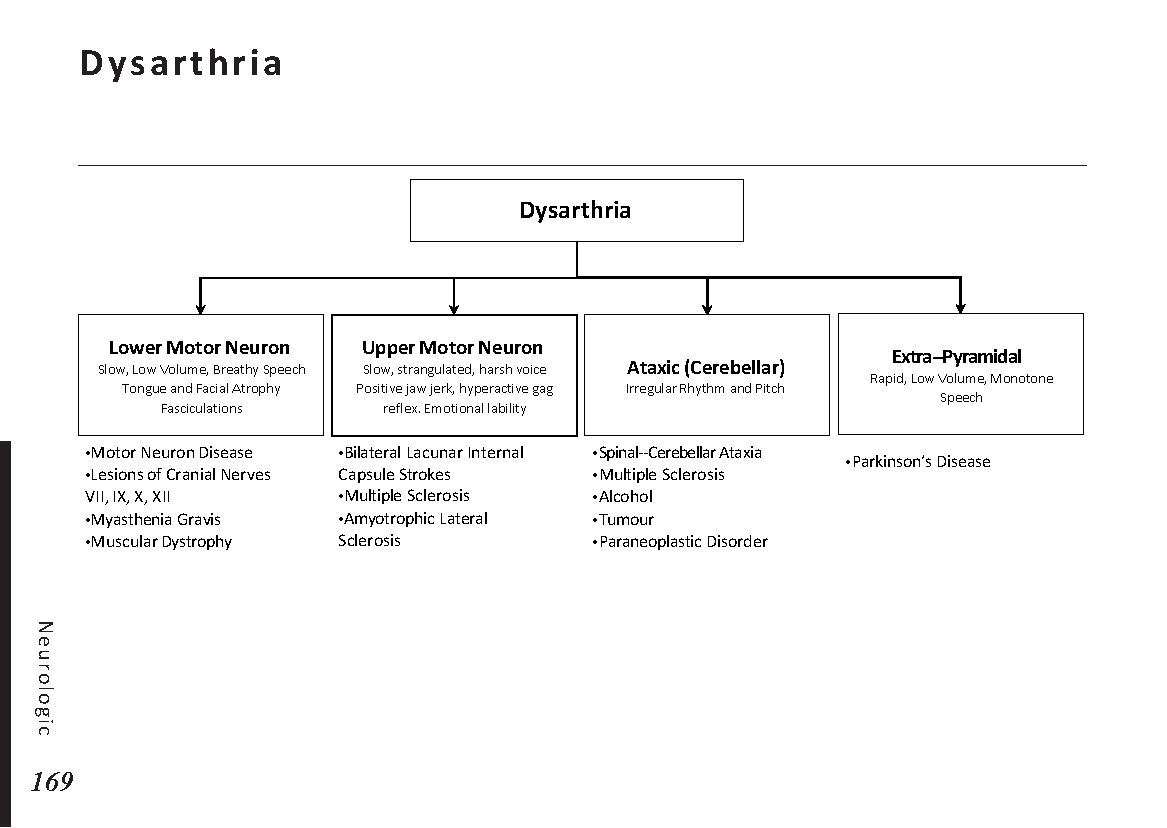
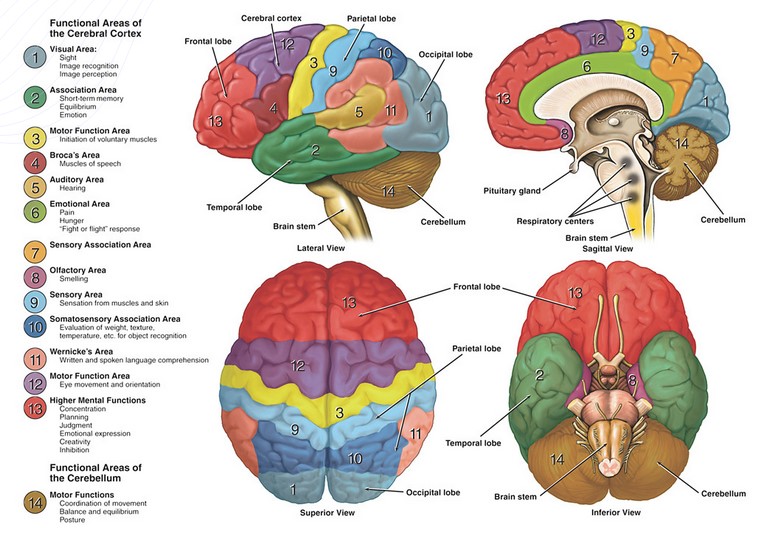
Major brain regions and their functions:
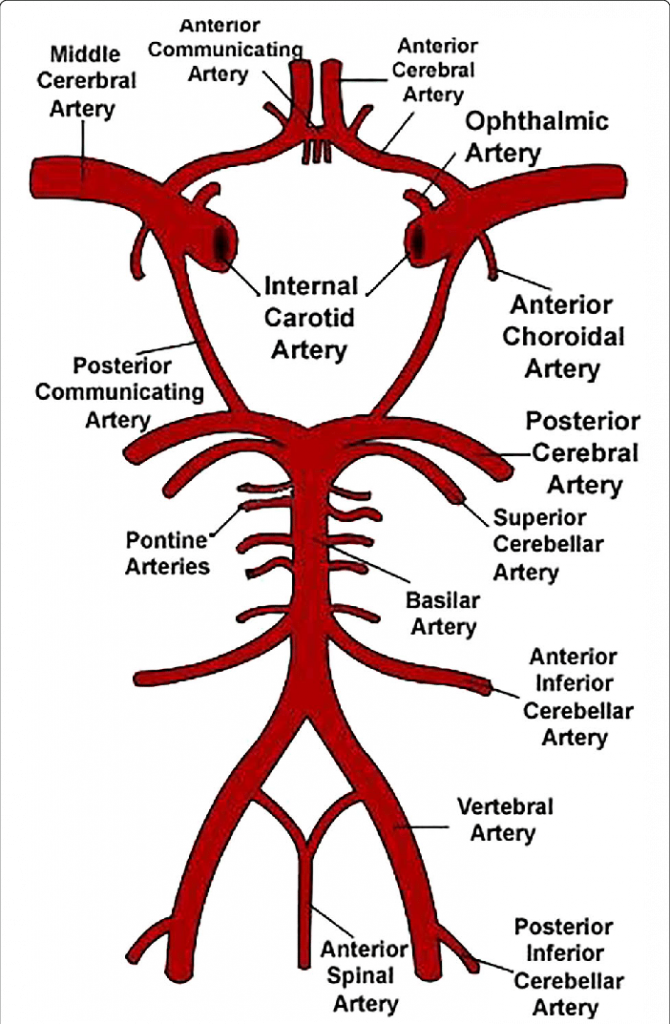
Circle of Willis:
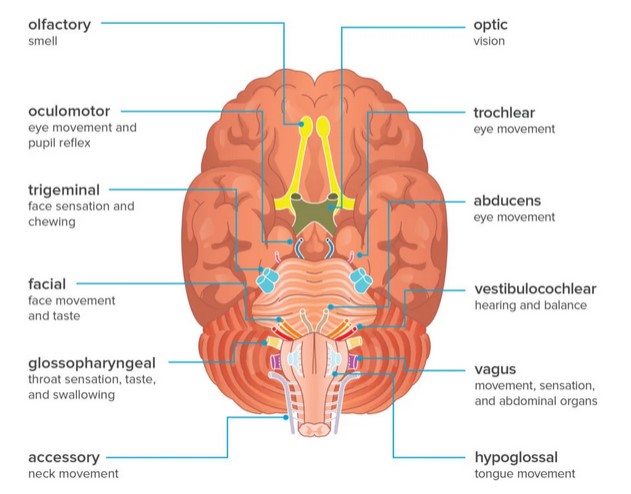
Cranial nerves and their functions:
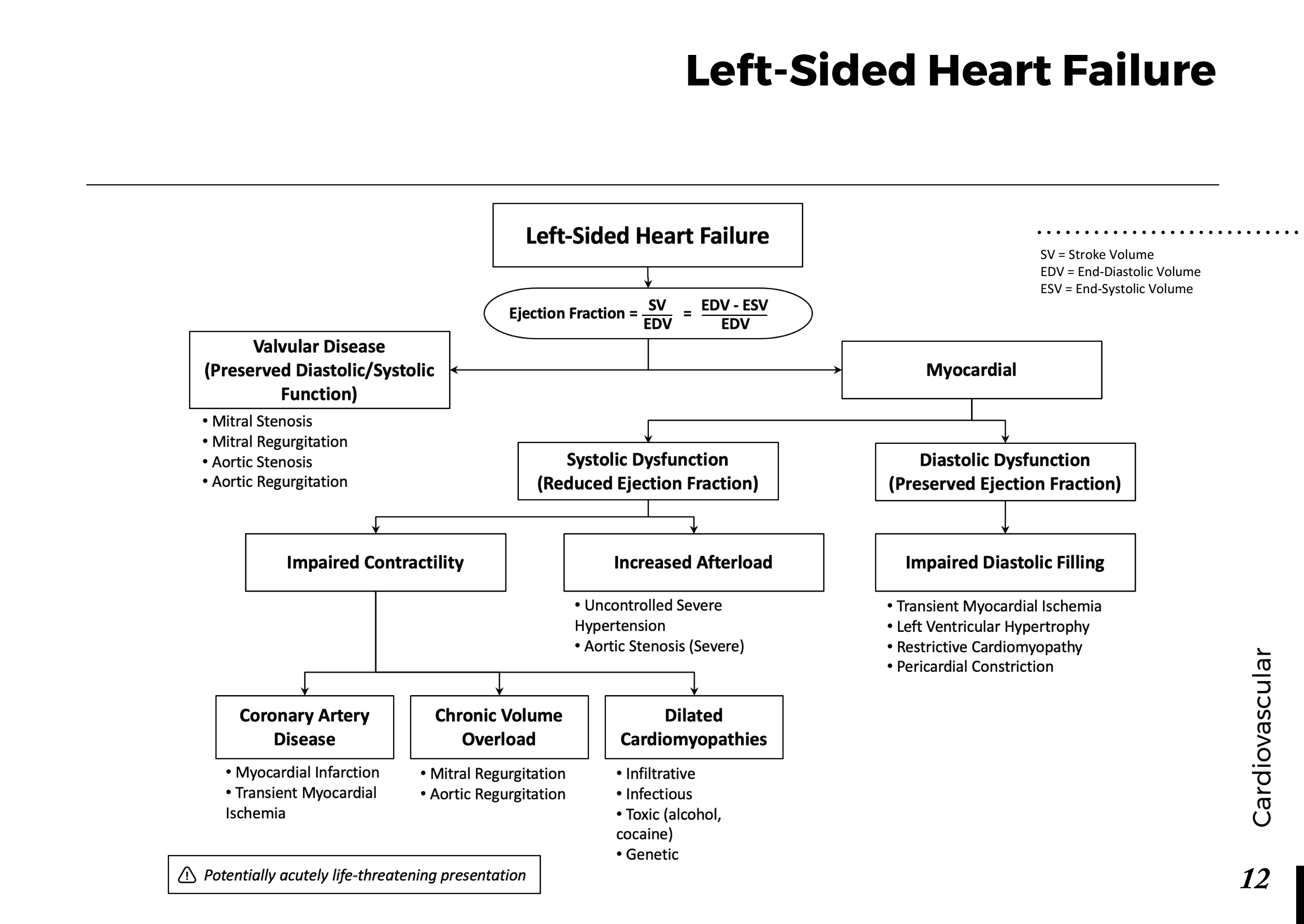
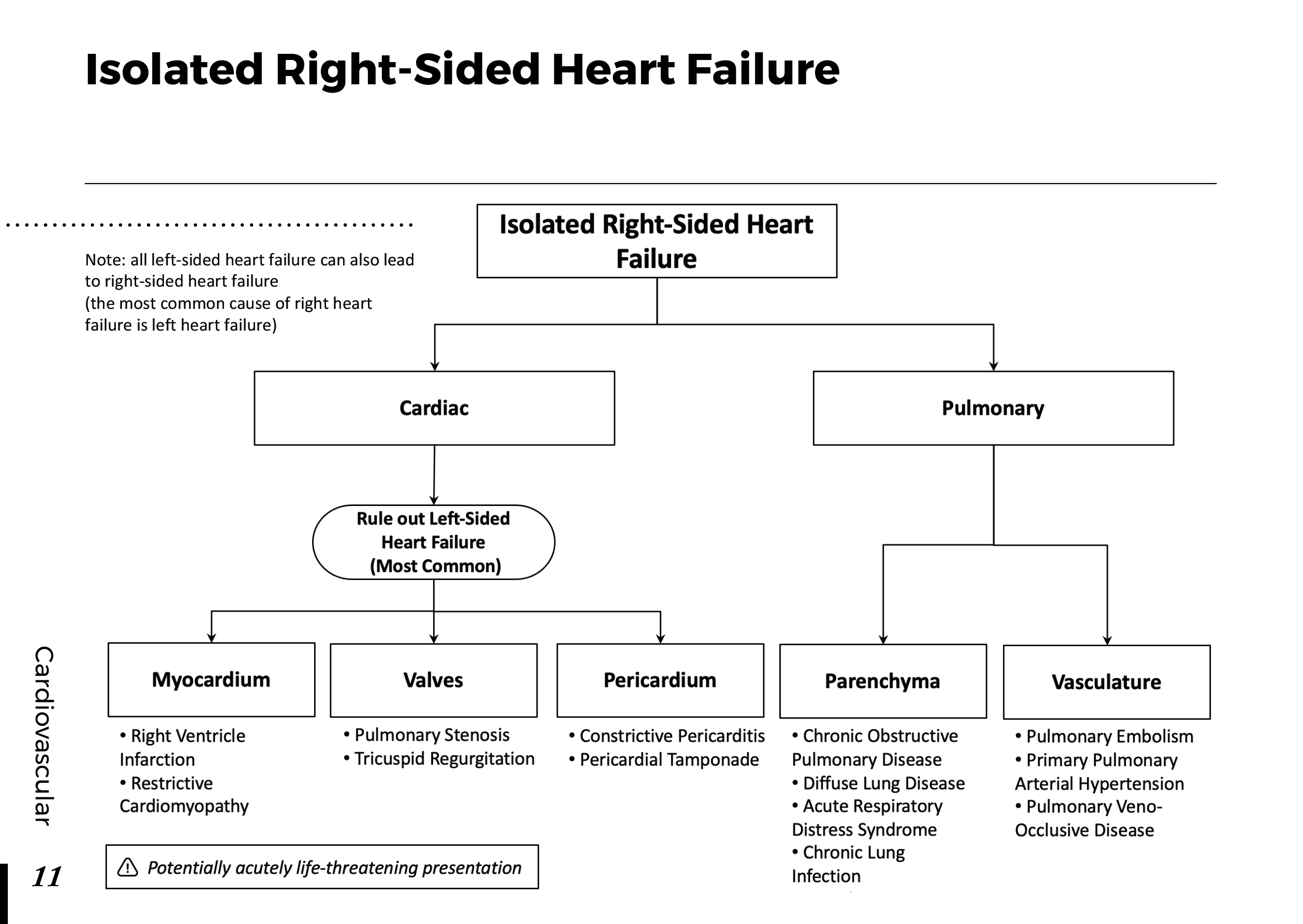
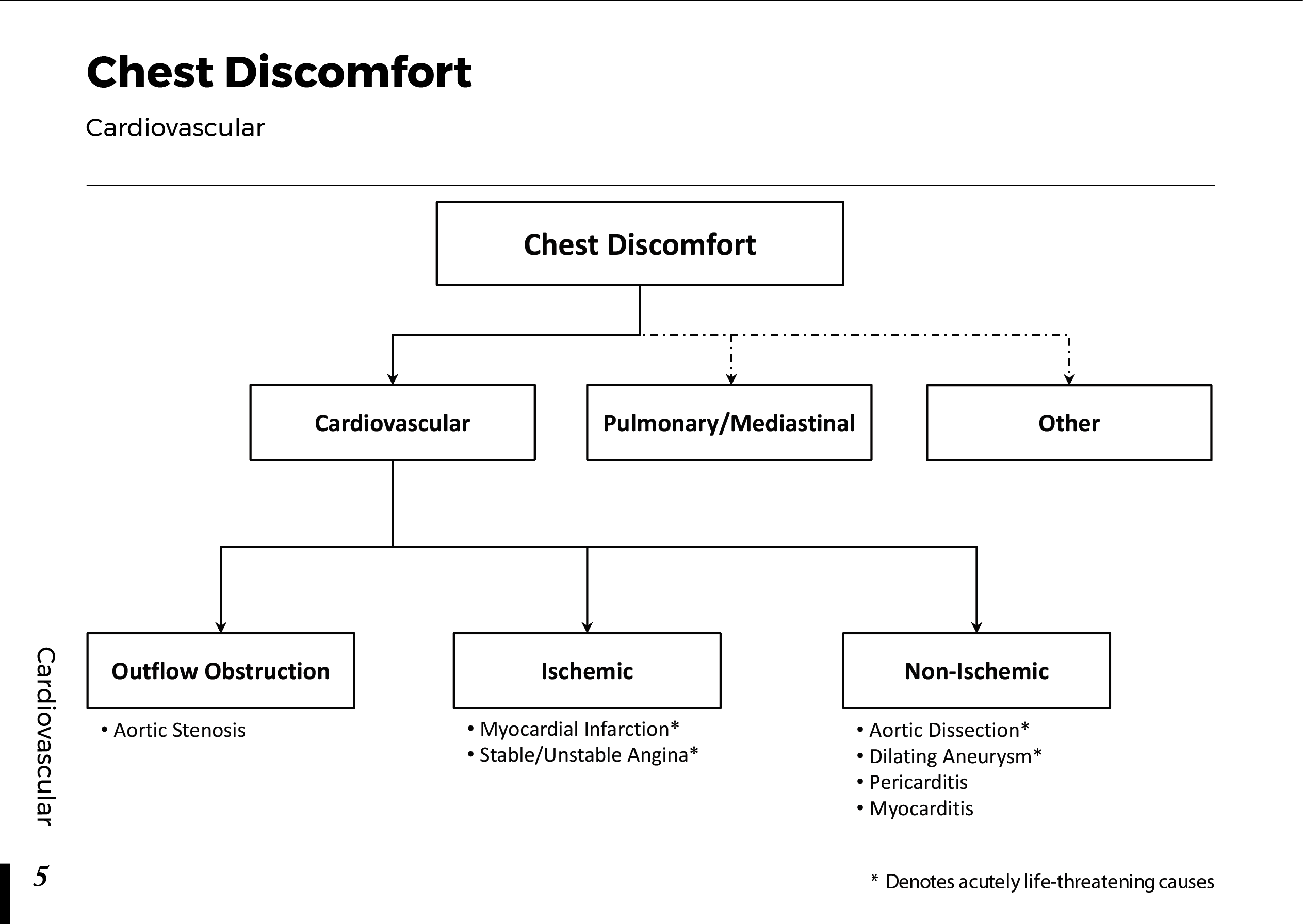
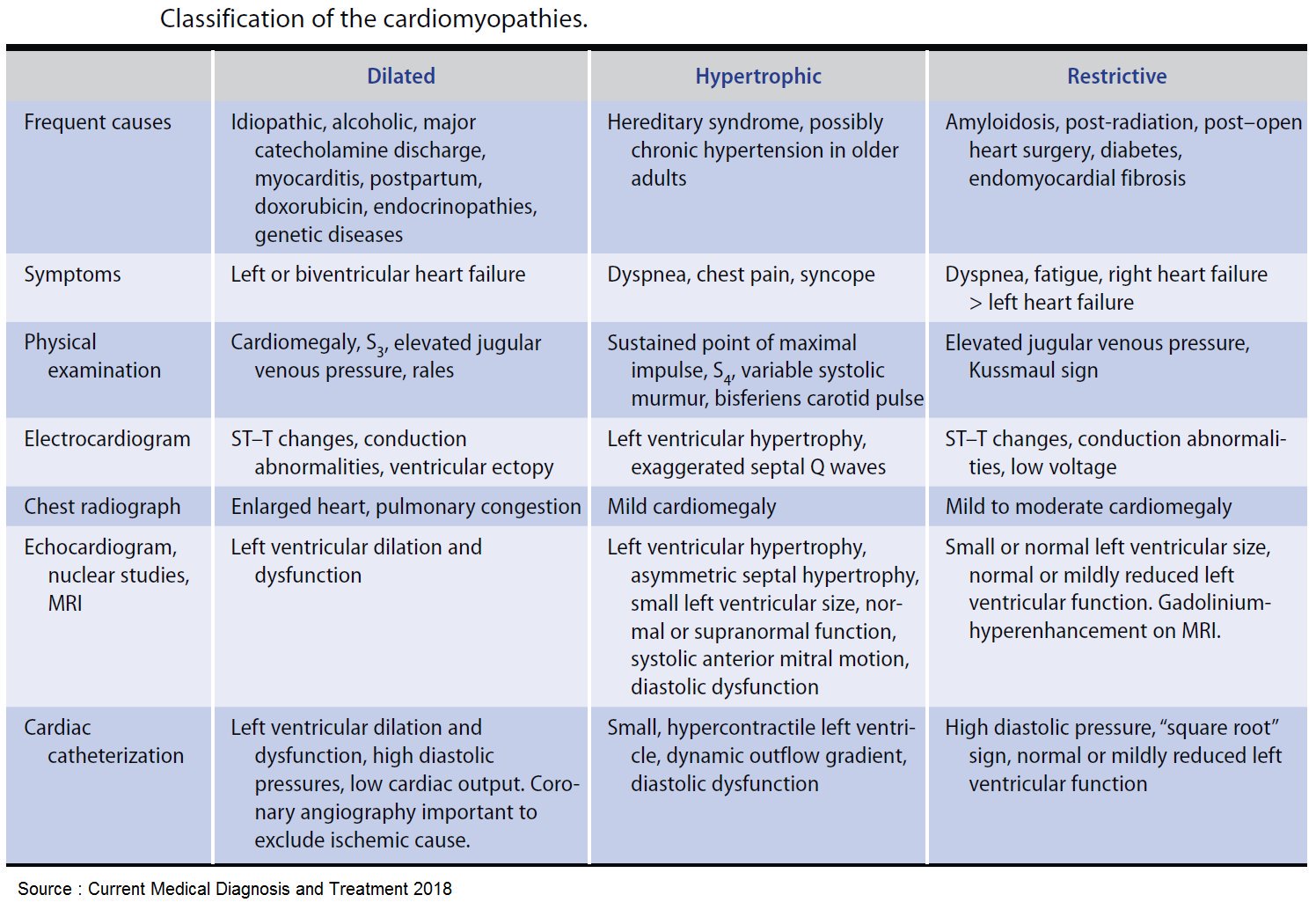
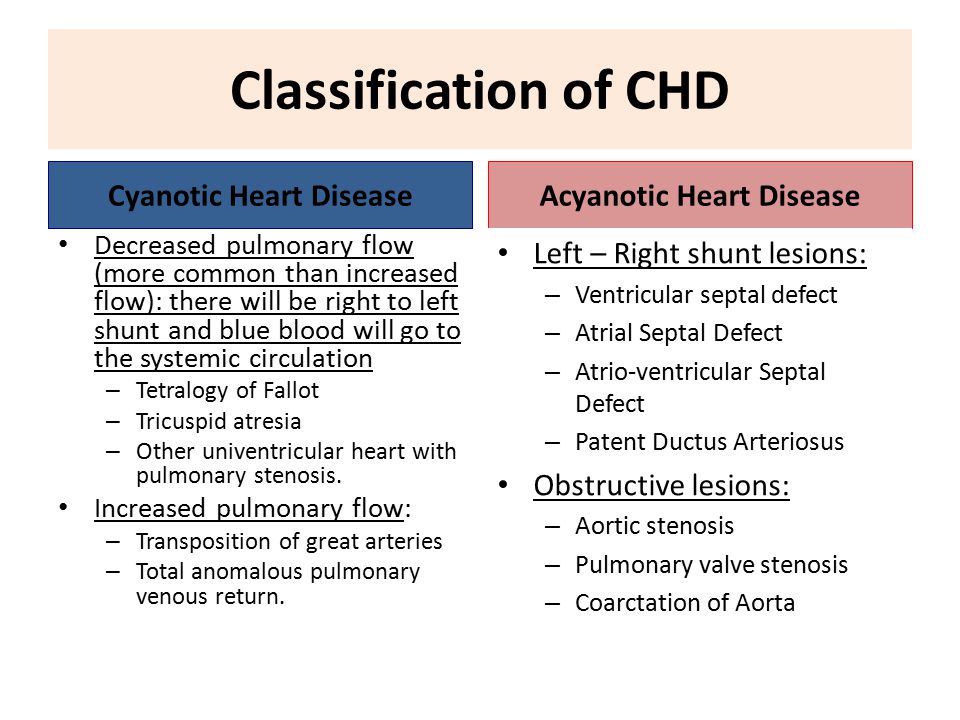
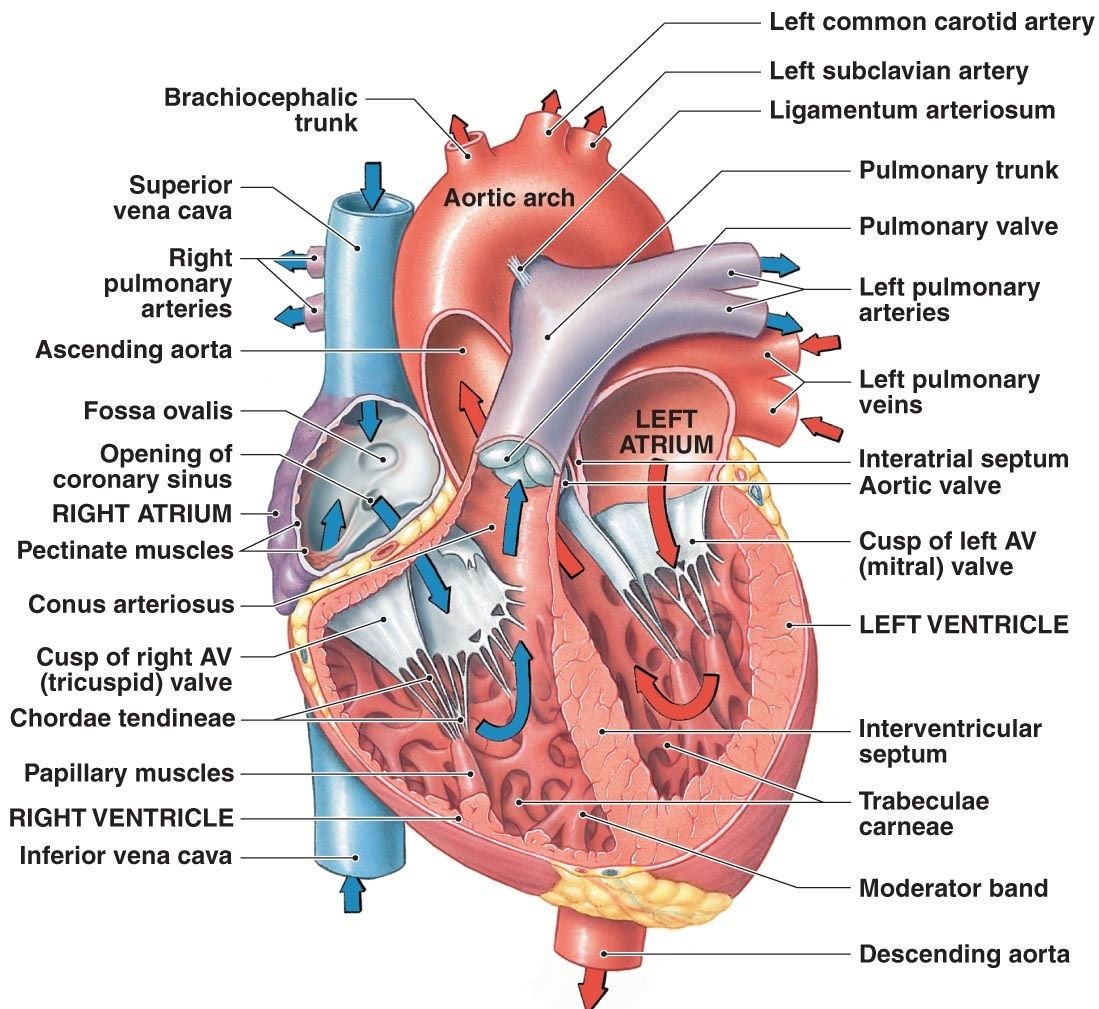
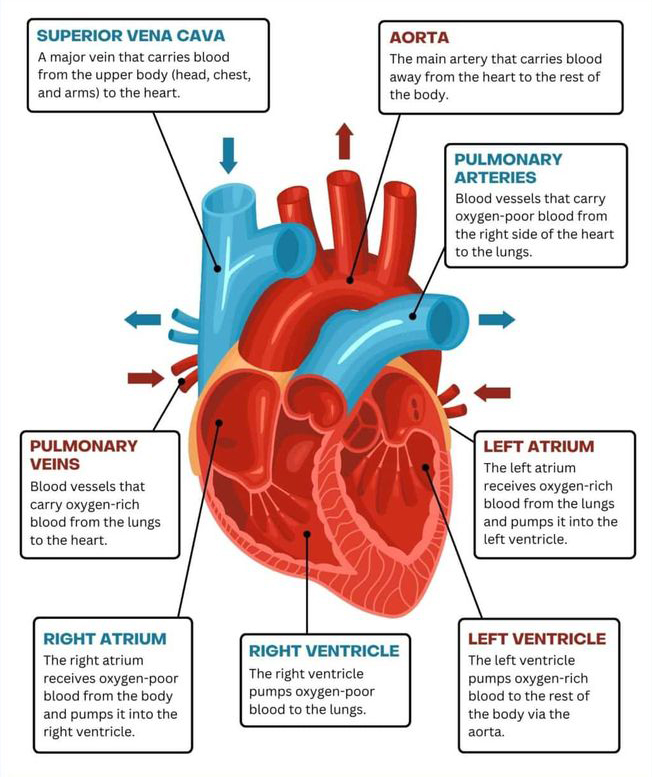
Heart anatomy and Physiology:
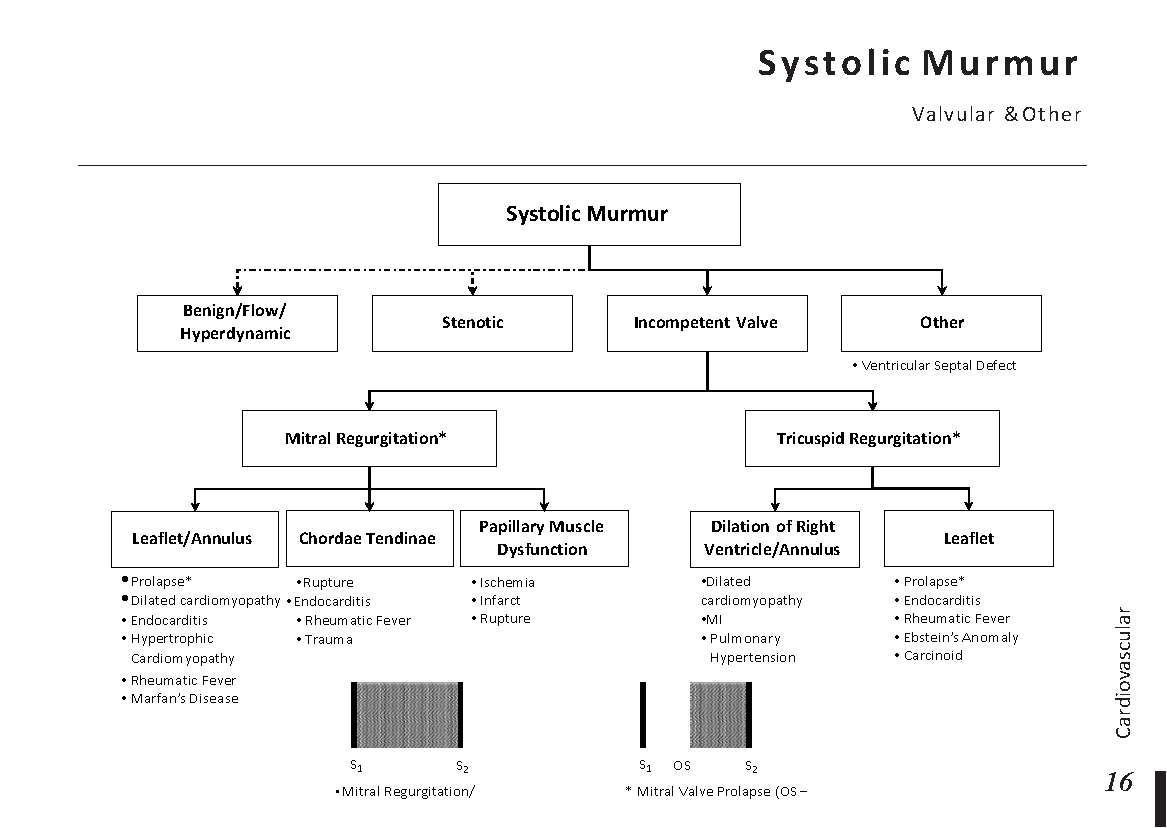
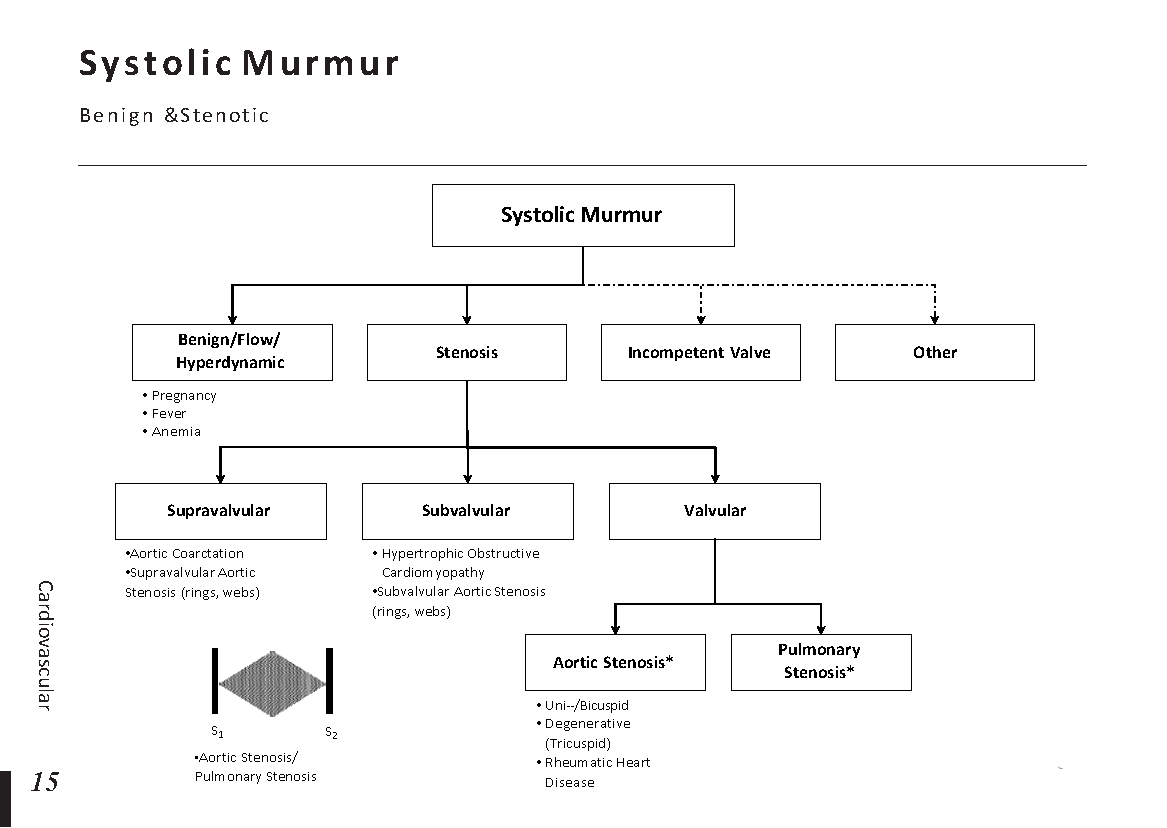
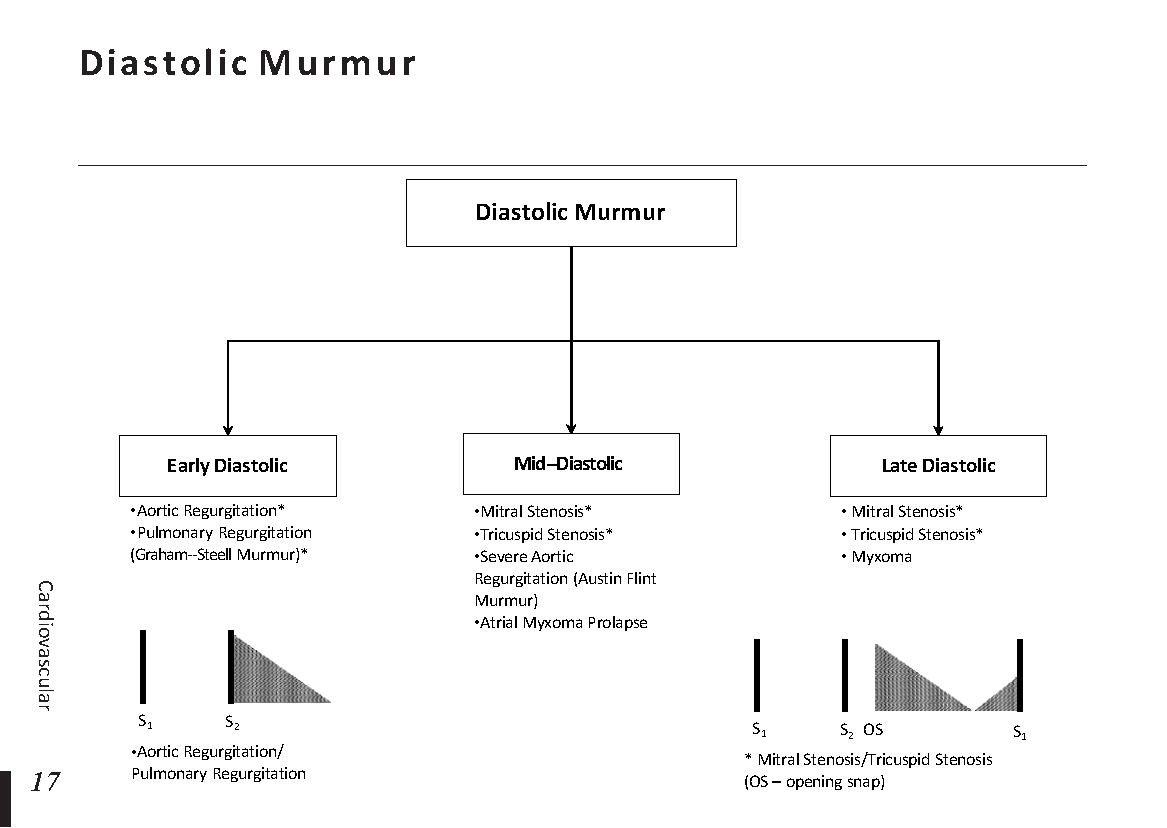
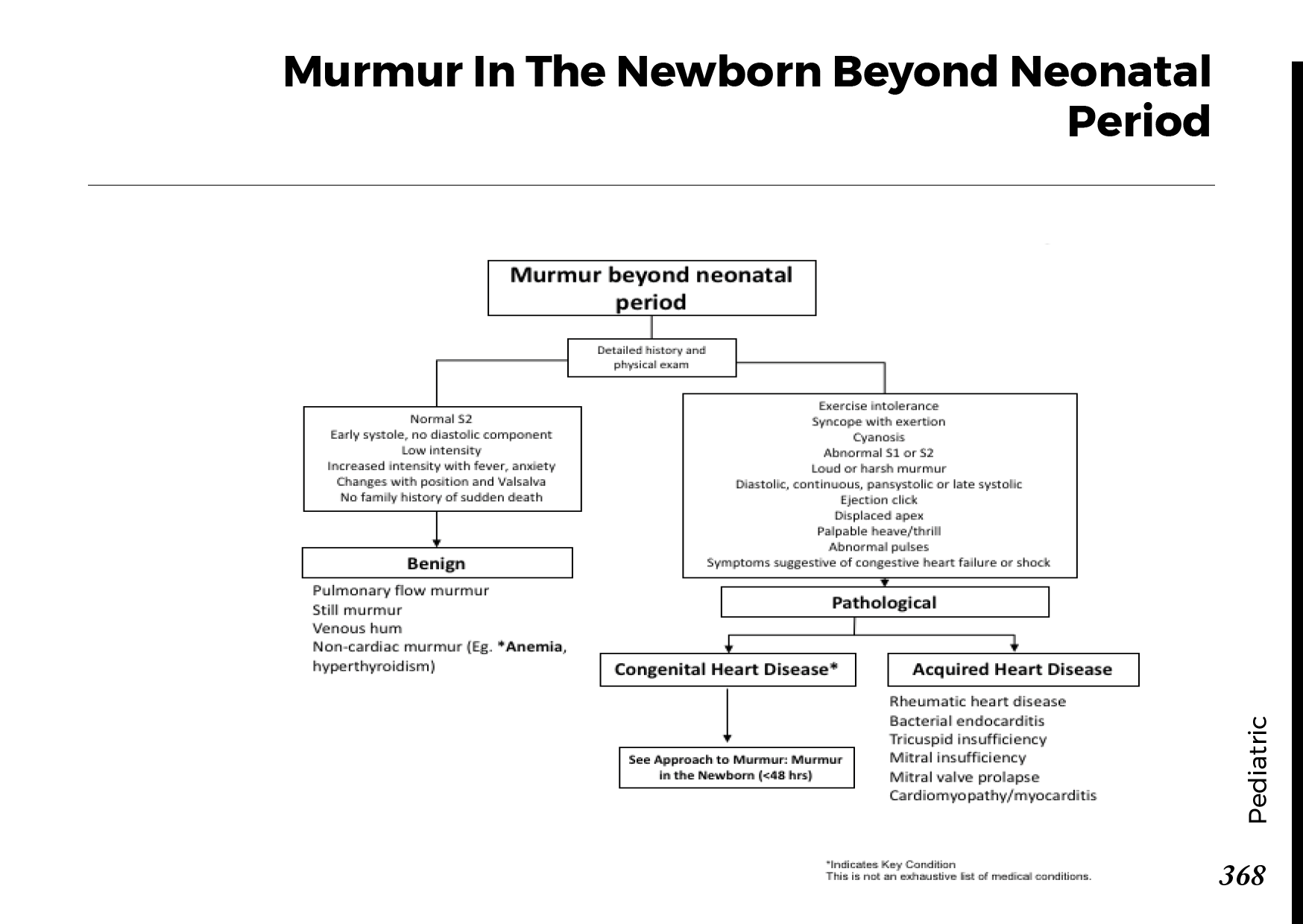
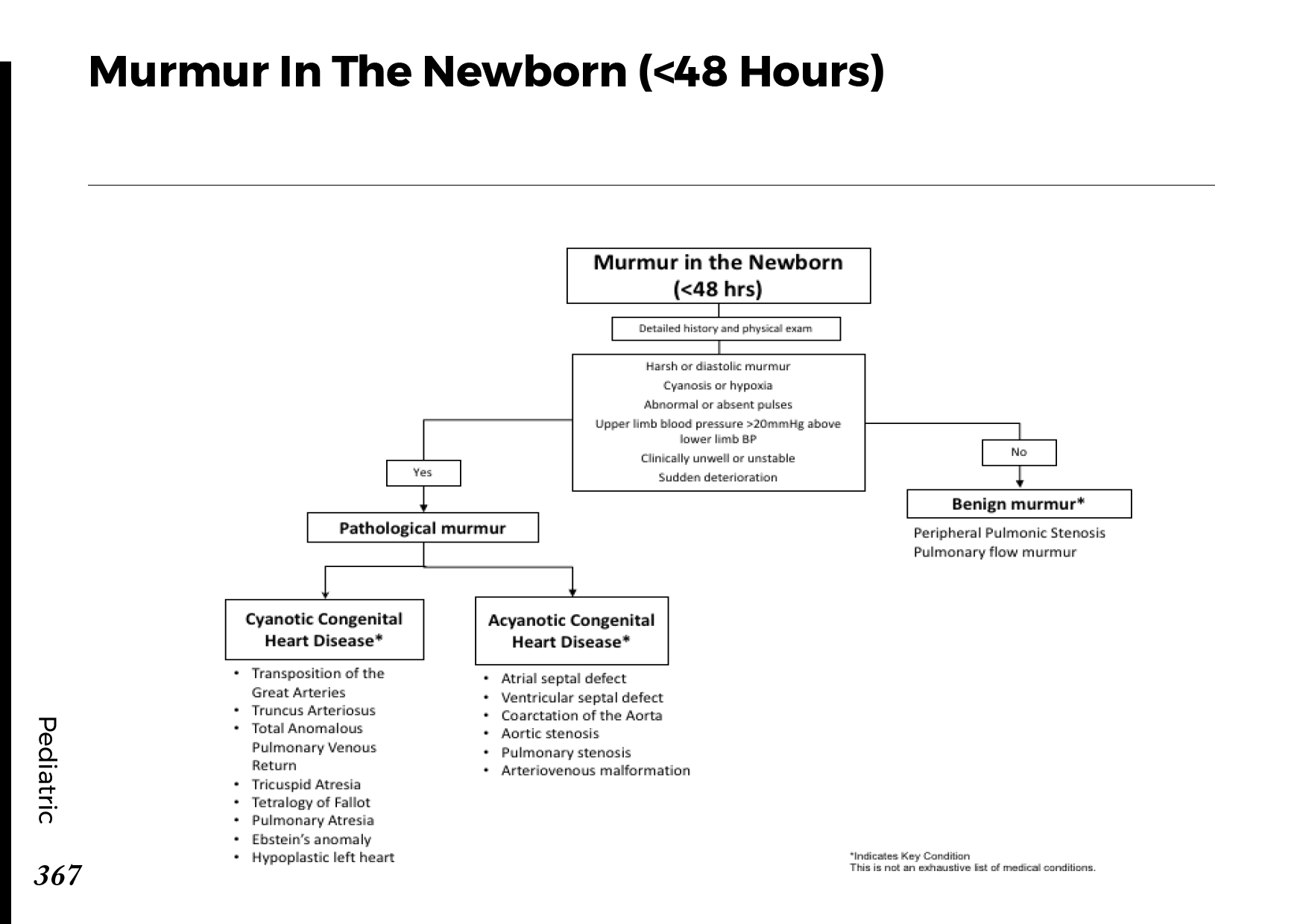
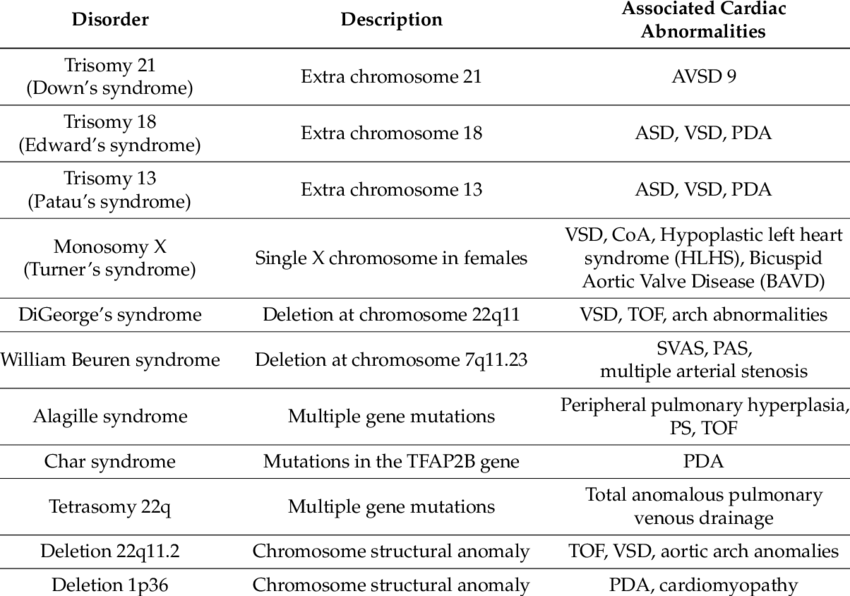
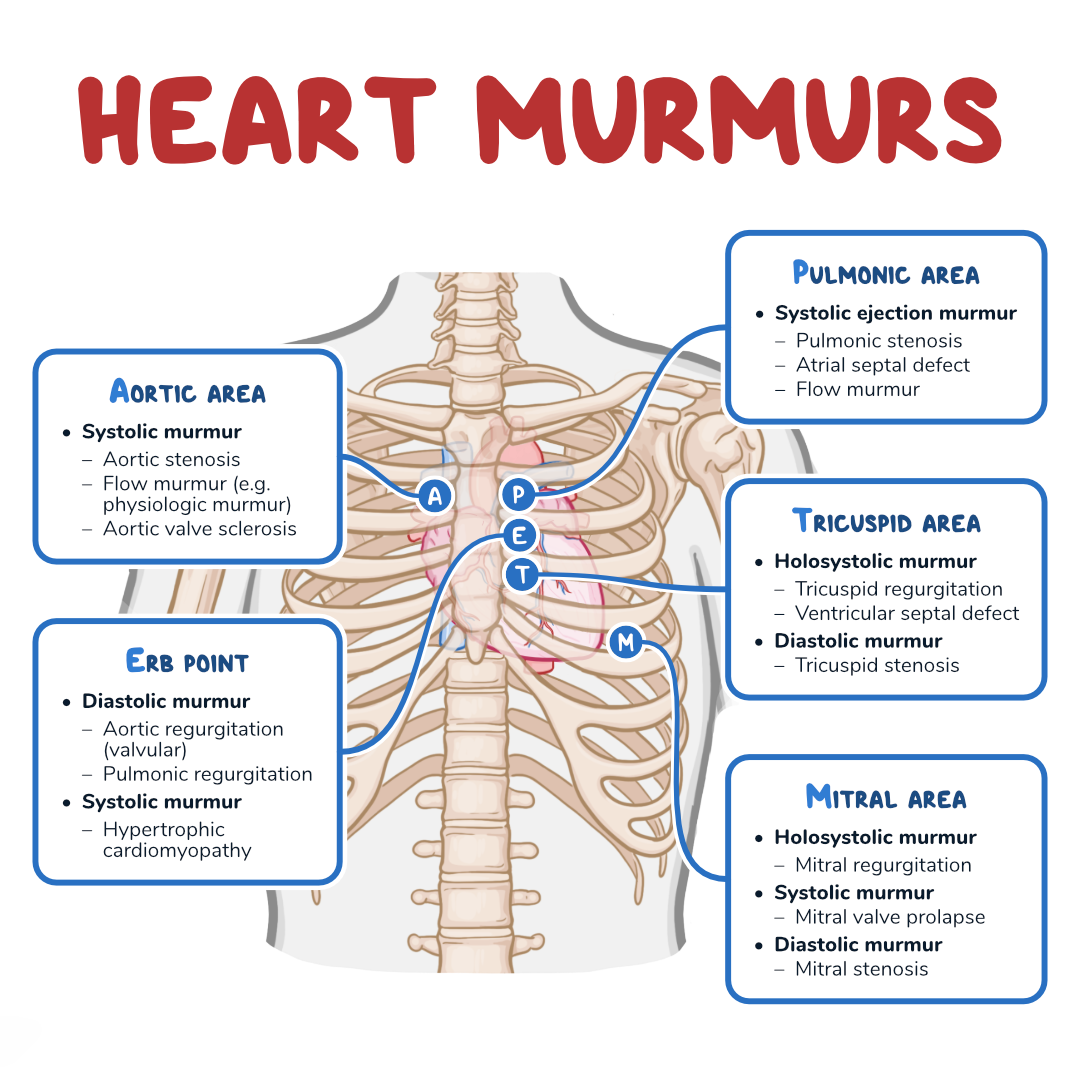
Heart Murmurs:
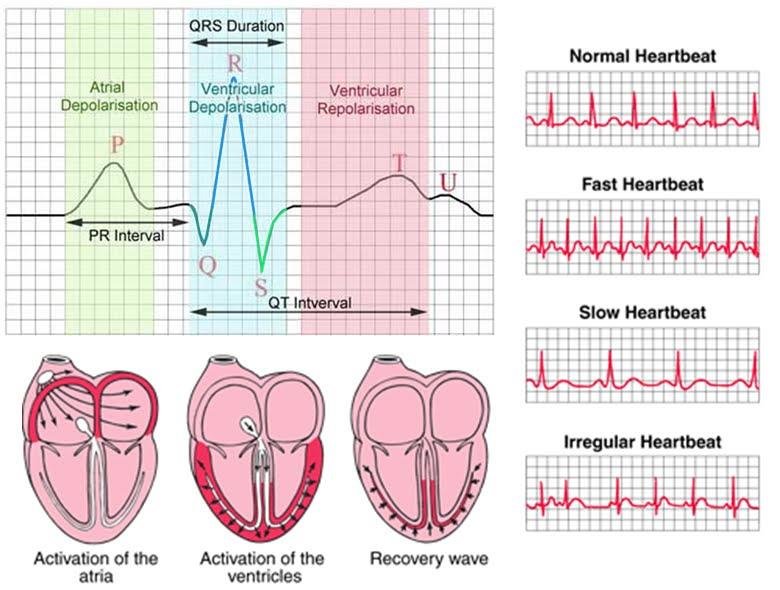
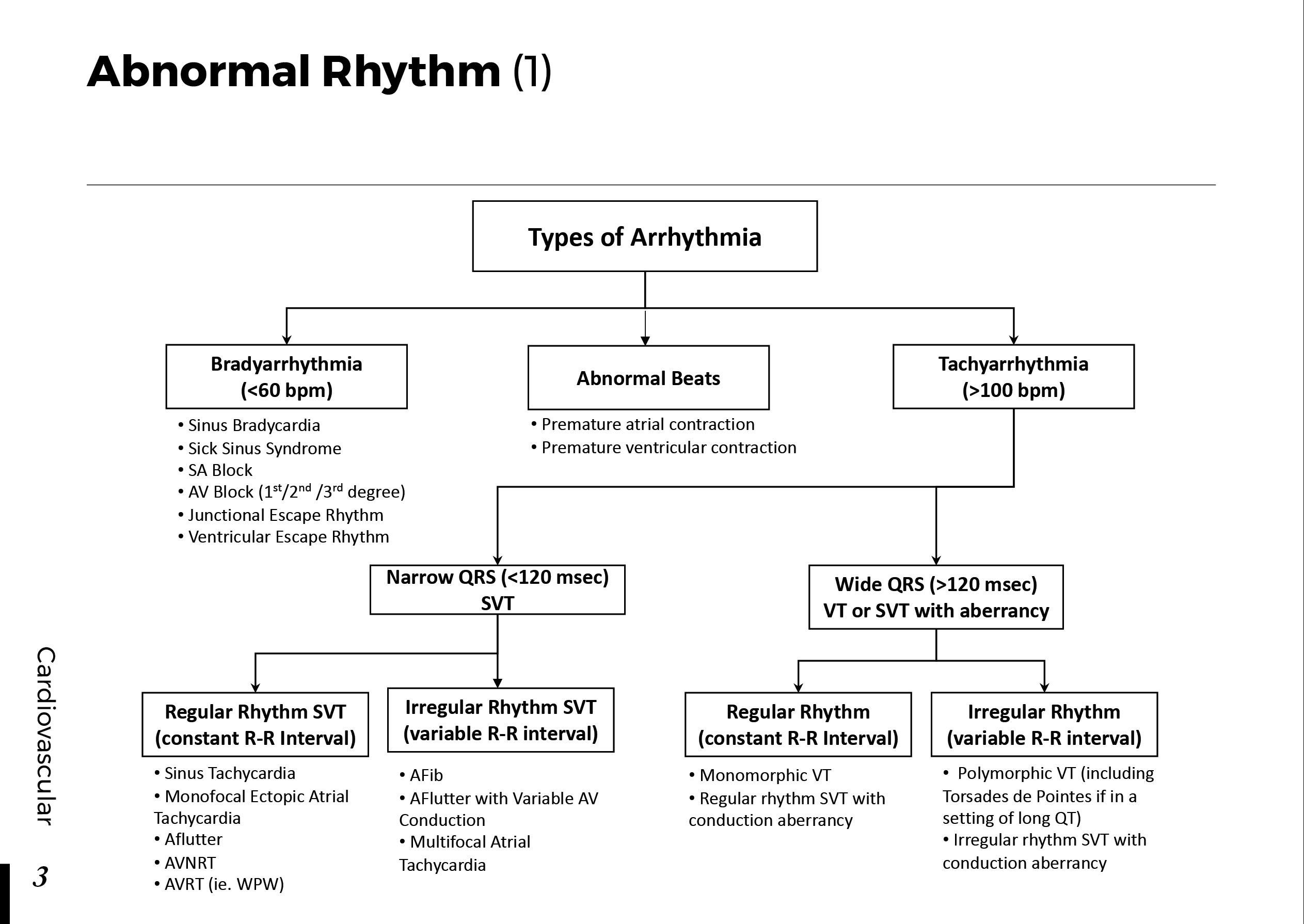
ECG Basics: